|
Batylykh Formation
The Batylykh Formation is a geological formation in Yakutia, Russia. It is of an uncertain Early Cretaceous age, probably dating between the Berriasian and the Barremian. It is the oldest unit of the thick Sangar Series within the Vilyuy syneclise. The mudstones, sandstones and shales of the formation were deposited in a fluvial to lacustrine environment. Fossil content The formation is best known for the Teete locality, which has revealed remains of numerous vertebrates, including sauropods,Averianov et al., 2019 and other dinosaur teeth as well as numerous species of mammal, including '' Sangarotherium'', '' Khorotherium''Averianov et al., 2018 and tritylodontid '' XenocretosuchusLopatin & Agadjanian, 2008''. as well as choristodere ''Khurendukhosaurus''.Kolosov et al., 2009 Other fossils recovered from the formation are: [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous ( geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma. Geology Proposals for the exact age of the Barremian-Aptian boundary ranged from 126 to 117 Ma until recently (as of 2019), but based on drillholes in Svalbard the defining early Aptian Oceanic Anoxic Event 1a (OAE1a) was carbon isotope dated to 123.1±0.3 Ma, limiting the possible range for the boundary to c. 122–121 Ma. There is a possible link between this anoxic event and a series of Early Cretaceous large igneous provinces (LIP). The Ontong Java-Manihiki-Hikurangi large igneous province, emplaced in the South Pacific at c. 120 Ma, is by far the largest LIP in Earth's history. The Ontong Java Plateau today covers an area of 1,860,000 km2. In the Indian Ocean another LIP began to form at c. 120 Ma, the Kerguelen P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacustrine
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger oceans, they do form part of the Earth's water cycle. Lakes are distinct from lagoons, which are generally coastal parts of the ocean. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which also lie on land, though there are no official or scientific definitions. Lakes can be contrasted with rivers or streams, which usually flow in a channel on land. Most lakes are fed and drained by rivers and streams. Natural lakes are generally found in mountainous areas, rift zones, and areas with ongoing glaciation. Other lakes are found in endorheic basins or along the courses of mature rivers, where a river channel has widened into a basin. Some parts of the world have many lakes formed by the chaotic drainage patterns left over from the last ice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelurosauria
Coelurosauria (; from Greek, meaning "hollow tailed lizards") is the clade containing all theropod dinosaurs more closely related to birds than to carnosaurs. Coelurosauria is a subgroup of theropod dinosaurs that includes compsognathids, tyrannosaurs, ornithomimosaurs, and maniraptorans; Maniraptora includes birds, the only known dinosaur group alive today. Most feathered dinosaurs discovered so far have been coelurosaurs. Philip J. Currie had considered it likely and probable that all coelurosaurs were feathered. However, several skin impressions found for some members of this group show pebbly, scaly skin, indicating that feathers did not completely replace scales in all taxa. In the past, Coelurosauria was used to refer to all small theropods, but this classification has since been abolished. Anatomy Bodyplan The studying of anatomical traits in coelurosaurs indicates that the last common ancestor had evolved the ability to eat and digest plant matter, adapting to an omniv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
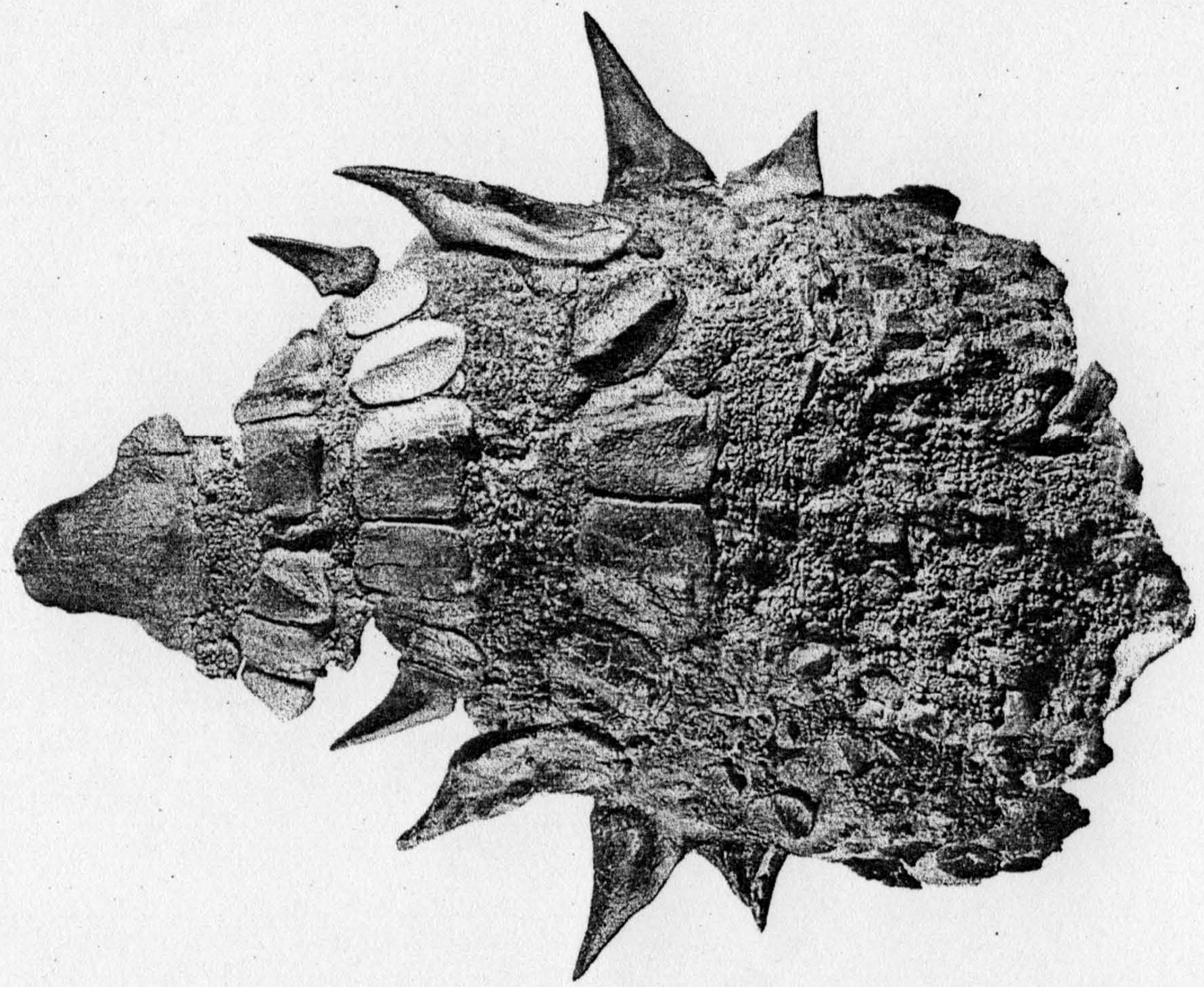
Ankylosauria
Ankylosauria is a group of herbivorous dinosaurs of the order Ornithischia. It includes the great majority of dinosaurs with armor in the form of bony osteoderms, similar to turtles. Ankylosaurs were bulky quadrupeds, with short, powerful limbs. They are known to have first appeared in the Middle Jurassic, and persisted until the end of the Cretaceous Period. The two main families of Ankylosaurs, Nodosauridae and Ankylosauridae are primarily known from the Northern Hemisphere, but the more basal Parankylosauria are known from southern Gondwana during the Cretaceous. Ankylosauria was first named by Henry Fairfield Osborn in 1923.Osborn, H. F. (1923). "Two Lower Cretaceous dinosaurs of Mongolia." ''American Museum Novitates'', 95: 1–1/ref> In the Linnaean classification system, the group is usually considered either a suborder or an infraorder. It is contained within the group Thyreophora, which also includes the stegosaurs, armored dinosaurs known for their combination of plate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Docodonta
Docodonta is an Order (biology), order of extinct Mammaliaformes, mammaliaforms that lived during the Mesozoic, from the Middle Jurassic to Early Cretaceous. They are distinguished from other early Mammaliaformes, mammaliaforms by their relatively complex Molar (tooth), molar teeth, from which the order gets its name. Until recently, Docodonta were represented primarily by teeth and jaws found across former Laurasia, (modern-day North America, Europe, and Asia). However, recent discoveries in China include some exceptionally well preserved, almost complete body fossils. Description Skeletal traits Docodonts have a long and low mandible (lower jaw), formed primarily by the tooth-bearing dentary bone. The dentary connects to the cranium via a joint with the Squamosal bone, squamosal, a connection which is strengthened relative to earlier mammaliaforms. The other bones in the jaw, known as postdentary elements, are still connected to the dentary and lie within a groove (the postd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sineleutherus
''Sineleutherus'' is an extinct genus of euharamiyids which existed in Asia during the Jurassic period. The type species is ''Sineleutherus uyguricus'', which was described by Thomas Martin, Alexander O. Averianov and Hans-Ulrich Pfretzschner in 2010; it lived in what is now China during the late Jurassic ( Oxfordian age) Qigu Formation. A second species, ''Sineleutherus issedonicus'', was described by A. O. Averianov, A. V. Lopatin and S. A. Krasnolutskii in 2011. It lived in what is now Sharypovsky District (Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia) during the middle Jurassic (Bathonian age); its fossils were collected from the upper part of the Itat Formation The Itat Formation (Russian: итатская свита) is a geologic formation in western Siberia. It was deposited in the Bajocian to Bathonian ages of the Middle Jurassic. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from t .... However, this is now believed to represent several euharamiyid taxa not closey related ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossilworks
Fossilworks is a portal which provides query, download, and analysis tools to facilitate access to the Paleobiology Database The Paleobiology Database is an online resource for information on the distribution and classification of fossil animals, plants, and microorganisms. History The Paleobiology Database (PBDB) originated in the NCEAS-funded Phanerozoic Marine Pale ..., a large relational database assembled by hundreds of paleontologists from around the world. History Fossilworks was created in 1998 by John Alroy and is housed at Macquarie University. It includes many analysis and data visualization tools formerly included in the Paleobiology Database.{{cite web, title=Frequently asked questions, url=http://www.fossilworks.org/cgi-bin/bridge.pl?page=FAQ, publisher=Fossilworks, access-date=17 December 2021 References {{Reflist External links {{Wikidata property, P842 * [Baidu] |
Khurendukhosaurus
''Khurendukhosaurus'' is a genus of choristodere, a type of amphibious reptile. It is known from Lower Cretaceous rocks of Mongolia and Russia. Two species have been named. The type species, ''K. orlovi'', was named in 1984 by Sigogneau–Russell and Efimov for the fragmentary postcranial skeleton PIN 3386/3. This specimen was discovered in the Albian-age Lower Cretaceous Khuren Dukh Formation Formation at Hüren Dukh, central Mongolia. The lake deposits at this site also contain fossils of the choristoderes ''Irenosaurus'' and ''Tchoiria''. Other postcranial bones of ''K. orlovi'' have been found at this site as well. Second species ''K. bajkalensis'' was named by Efimov in 1996 for PIN 2234/201, consisting of a scapulocoracoid and a rib. These bones were found in the Lower Cretaceous Murtoi Formation at Lake Gusinoye, Buryatia, Russia. The first Russian choristodere, Efimov and Storrs (2000) found it difficult to distinguish from ''K. orlovi'' based on the smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choristodere
Choristodera (from the Greek χωριστός ''chōristos'' + δέρη ''dérē'', 'separated neck') is an extinct order of semiaquatic diapsid reptiles that ranged from the Middle Jurassic, or possibly Triassic, to the late Miocene (168 to 11.6 million years ago). Choristoderes are morphologically diverse, with the best known members being the crocodile-like neochoristoderes such as ''Champsosaurus''. Other choristoderans had lizard-like or long necked morphologies. Choristoderes appear to have been confined to the Northern Hemisphere, having been found in North America, Asia, and Europe, and possibly also North Africa. Choristoderes are generally thought to be derived neodiapsids that are close relatives or members of Sauria. History of Discovery Choristodera was erected in 1876, originally as a suborder of Rhynchocephalia by Edward Drinker Cope to contain ''Champsosaurus,'' which was described from Late Cretaceous strata of Montana by Cope in the same paper. A year late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenocretosuchus
''Xenocretosuchus'' is an extinct genus of tritylodont therapsids from the Aptian (Early Cretaceous) Ilek Formation of Siberia, in the Russian Federation. The type species, ''X. sibiricus'', is known only from dental elements, as is ''X. kolossovi'', described from the Batylykh Formation in 2008.Lopatin & Agadjanian, 2008. "A Tritylodont (Tritylodontidae, Synapsida) from the Mesozoic of Yakutia." Retrieved fro/ref> Some authors have treated these species as part of the genus ''Stereognathus,'' otherwise known from the Middle Jurassic of Britain But this is rejected by other authors. Alongside ''Montirictus'' and '' Fossiomanus'', it is amongst the latest known non-mammaliform-synapsid Synapsids + (, 'arch') > () "having a fused arch"; synonymous with ''theropsids'' (Greek, "beast-face") are one of the two major groups of animals that evolved from basal amniotes, the other being the sauropsids, the group that includes reptil ..., extending their range to the Early Cretaceous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tritylodontid
Tritylodontidae ("three-knob teeth", named after the shape of their cheek teeth) is an extinct family of small to medium-sized, highly specialized mammal-like cynodonts, bearing several mammalian traits like erect limbs, endothermy and details of the skeleton. They were the last-known family of the non-mammaliaform synapsids, persisting into the Early Cretaceous. Most tritylodontids are thought to have been herbivorous, feeding on vegetation, such as stems, leaves, and roots, although at least one may have had a more omnivorous diet. Tritylodontid fossils are found in the Americas, South Africa, and Eurasia—they appear to have had an almost global distribution, including Antarctica. Description The skull of tritylodontids had a high sagittal crest. They retained the primitive condition of the joint between the quadrate bone of the skull and the articular bone of the lower jaw—the retention of the joint is one of the reasons they are technically regarded to not be mammals, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |