|
Battle Of Évora (1808)
The Battle of Évora (29 July 1808) saw an Imperial French division under Louis Henri Loison attack a combined Portuguese-Spanish force led by Francisco de Paula Leite de Sousa. Encountering Leite's smaller body of soldiers outside Évora, the French easily brushed them aside and went on to storm the city, which was held by poorly armed townsmen and militia. The French butchered the Portuguese defenders and brutally sacked the town. Loison was known among the Portuguese as the ''Maneta'' (One-Hand), because of his amputated arm. From savage acts such as those committed at Évora, the saying ''ir para o Maneta'' (going to the One-Hand) appeared. The clash occurred during the Peninsular War, phase of the Napoleonic Wars. Évora is located about east of Lisbon. In November 1807, a French army led by Jean-Andoche Junot mounted a successful Invasion of Portugal (1807), Invasion of Portugal supported by allied Spanish troops. For several months, the French were able to maintain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peninsular War
The Peninsular War (1807–1814) was the military conflict fought in the Iberian Peninsula by Spain, Portugal, and the United Kingdom against the invading and occupying forces of the First French Empire during the Napoleonic Wars. In Spain, it is considered to overlap with the Spanish War of Independence. The war started when the French and Spanish armies invaded and occupied Portugal in 1807 by transiting through Spain, and it escalated in 1808 after Napoleonic France occupied Spain, which had been its ally. Napoleon Bonaparte forced the abdications of Ferdinand VII and his father Charles IV and then installed his brother Joseph Bonaparte on the Spanish throne and promulgated the Bayonne Constitution. Most Spaniards rejected French rule and fought a bloody war to oust them. The war on the peninsula lasted until the Sixth Coalition defeated Napoleon in 1814, and is regarded as one of the first wars of national liberation. It is also significant for the emergence of larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Grijó
The Battle of Grijó () (10–11 May 1809) was a battle that ended in victory for the Anglo-Portuguese Army commanded by Sir Arthur Wellesley (the future 1st Duke of Wellington) over the French army commanded by Marshal Nicolas Soult during the second French invasion of Portugal in the Peninsular War. The next day, Wellesley drove Soult from Porto in the Second Battle of Porto. Background The Second Portuguese campaign started with the Battle of Braga. Battle On 10 May British Cavalry under the command of General Sir Stapleton Cotton came into contact with outlying French Forces, after a short engagement they were scatted, both sides only suffering light casualties, but many French prisoners were taken. The following day, on the 10th, a larger force commanded by General Julien Augustin Joseph Mermet defended the forested ridge, south of Grijo. the Anglo-allied forces under the command of Sir Arthur Wellesley (later Duke of Wellington) attacked them from the south, using a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elvas Municipality
Elvas () is a Portuguese municipality, former episcopal city and frontier fortress of easternmost central Portugal, located in the district of Portalegre in Alentejo. It is situated about east of Lisbon, and about west of the Spanish fortress of Badajoz, by the Madrid-Badajoz-Lisbon railway. The municipality population was 23,078, in an area of . The city itself had a population of 16,640 . Elvas is among the finest examples of intensive usage of the ''trace italienne'' (star fort) in military architecture, and has been a World Heritage Site since 30June 2012. The inscribed site name is Garrison Border Town of Elvas and its Fortifications. History Elvas lies on a hill northwest of the Guadiana river. The Amoreira Aqueduct long supplies the city with pure water; it was begun early in the 15th century and completed in 1622. For some distance it includes four tiers of superimposed arches, with a total height of . It was wrested from the Moors by Afonso I of Portugal in 1166 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elvas Castle
The Castle of Elvas ( pt, Castelo de Elvas) is a medieval military fortification in Portugal, in the civil parish of Alcáçova, municipality of Elvas, part of a first line of defense in the Portuguese Alentejo, in conjunction with the military forts of Ouguela, Campo Maior, Olivença and Juromenha. History Between the 8th and 12th century Muslim forces occupied Elvas, resulting in the construction of the fortress. It was briefly conquered by forces loyal to Afonso Henriques around 1166, an action that was repeated in successive years with Moorish capture, and recapture, of the strategic point. In 1200 Sancho I encircled the citadel, and his successor, Sancho II made a tentative attempt to capture Elvas in 1226, at the same time Alfonso IX of León was trying to take Badajoz: although concerted, it was unsuccessful. This was followed in 1228 by another attempt, also unsuccessful, until 1230, after the castle and surrounding territory was abandoned by Muslim forces, who had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dos De Mayo Uprising
On the 2 and 3 May 1808 the Dos de Mayo or Second of May Uprising of 1808 took place in Madrid, Spain. It was a rebellion by civilians alongside some military against the occupation of the city by French troops, provoking a heavy-hand repression by the French Imperial forces. Background The city had been under the occupation of Napoleon's army since 23 March of the same year. King Charles IV had been forced by the Spanish people during the Tumult of Aranjuez to abdicate in favor of his son Ferdinand VII, and at the time of the uprising both were in the French city of Bayonne at the insistence of Napoleon. An attempt by the French general Joachim Murat to move the daughter and her children along with the youngest son of Charles IV to Bayonne sparked a rebellion. Social aspects The ''Dos de Mayo'' was among the few spontaneous popular uprisings of the war, launched without significant fore-planning, funding, or leadership by government elites. While element ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Andoche Junot
Jean-Andoche Junot, 1st Duke of Abrantes (24 September 1771 – 29 July 1813) was a French military officer during the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars. Biography Early life Junot was born in Bussy-le-Grand, Côte-d'Or, son of Michel Junot, a farmer (1739–1814), and wife Marie Antoinette Bienaymé (1735–1806). His father was the son of François Junot (?–1759) and wife Edmée Laurain (1703–1784), while his mother was the daughter of Guy Bienaymé and wife Ursule Rigoley. Jean-Andoche went to school in Châtillon. He was studying law in Dijon when the French Revolution started. After joining a battalion as volunteer, he was twice wounded and also made sergeant. He first met Napoleon Bonaparte during the siege of Toulon in 1793, when he became his secretary (aide de camp). Italian campaign He distinguished himself in Italy but received a serious head wound at Lonato, which some claim led to a permanent change in his character, reduced the quality ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lisbon
Lisbon (; pt, Lisboa ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 544,851 within its administrative limits in an area of 100.05 km2. Grande Lisboa, Lisbon's urban area extends beyond the city's administrative limits with a population of around 2.7 million people, being the List of urban areas of the European Union, 11th-most populous urban area in the European Union.Demographia: World Urban Areas - demographia.com, 06.2021 About 3 million people live in the Lisbon metropolitan area, making it the third largest metropolitan area in the Iberian Peninsula, after Madrid and Barcelona. It represents approximately 27% of the country's population. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of French domination over most of continental Europe. The wars stemmed from the unresolved disputes associated with the French Revolution and the French Revolutionary Wars consisting of the War of the First Coalition (1792–1797) and the War of the Second Coalition (1798–1802). The Napoleonic Wars are often described as five conflicts, each termed after the coalition that fought Napoleon: the Third Coalition (1803–1806), the Fourth (1806–1807), the Fifth (1809), the Sixth (1813–1814), and the Seventh (1815) plus the Peninsular War (1807–1814) and the French invasion of Russia (1812). Napoleon, upon ascending to First Consul of France in 1799, had inherited a republic in chaos; he subsequently created a state with stable financ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Fuentes De Oñoro
In the Battle of Fuentes de Oñoro (3–5 May 1811), the British–Portuguese Army under Wellington checked an attempt by the French Army of Portugal under Marshal André Masséna to relieve the besieged city of Almeida. A bloody stalemate was not the sort of battle that had been expected to follow André Masséna's expulsion from Portugal. His confidence and moral authority having been much boosted by Torres Vedras, the spring of 1811 found Wellington intending to move over to the offensive, for which policy he had received de facto authorisation from his political masters in London, where talks of major reductions in the size of the army employed in Portugal had been replaced by promises of major reinforcements. Supply difficulties, sickness amongst the troops and want of siege artillery ensured that in the short term no great strokes of strategy could be envisaged, but it was hoped that Almeida, Ciudad Rodrigo and Badajoz might be all recaptured, thereby opening the wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Sabugal
The Battle of Sabugal was an engagement of the Peninsular War which took place on 3 April 1811 between Anglo-Portuguese forces under Arthur Wellesley (later the Duke of Wellington) and French troops under the command of Marshal André Masséna. It was the last of many skirmishes between Masséna's retreating French forces and those of the Anglo-Portuguese under Wellington, who were pursuing him after the failed 1810 French invasion of Portugal. In poor weather, with heavy rain and fog, Allied forces succeeded in forcing the demoralized French force into retreat. The victory was lauded by the British; Sir Harry Smith, then a junior officer of the 95th Rifles and a participant in the battle, remarked "Oh, you Kings and usurpers should view these scenes and moderate ambition" while Wellesley later referred to the Light Division's action in the battle as "one of the most glorious that British troops were ever engaged in". Background By October 1810, Marshal Massena’s Fren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Redinha
The Battle of Redinha was a rearguard action which took place on March 12, 1811, during Masséna's retreat from Portugal, by a French division under Marshal Ney against a considerably larger Anglo-Portuguese force under Wellington. Challenging the Allies with only one or two divisions, Ney's 7,000 troops were pitched against 25,000 men. In a typical rearguard action, Ney delayed the Allied advance for a day and bought valuable time for the withdrawal of the main body of the French army. Redinha was the second and most successful rearguard action fought during Masséna's retreat from the Lines of Torres Vedras in the spring of 1811. Having held off the British at Pombal on 11 March, Marshal Ney and the French rearguard had retreated to Redinha. Here he took up an apparently vulnerable position, with Mermet's division on a plateau south of the village, and Marchand's division north of the village on the far side of the Ancos River, linked by a narrow bridge, but Wellington was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
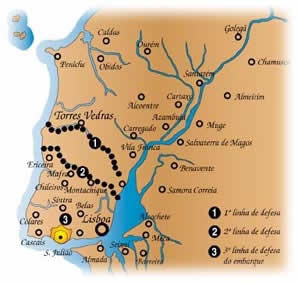
Lines Of Torres Vedras
The Lines of Torres Vedras were lines of forts and other military defences built in secrecy to defend Lisbon during the Peninsular War. Named after the nearby town of Torres Vedras, they were ordered by Arthur Wellesley, Viscount Wellington, constructed by Sir Richard Fletcher, 1st Baronet, and his Portuguese workers between November 1809 and September 1810, and used to stop Marshal Masséna's 1810 offensive. The Lines were declared a National Heritage by the Portuguese Government in March 2019. Development At the beginning of the Peninsular War (1807–14) France and Spain signed the Treaty of Fontainebleau in October 1807. This provided for the invasion and subsequent division of Portuguese territory into three kingdoms. Subsequently, French troops under the command of General Junot entered Portugal, which requested support from the British. In July 1808 troops commanded by Sir Arthur Wellesley, the later Duke of Wellington, landed in Portugal and defeated French tro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |