|
Beattie Peaks Formation
The Beattie Peaks Formation is a geologic formation of Early Cretaceous ( Valanginian) age in the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin that consists primarily of marine mudstone. It is present in the northern foothills of the Canadian Rockies and the adjacent plains in northeastern British Columbia.Stott, D.F. 1998. Fernie Formation and Minnes Group (Jurassic and lowermost Cretaceous), northern Rocky Mountain foothills, Alberta and British Columbia. Geological Survey of Canada, Bulletin 516.Glass, D.J. (editor) 1997. Lexicon of Canadian Stratigraphy, vol. 4, Western Canada including eastern British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan and southern Manitoba. Canadian Society of Petroleum Geologists, Calgary, 1423 p. on CD-ROM. . Lithology The Beattie Peaks Formation consists primarily of dark grey to brownish grey or black mudstones that contain abundant organic matter and are extensively burrowed. Interbeds of argillaceous siltstone and fine-grained sandstone increase toward the top of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formation (stratigraphy)
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics (lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exposed in a geographical region (the stratigraphic column). It is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy, the study of strata or rock layers. A formation must be large enough that it can be mapped at the surface or traced in the subsurface. Formations are otherwise not defined by the thickness (geology), thickness of their rock strata, which can vary widely. They are usually, but not universally, tabular in form. They may consist of a single lithology (rock type), or of alternating beds of two or more lithologies, or even a heterogeneous mixture of lithologies, so long as this distinguishes them from adjacent bodies of rock. The concept of a geologic formation goes back to the beginnings of modern scientific geology. The term was used by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
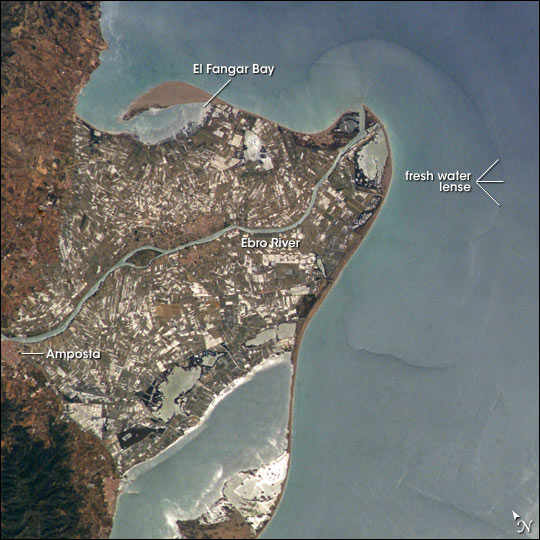
River Delta
A river delta is a landform shaped like a triangle, created by deposition (geology), deposition of sediment that is carried by a river and enters slower-moving or stagnant water. This occurs where a river enters an ocean, sea, estuary, lake, reservoir, or (more rarely) another river that cannot carry away the supplied sediment. It is so named because its triangle shape resembles the Greek letter Delta. The size and shape of a delta is controlled by the balance between watershed processes that supply sediment, and receiving basin processes that redistribute, sequester, and export that sediment. The size, geometry, and location of the receiving basin also plays an important role in delta evolution. River deltas are important in human civilization, as they are major agricultural production centers and population centers. They can provide Coast, coastline defense and can impact drinking water supply. They are also Ecology, ecologically important, with different species' assemblages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shallow Marine Deposits
Shallow may refer to: Places * Shallow (underwater relief), where the depth of the water is low compared to its surroundings * Shallow Bay (other), various places * Shallow Brook, New Jersey, United States * Shallow Inlet, Victoria, Australia * Shallow Lake, Idaho, United States * Shallow Pond (Plymouth, Massachusetts), United States People * Hyron Shallow (born 1982), West Indian cricketer * Parvati Shallow (born 1982), winner of the reality TV show ''Survivor: Micronesia'' Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Shallow'' (album) * Robert Shallow, a fictional character in two Shakespeare plays * Verbena (band) Verbena was an American rock band from Birmingham, Alabama, founded in the early 1990s by Scott Bondy, Anne Marie Griffin, Les Nuby, and Daniel Johnston. They released three albums, two of which were issued on Capitol Records. History The band ..., later known as Shallow Songs * "Shallow" (Lady Gaga and Bradley Cooper song), 2018 * "Shallow" (Porc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mudstone Formations
Mudstone, a type of mudrock, is a fine-grained sedimentary rock whose original constituents were clays or muds. Mudstone is distinguished from ''shale'' by its lack of fissility (parallel layering).Blatt, H., and R.J. Tracy, 1996, ''Petrology.'' New York, New York, W. H. Freeman, 2nd ed, 529 pp. The term ''mudstone'' is also used to describe carbonate rocks (limestone or dolomite) that are composed predominantly of carbonate mud. However, in most contexts, the term refers to siliciclastic mudstone, composed mostly of silicate minerals. The NASA Curiosity rover has found deposits of mudstone on Mars that contain organic substances such as propane, benzene and toluene. Definition There is not a single definition of mudstone that has gained general acceptance,Boggs 2006, p.143 though there is wide agreement that mudstones are fine-grained sedimentary rocks, composed mostly of silicate grains with a grain size less than . Individual grains this size are too small to be distinguishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valanginian Stage
In the geologic timescale, the Valanginian is an age or stage of the Early or Lower Cretaceous. It spans between 139.8 ± 3.0 Ma and 132.9 ± 2.0 Ma (million years ago). The Valanginian Stage succeeds the Berriasian Stage of the Lower Cretaceous and precedes the Hauterivian Stage of the Lower Cretaceous. Stratigraphic definitions The Valanginian was first described and named by Édouard Desor in 1853. It is named after Valangin, a small town north of Neuchâtel in the Jura Mountains of Switzerland. The base of the Valanginian is at the first appearance of calpionellid species ''Calpionellites darderi'' in the stratigraphic column. A global reference section (a GSSP) had in 2009 not yet been appointed. The top of the Valanginian (the base of the Hauterivian) is at the first appearance of the ammonite genus ''Acanthodiscus''. Subdivision The Valanginian is often subdivided in Lower and Upper substages. The Upper substage begins at the first appearance of ammonite species '' Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous British Columbia
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin ''creta'', "chalk", which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation ''Kreide''. The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now-extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was ice free, and forests extended to the poles. During this time, new groups of mammals and birds appeared. During the Early Cretaceous, flowering plants appeared and began to rapidly diversify, becoming the dominant group of plants across the Earth by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geologic Formations Of British Columbia
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology, and so is treated as one major aspect of integrated Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface, and the processes that have shaped that structure. It also provides tools to determine the relative and absolute ages of rocks found in a given location, and also to describe the histories of those rocks. By combining these tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole, and also to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and the Earth's past climates. Geologists broadly study the properties and processes of E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Fossiliferous Stratigraphic Units In British Columbia
This is a list of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in British Columbia, Canada. References * {{Lists of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Canada British Columbia British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ... Geology of British Columbia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorman Creek Formation
The Gorman Creek Formation is a geologic formation of Early Cretaceous ( Valanginian) age in the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin that consists primarily of nonmarine sediments. It is present in the northern foothills of the Canadian Rockies and the adjacent plains in northeastern British Columbia. Plant fossils and dinosaur tracks have been described from its strata.Stott, D.F. 1998. Fernie Formation and Minnes Group (Jurassic and lowermost Cretaceous), northern Rocky Mountain foothills, Alberta and British Columbia. Geological Survey of Canada, Bulletin 516.Glass, D.J. (editor) 1997. Lexicon of Canadian Stratigraphy, vol. 4, Western Canada including eastern British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan and southern Manitoba. Canadian Society of Petroleum Geologists, Calgary, 1423 p. on CD-ROM. . Lithology The Gorman Creek Formation consists of repetitive successions of argillaceous sandstone, siltstone, coaly mudstone, and coal beds. Beds of conglomeratic sandstone are pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichnofacies
An ichnofacies is an assemblage of trace fossils that provides an indication of the conditions that their formative organisms inhabited. Concept Trace fossil assemblages are far from random; the range of fossils recorded in association is constrained by the environment in which the trace-making organisms dwelt. Palaeontologist Adolf Seilacher pioneered the concept of ichnofacies, whereby the state of a sedimentary system at its time of deposition could be deduced by noting the trace fossils in association with one another. Significance Ichnofacies can provide information about water depth, salinity, turbidity and energy. In general, traces found in shallower water are vertical, those in deeper water are more horizontal and patterned. This is partly because of the relative abundance of suspended food particles, such as plankton, in the shallower waters of the photic zone, and partly because vertical burrows are more secure in the turbulent conditions of shallow water. In deeper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microfossils
A microfossil is a fossil that is generally between 0.001 mm and 1 mm in size, the visual study of which requires the use of light or electron microscopy. A fossil which can be studied with the naked eye or low-powered magnification, such as a hand lens, is referred to as a macrofossil. Microfossils are a common feature of the geological record, from the Precambrian to the Holocene. They are most common in deposits of marine environments, but also occur in brackish water, fresh water and terrestrial sedimentary deposits. While every kingdom of life is represented in the microfossil record, the most abundant forms are protist skeletons or microbial cysts from the Chrysophyta, Pyrrhophyta, Sarcodina, acritarchs and chitinozoans, together with pollen and spores from the vascular plants. Overview A microfossil is a descriptive term applied to fossilized plants and animals whose size is just at or below the level at which the fossil can be analyzed by the naked eye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
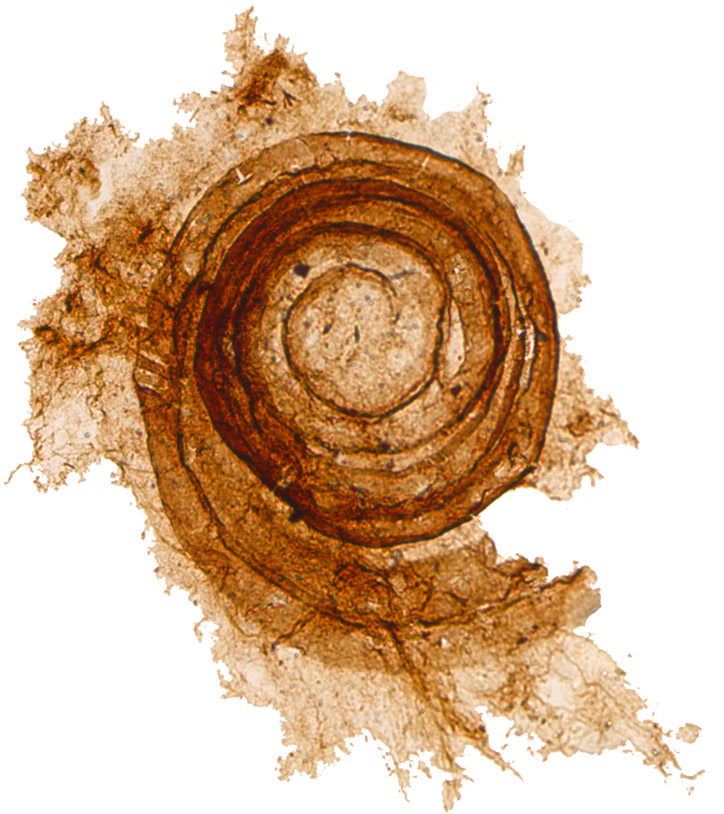
Ammonoidea
Ammonoids are a group of extinct marine mollusc animals in the subclass Ammonoidea of the class Cephalopoda. These molluscs, commonly referred to as ammonites, are more closely related to living coleoids (i.e., octopuses, squid and cuttlefish) than they are to shelled nautiloids such as the living ''Nautilus'' species. The earliest ammonites appeared during the Devonian, with the last species vanishing during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. Ammonites are excellent index fossils, and linking the rock layer in which a particular species or genus is found to specific geologic time periods is often possible. Their fossil shells usually take the form of planispirals, although some helically spiraled and nonspiraled forms (known as heteromorphs) have been found. The name "ammonite", from which the scientific term is derived, was inspired by the spiral shape of their fossilized shells, which somewhat resemble tightly coiled rams' horns. Pliny the Elder ( 79 AD nea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |