|
Battle Of Panipat (1526)
The first Battle of Panipat, on 20 April 1526, was fought between the invading forces of Babur and the Lodi dynasty. It took place in North India and marked the beginning of the Mughal Empire and the end of the Delhi Sultanate. This was one of the earliest battles involving gunpowder firearms and field artillery in the Indian subcontinent which were introduced by Mughals in this battle. Background After losing Samarkand for the second time, Babur gave attention to conquer Hindustan as he reached the banks of the Chenab in 1519. Until 1524, his aim was to only expand his rule to Punjab, mainly to fulfil his ancestor Timur's legacy, since it used to be part of his empire. At that time, most of North India was under the rule of Ibrahim Lodi of the Lodi dynasty, but the empire was crumbling and there were many defectors. He received invitations from Daulat Khan Lodi, Governor of Punjab and Ala-ud-Din, uncle of Ibrahim. He sent an ambassador to Ibrahim, claiming himself th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the dynasty and the empire itself became indisputably Indian. The interests and futures of all concerned were in India, not in ancestral homelands in the Middle East or Central Asia. Furthermore, the Mughal empire emerged from the Indian historical experience. It was the end product of a millennium of Muslim conquest, colonization, and state-building in the Indian subcontinent." For some two hundred years, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus river basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to the highlands of present-day Assam and Bangladesh in the east, and the uplands of the Deccan Plateau in South India. Quote: "The realm so defined and governed was a vast territory of some , ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
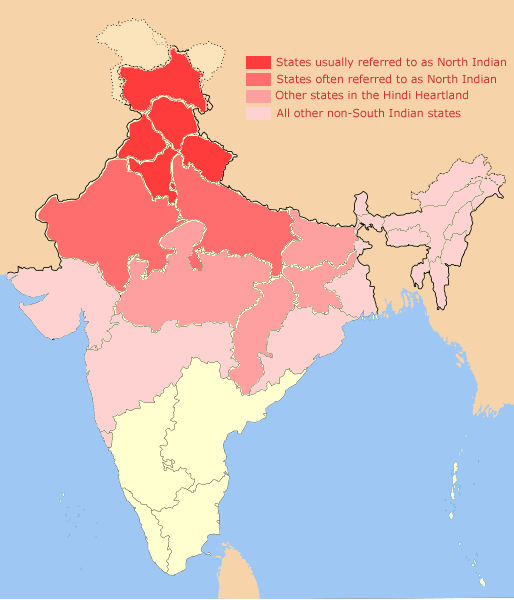
North India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central Asia. The term North India has varying definitions. The Ministry of Home Affairs in its Northern Zonal Council Administrative division included the states of Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab and Rajasthan and Union Territories of Chandigarh, Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh. The Ministry of Culture in its ''North Culture Zone'' includes the state of Uttarakhand but excludes Delhi whereas the Geological Survey of India includes Uttar Pradesh and Delhi but excludes Rajasthan and Chandigarh. Other states sometimes included are Bihar, Gujarat, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh and West Bengal. North India has been the historical centre of the Mughal Empire, the Delhi Sultanate and the British Indian Empire. It has a diverse c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) // CITED: p. 36 (PDF p. 38/338) also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and North Africa, Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe and, with the Ottoman wars in Europe, conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman Anatolian beyliks, beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the Fall of Constantinople, conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror. Under the reign of Sule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipalpur
Dipalpur ( pa, ; ur, ), also spelt Depalpur, is a city in the Okara District of Pakistani province of Punjab that served as headquarters of Depalpur Tehsil, the largest Tehsil of Pakistan. It is situated 25 kilometres from the district capital Okara on a bank of river Satluj in Bari Doab. It is located in the west of District Kasur. History Early Depalpur has a great historic past and is a very ancient town. The fortified town of Dipalpur is built on an old Kushan site ( 40 A.D. to 172 A.D.). The fortifications themselves are very ancient; though it is impossible determine their dates. All that can be said is that they are older than the visitation of Timur in 1398 A.D. From the time of Alexander to the time of Mahmud Ghaznavi, there were no found accounts of Dipalpur. According to the Gazetteer of 1935, the town was claimed to be founded by Sri Chand Khanna it was called Sri Nagar at that time, The modern name is claimed to have been named by Raja Deva Pala after he r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lahore
Lahore ( ; pnb, ; ur, ) is the second most populous city in Pakistan after Karachi and 26th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 13 million. It is the capital of the province of Punjab where it is the largest city. Lahore is one of Pakistan's major industrial and economic hubs, with an estimated GDP ( PPP) of $84 billion as of 2019. It is the largest city as well as the historic capital and cultural centre of the wider Punjab region,Lahore Cantonment globalsecurity.org and is one of Pakistan's most socially liberal, |
Daulat Khan Lodi
Daulat Khan Lodi (Pashto: دولت خان لودی) was the governor of Lahore during the reign of Ibrahim Lodi, the last ruler of the Lodi dynasty. Due to disaffection with Ibrahim, Daulat invited Babur to invade the kingdom. He was initially governor of the Jalandhar Doab before being promoted with the governorship of the entire Punjab. He was the son of Tatar Khan, the previous Nizam of Punjab, who had asserted his independence from Lodi dynasty under Behlol Lodi, father of Sikander Lodi (also known as Nizam Khan Lodi). Daulat Khan was loyal to the dynasty but betrayed Ibrahim due to his rigid, proud and suspicious nature. Aid of Babur In 1523, Ibrahim Lodi, Daulat Khan's sovereign, was locked in a power struggle with his relatives and minister. Daulat Khan was one of Ibrahim's chief opponents, along with the ruler's own uncle, Alam Khan (also known as Ala-ud-din), who at that time was living under the protection of Sultan Muzaffar of Gujarat. There was rebellion throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timur
Timur ; chg, ''Aqsaq Temür'', 'Timur the Lame') or as ''Sahib-i-Qiran'' ( 'Lord of the Auspicious Conjunction'), his epithet. ( chg, ''Temür'', 'Iron'; 9 April 133617–19 February 1405), later Timūr Gurkānī ( chg, ''Temür Küregen''), was a Turco-Mongol tradition, Turco-Mongol conqueror who founded the Timurid Empire in and around modern-day Afghanistan, Iran, and Central Asia, becoming the first ruler of the Timurid dynasty. An undefeated commander, he is widely regarded as one of the greatest military leaders and tacticians in history, as well as one of the most brutal. Timur is also considered a great patron of art and architecture as he interacted with intellectuals such as Ibn Khaldun, Hafez, and Hafiz-i Abru and his reign introduced the Timurid Renaissance. Born into the Barlas confederation in Transoxiana (in modern-day Uzbekistan) on 9 April 1336, Timur gained control of the western Chagatai Khanate by 1370. From that base, he led military campaigns acr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of eastern Pakistan and northwestern India. Punjab's capital and largest city and historical and cultural centre is Lahore. The other major cities include Faisalabad, Rawalpindi, Gujranwala, Multan, Ludhiana, Amritsar, Sialkot, Chandigarh, Jalandhar, and Bahawalpur. Punjab grew out of the settlements along the five rivers, which served as an important route to the Near East as early as the ancient Indus Valley civilization, dating back to 3000 BCE, and had numerous migrations by the Indo-Aryan peoples. Agriculture has been the major economic feature of the Punjab and has therefore formed the foundation of Punjabi culture, with one's social status being determined by land ownership. The Punjab emerged as an important agricultur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chenab River
The Chenab River () is a major river that flows in India and Pakistan, and is one of the 5 major rivers of the Punjab region. It is formed by the union of two headwaters, Chandra and Bhaga, which rise in the upper Himalayas in the Lahaul region of Himachal Pradesh, India. The Chenab flows through the Jammu region of Jammu and Kashmir, India into the plains of Punjab, Pakistan, before ultimately flowing into the Indus River. The waters of the Chenab were allocated to Pakistan under the terms of the Indus Waters Treaty. India is allowed non-consumptive uses such as power generation. The Chenab River is extensively used in Pakistan for irrigation. Its waters are also transferred to the channel of the Ravi River via numerous link canals. Name The Chenab river was called ' ( sa, असिक्नी) in the Rigveda (VIII.20.25, X.75.5). The name meant that it was seen to have dark-coloured waters. The term Krishana is also found in the Atharvaveda. A later form of Askikni wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindustan
''Hindūstān'' ( , from '' Hindū'' and ''-stān''), also sometimes spelt as Hindōstān ( ''Indo-land''), along with its shortened form ''Hind'' (), is the Persian-language name for the Indian subcontinent that later became commonly used by its inhabitants in the Hindi–Urdu language. Hindustan was the Persian word for ''India'', but when introduced to the subjects under Persianate rule, the subsequent culture which resulted from these events gave it another specific meaning that of the cultural region between the river Sutlej (end of Northwestern India) and the city Varanasi (start of Eastern India). As the area where Ganga-Jamuni Tehzeeb and the Hindustani language traces its origins, it corresponds to the plains where the river Yamuna flows or the regions/states encompassing Haryana, Delhi, Harit Pradesh, and Awadh. Other toponyms for the subcontinent include '' Jambudvīpa'' and ''Bharata Khanda''. Since the Partition of India in 1947, although limitedly, ''H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Samarkand (1501)
{{Infobox military conflict , conflict = Siege of Samarkand , partof = Campaigns of Babur , image = Shaybani.jpg , image_size = 250 , caption = Muhammad Shaybani , date = 1501 , place = Samarkand, Uzbekistan , result = Mughal victory , combatant1 = Mughal Empire , combatant2 = Khanate of Bukhara , commander1 = Babur , commander2 = Muhammad Shaybani , strength1=Unknown, strength2=Unknown, casualties1=Unknown, casualties2=Unknown , campaignbox = {{Campaignbox Babur The siege of Samarkand was the third and last campaign against the city by both belligerents. Four years after its recapture by the forces of Babur Babur ( fa, , lit= tiger, translit= Bābur; ; 14 February 148326 December 1530), born Mīrzā Zahīr ud-Dīn Muhammad, was the founder of the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. He was a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |