|
Beacon Heights
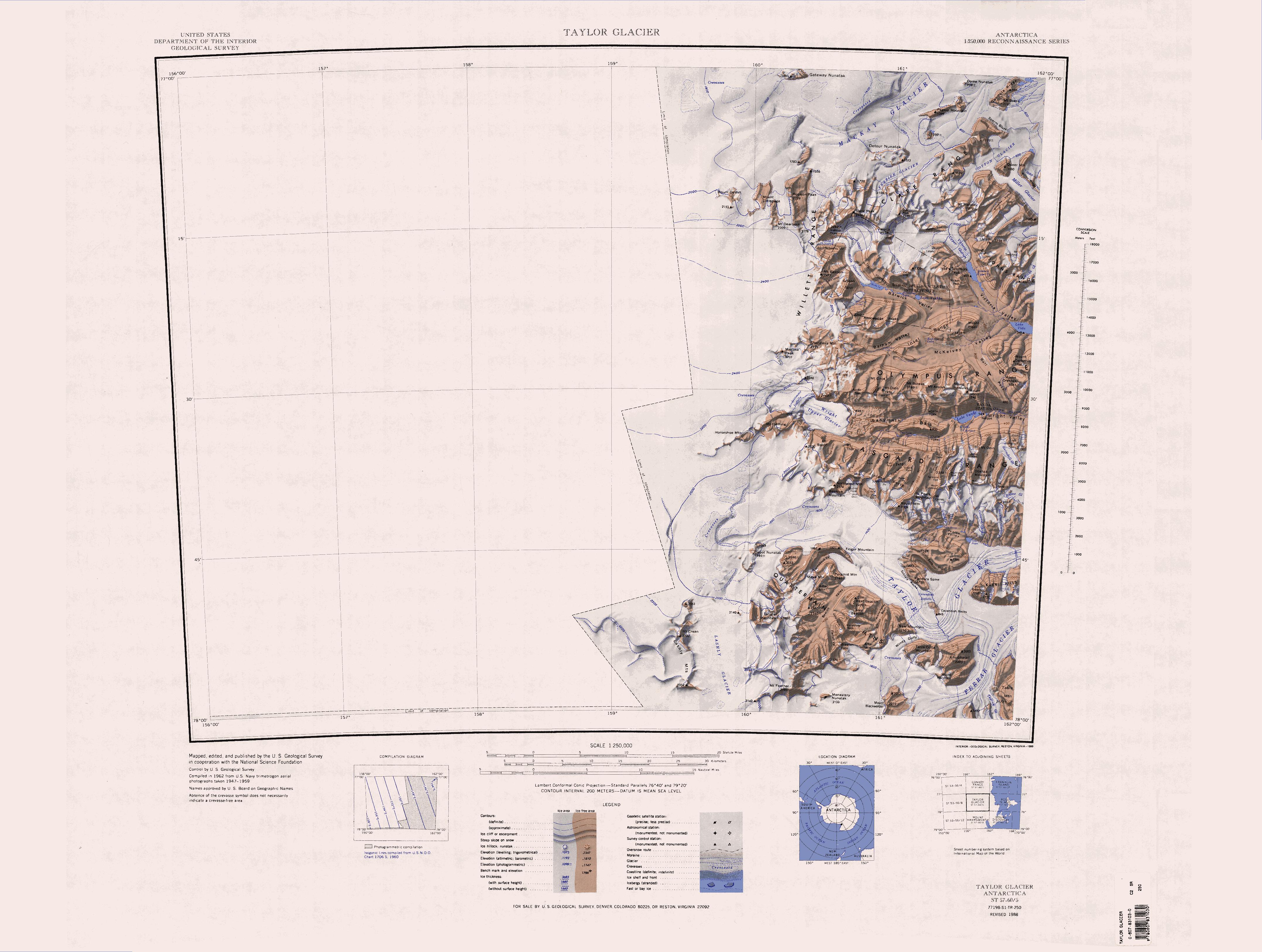
The Beacon Heights () are a small cluster of peaks between Beacon Valley and Arena Valley in Quartermain Mountains, Victoria Land, rising to in West Beacon, and also including East Beacon and South Beacon. They were named by Hartley Ferrar, geologist with the British National Antarctic Expedition (1901–04). According to the USGS GNIS gazetteer, the heights were named after the Beacon Supergroup The Beacon Supergroup is a geological formation exposed in Antarctica and deposited from the Devonian to the Triassic (). The unit was originally described as either a formation or sandstone, and upgraded to group and supergroup as time passed. It ... which caps them, though another source indicates that the type of rock was named after these hills. References * Mountains of Victoria Land Scott Coast {{ScottCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beacon Valley
Beacon Valley () is an ice-free valley between Pyramid Mountain and Beacon Heights, in Victoria Land. It was mapped by the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13, and named by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition (VUWAE) (1958–59) after Beacon Heights. Named features Beacon Valley includes several smaller geographic features, named during various scientific surveys. * Profile Bluff (), a prominent cliff (2,070 m) midway between Mount Weller and Horizon Bluff on the west side of the valley. Named in 1993 by the New Zealand Geographic Board (NZGB). * Horizon Bluff (), a steep bluff at the head of the valley, rising to . It is west of Friedmann Valley. Named in 1993 by the NZGB. *Rector Ridge (), a bold rock ridge at the head of the valley, rising to 2,105 m. It was named in 1992 by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) after Commander Jack Rector, U.S. Navy, Commanding Officer, Antarctic Development Squadron Six (VXE-6), May 1987 to May 1988. * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arena Valley
Arena Valley () is an ice-free valley, between East Beacon and New Mountain, which opens to the south side of Taylor Glacier in Victoria Land. It was given this descriptive name by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition The Antarctic Research Centre (ARC) is part of the School of Geography, Environment and Earth Sciences at Victoria University of Wellington. Its mission is to research "Antarctic climate history and processes, and their influence on the global clima ... (VUWAE), 1958–59. See also * Ashtray Basin References * Valleys of Victoria Land McMurdo Dry Valleys {{McMurdoDryValleys-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartermain Mountains
The Quartermain Mountains are a group of exposed mountains in Antarctica, about long, typical of ice-free features of the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Victoria Land, located south of Taylor Glacier and bounded by Finger Mountain, Mount Handsley, Mount Feather and Tabular Mountain; also including Knobhead, Terra Cotta Mountain, New Mountain, Beacon Heights, Pyramid Mountain, Arena Valley, Kennar Valley, Turnabout Valley and the several valleys and ridges within Beacon Valley. Exploration The mountains were visited by British expeditions led by Robert Falcon Scott (1901–04 and 1910–13) and Ernest Shackleton (1907–09), who applied several names. Names were added in the years subsequent to the International Geophysical Year, 1957–58, concurrent with research carried out by New Zealand Antarctic Research Programme and United States Antarctic Research Program field parties, and to fulfill the requirement for maps compiled from United States Navy aerial photographs, 1947–83. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria Land
Victoria Land is a region in eastern Antarctica which fronts the western side of the Ross Sea and the Ross Ice Shelf, extending southward from about 70°30'S to 78°00'S, and westward from the Ross Sea to the edge of the Antarctic Plateau. It was discovered by Captain James Clark Ross in January 1841 and named after Queen Victoria. The rocky promontory of Minna Bluff is often regarded as the southernmost point of Victoria Land, and separates the Scott Coast to the north from the Hillary Coast of the Ross Dependency to the south. The region includes ranges of the Transantarctic Mountains and the McMurdo Dry Valleys (the highest point being Mount Abbott in the Northern Foothills), and the flatlands known as the Labyrinth. The Mount Melbourne is an active volcano in Victoria Land. Early explorers of Victoria Land include James Clark Ross and Douglas Mawson. In 1979, scientists discovered a group of 309 meteorites in Antarctica, some of which were found near the Allan Hills in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Beacon
The Quartermain Mountains are a group of exposed mountains in Antarctica, about long, typical of ice-free features of the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Victoria Land, located south of Taylor Glacier and bounded by Finger Mountain, Mount Handsley, Mount Feather and Tabular Mountain; also including Knobhead, Terra Cotta Mountain, New Mountain, Beacon Heights, Pyramid Mountain, Arena Valley, Kennar Valley, Turnabout Valley and the several valleys and ridges within Beacon Valley. Exploration The mountains were visited by British expeditions led by Robert Falcon Scott (1901–04 and 1910–13) and Ernest Shackleton (1907–09), who applied several names. Names were added in the years subsequent to the International Geophysical Year, 1957–58, concurrent with research carried out by New Zealand Antarctic Research Programme and United States Antarctic Research Program field parties, and to fulfill the requirement for maps compiled from United States Navy aerial photographs, 1947–83. In 197 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Beacon
The Quartermain Mountains are a group of exposed mountains in Antarctica, about long, typical of ice-free features of the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Victoria Land, located south of Taylor Glacier and bounded by Finger Mountain, Mount Handsley, Mount Feather and Tabular Mountain; also including Knobhead, Terra Cotta Mountain, New Mountain, Beacon Heights, Pyramid Mountain, Arena Valley, Kennar Valley, Turnabout Valley and the several valleys and ridges within Beacon Valley. Exploration The mountains were visited by British expeditions led by Robert Falcon Scott (1901–04 and 1910–13) and Ernest Shackleton (1907–09), who applied several names. Names were added in the years subsequent to the International Geophysical Year, 1957–58, concurrent with research carried out by New Zealand Antarctic Research Programme and United States Antarctic Research Program field parties, and to fulfill the requirement for maps compiled from United States Navy aerial photographs, 1947–83. In 197 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Beacon
The Quartermain Mountains are a group of exposed mountains in Antarctica, about long, typical of ice-free features of the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Victoria Land, located south of Taylor Glacier and bounded by Finger Mountain, Mount Handsley, Mount Feather and Tabular Mountain; also including Knobhead, Terra Cotta Mountain, New Mountain, Beacon Heights, Pyramid Mountain, Arena Valley, Kennar Valley, Turnabout Valley and the several valleys and ridges within Beacon Valley. Exploration The mountains were visited by British expeditions led by Robert Falcon Scott (1901–04 and 1910–13) and Ernest Shackleton (1907–09), who applied several names. Names were added in the years subsequent to the International Geophysical Year, 1957–58, concurrent with research carried out by New Zealand Antarctic Research Programme and United States Antarctic Research Program field parties, and to fulfill the requirement for maps compiled from United States Navy aerial photographs, 1947–83. In 197 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hartley Ferrar
Hartley Travers Ferrar (28 January 1879 – April 1932) was a geologist who accompanied Captain Scott's first Antarctic expedition. Biography Ferrar was born at 3 Grosvenor Place, Dalkey, near Dublin, in 1879, the son of John Edgar Ferrar, a bank clerk, and Mary Holmes Hartley. He moved to South Africa at an early age with his parents, receiving his early schooling at Simonstown school near Cape Town. He was sent back to Oundle School in England for his secondary education, and then went to Sidney Sussex College, Cambridge, where he studied geology. He excelled at sports, and many of his team photographs are archived at his old school and college respectively. On going down from Cambridge, when rowing at Henley, he was offered the post of Geologist on Captain Scott's first Antarctic expedition, and became the youngest member of the scientific staff. He sailed on the ''RRS Discovery'', and met his future wife (Gladys Anderson) when the ship was in New Zealand. The ''Discovery'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British National Antarctic Expedition
The ''Discovery'' Expedition of 1901–1904, known officially as the British National Antarctic Expedition, was the first official British exploration of the Antarctic regions since the voyage of James Clark Ross sixty years earlier (1839–1843). Organized on a large scale under a joint committee of the Royal Society and the Royal Geographical Society (RGS), the new expedition carried out scientific research and geographical exploration in what was then largely an untouched continent. It launched the Antarctic careers of many who would become leading figures in the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration, including Robert Falcon Scott who led the expedition, Ernest Shackleton, Edward Wilson, Frank Wild, Tom Crean and William Lashly. Its scientific results covered extensive ground in biology, zoology, geology, meteorology and magnetism. The expedition discovered the existence of the only snow-free Antarctic valleys, which contains the longest river of Antarctica. Further ach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USGS GNIS
The Geographic Names Information System (GNIS) is a database of name and locative information about more than two million physical and cultural features throughout the United States and its territories, Antarctica, and the associated states of the Marshall Islands, Federated States of Micronesia, and Palau. It is a type of gazetteer. It was developed by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) in cooperation with the United States Board on Geographic Names (BGN) to promote the standardization of feature names. Data were collected in two phases. Although a third phase was considered, which would have handled name changes where local usages differed from maps, it was never begun. The database is part of a system that includes topographic map names and bibliographic references. The names of books and historic maps that confirm the feature or place name are cited. Variant names, alternatives to official federal names for a feature, are also recorded. Each feature receives a perm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beacon Supergroup
The Beacon Supergroup is a geological formation exposed in Antarctica and deposited from the Devonian to the Triassic (). The unit was originally described as either a formation or sandstone, and upgraded to group and supergroup as time passed. It contains a sandy member known as the Beacon Heights Orthoquartzite. Overview The base of the Beacon Supergroup is marked by an unconformity and is composed of the Devonian Taylor Group, a quartzose sandstone sequence; and the Late Carboniferous to Early Jurassic Victoria Group, consisting of glacial beds, sandstone, shale, conglomerate, and coal. The Beacon Sandstone was named by Hartley T. Ferrar during Scott's Discovery Expedition (1901–1904), using the Beacon Heights survey points as reference. ''Glossopteris'' fossils dated the sandstone to the Permian and linked the lithology to similar sequences on neighboring continents. Generally flat lying, the supergroup is up to 3.2 km thick and is fairly continuous from south Victor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |