|
Beaumont Bay
Beaumont Bay () is an ice-filled reentrant on the west side of the Ross Ice Shelf between Young Head and Harris Point, into which Dickey Glacier flows. It was discovered by the British National Antarctic Expedition (1901–04) and named for Admiral Sir Lewis Beaumont, Royal Navy, an Arctic explorer who took a special interest in this expedition. See also * Howard-Williams Point Howard-Williams Point () is a prominent point extending into the Ross Ice Shelf, located just north of Beaumont Bay, north east of the Surveyors Range, Antarctica. It was named in honor of Clive Howard-Williams, an ecologist who led several rese ... References * Bays of the Ross Dependency Shackleton Coast {{ShackletonCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
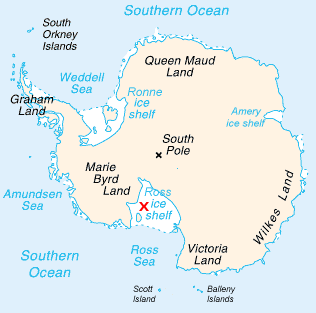
Ross Ice Shelf
The Ross Ice Shelf is the largest ice shelf of Antarctica (, an area of roughly and about across: about the size of France). It is several hundred metres thick. The nearly vertical ice front to the open sea is more than long, and between high above the water surface. Ninety percent of the floating ice, however, is below the water surface. Most of Ross Ice Shelf is in the Ross Dependency claimed by New Zealand. It floats in, and covers, a large southern portion of the Ross Sea and the entire Roosevelt Island located in the east of the Ross Sea. The ice shelf is named after Sir James Clark Ross, who discovered it on 28 January 1841. It was originally called "The Barrier", with various adjectives including "Great Ice Barrier", as it prevented sailing further south. Ross mapped the ice front eastward to 160° W. In 1947, the U.S. Board on Geographic Names applied the name "Ross Shelf Ice" to this feature and published it in the original U.S. Antarctic Gazetteer. In Janu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Young Head
Young Head () is a prominent rock headland, 350 meters high, marking the north side of the entrance to Beaumont Bay on the west side of the Ross Ice Shelf named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for CWO Victor Young, U.S. Navy, member of the Mobile Construction Battalion party at Little America V Little America was a series of Antarctic exploration bases from 1929 to 1958, located on the Ross Ice Shelf, south of the Bay of Whales. The coordinates are approximate. Little America I The first base in the series was established in January ..., winter 1956. Headlands of the Ross Dependency Shackleton Coast {{ShackletonCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harris Point
Harris Point () is a rocky coastal point along the west side of the Ross Ice Shelf, Antarctica. Located south of Young Head at the south side of Beaumont Bay, it was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Herman D. Harris, a chief hospital corpsman with U.S. Navy Squadron VX-6. Harris built a sick bay at South Pole Station during U.S. Navy Operation Deep Freeze Operation Deep Freeze (OpDFrz or ODF) is codename for a series of United States missions to Antarctica, beginning with "Operation Deep Freeze I" in 1955–56, followed by "Operation Deep Freeze II", "Operation Deep Freeze III", and so on. (There w ... 1961. References Headlands of the Ross Dependency Shackleton Coast {{ShackletonCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dickey Glacier
Dickey Glacier () is a glacier long, flowing north along the east side of the Surveyors Range to enter Beaumont Bay, Ross Ice Shelf. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Captain Willie M. Dickey, U.S. Navy, commander of the Naval Support Units, Antarctica, at Little America V Little America was a series of Antarctic exploration bases from 1929 to 1958, located on the Ross Ice Shelf, south of the Bay of Whales. The coordinates are approximate. Little America I The first base in the series was established in January ... in winter 1957. References Glaciers of the Ross Dependency Shackleton Coast {{ShackletonCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British National Antarctic Expedition
The ''Discovery'' Expedition of 1901–1904, known officially as the British National Antarctic Expedition, was the first official British exploration of the Antarctic regions since the voyage of James Clark Ross sixty years earlier (1839–1843). Organized on a large scale under a joint committee of the Royal Society and the Royal Geographical Society (RGS), the new expedition carried out scientific research and geographical exploration in what was then largely an untouched continent. It launched the Antarctic careers of many who would become leading figures in the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration, including Robert Falcon Scott who led the expedition, Ernest Shackleton, Edward Wilson, Frank Wild, Tom Crean and William Lashly. Its scientific results covered extensive ground in biology, zoology, geology, meteorology and magnetism. The expedition discovered the existence of the only snow-free Antarctic valleys, which contains the longest river of Antarctica. Further achieve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Admiral Sir Lewis Beaumont
Admiral Sir Lewis Anthony Beaumont, (19 May 1847 – 20 June 1922) was a Royal Navy officer who served as Commander-in-Chief, Plymouth. Naval career Beaumont joined the Royal Navy as a boy in 1860 and was engaged in operations in Malaya by 1875. Between 1875 and 1876 he took part as senior lieutenant in the British Arctic Expedition led by George Nares on HMS Discovery, an attempt to reach the North Pole and to explore the NW coast of Greenland. Beaumont led a dogsled party that reached Sherard Osborn Fjord in May 1876 and left a cairn at Repulse Harbour. He was given command of HMS ''Excellent'' in 1893, before becoming Director of Naval Intelligence in 1895. He went on to be Commander-in-Chief, Pacific Station in 1899 and Commander-in-Chief, Australia Station in 1900. During his time in Australia, he was knighted as a Knight Commander of the Order of St Michael and St George (KCMG) on the occasion of the visit of the Duke and Duchess of Cornwall and York (later Kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority globally. Owing to this historical prominence, it is common, even among non-Britons, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Howard-Williams Point
Howard-Williams Point () is a prominent point extending into the Ross Ice Shelf, located just north of Beaumont Bay, north east of the Surveyors Range, Antarctica. It was named in honor of Clive Howard-Williams, an ecologist who led several research events in the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Darwin Glacier, and Bratina Island areas from 1984 onwards. Howard-Williams was an Antarctica New Zealand Board member 1996–2000, and provided considerable input to international Antarctic science and environmental management, including development of a McMurdo Dry Valleys Antarctic Specially Managed Area. He went on to become the Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research The Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR) is an interdisciplinary body of the International Science Council (ISC). SCAR coordinates international scientific research efforts in Antarctica, including the Southern Ocean. SCAR's scien ... (SCAR) delegate for New Zealand and also one of the four SCAR Vice-Presiden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bays Of The Ross Dependency
A bay is a recessed, coastal body of water that directly connects to a larger main body of water, such as an ocean, a lake, or another bay. A large bay is usually called a gulf, sea, sound, or bight. A cove is a small, circular bay with a narrow entrance. A fjord is an elongated bay formed by glacial action. A bay can be the estuary of a river, such as the Chesapeake Bay, an estuary of the Susquehanna River. Bays may also be nested within each other; for example, James Bay is an arm of Hudson Bay in northeastern Canada. Some large bays, such as the Bay of Bengal and Hudson Bay, have varied marine geology. The land surrounding a bay often reduces the strength of winds and blocks waves. Bays may have as wide a variety of shoreline characteristics as other shorelines. In some cases, bays have beaches, which "are usually characterized by a steep upper foreshore with a broad, flat fronting terrace".Maurice Schwartz, ''Encyclopedia of Coastal Science'' (2006), p. 129. Bays were s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |