|
Battle Of Adramyttion (1205)
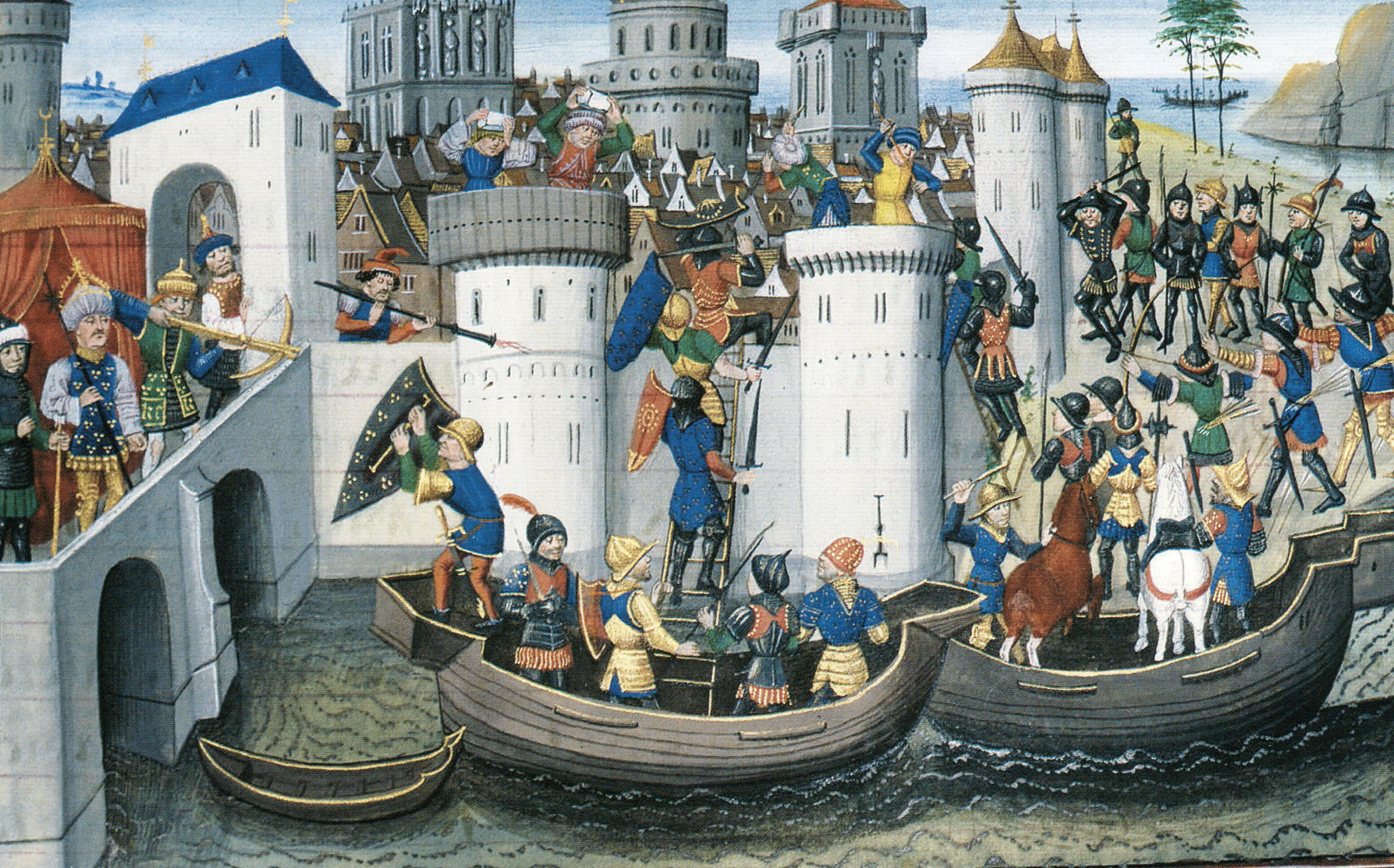
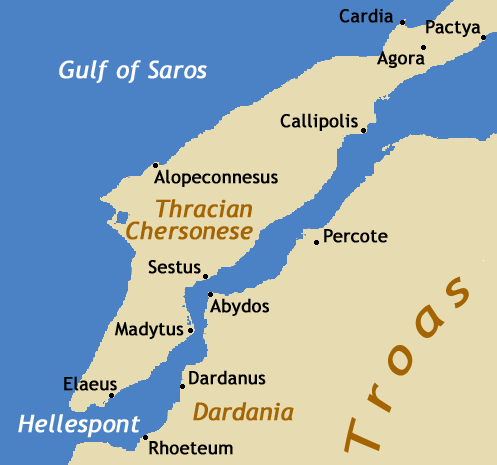
The Battle of Adramyttion occurred on 19 March 1205 between the Latin Crusaders and the Byzantine Greek Empire of Nicaea, one of the kingdoms established after the fall of Constantinople to the Fourth Crusade in 1204. It resulted in a comprehensive victory for the Latins. There are two accounts of the battle, one by Geoffrey de Villehardouin, and the other by Nicetas Choniates, which differ significantly. Villehardouin's account Henry of Flanders, brother to Emperor Baldwin I of Constantinople, was encouraged by the Armenians to make an attempt on the city of Adramyttion. He left from Abydos, after leaving a garrison in the town, and rode for two days before encamping before Adramyttion. The city soon surrendered, and Henry proceeded to occupy it, using it as a base to attack the Byzantines. Theodore Laskaris, who had been troubled by his defeat at Battle of Poemanenum, collected as many people as he could from around Nicaea and assembled a large army. He gave the command of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicaean–Latin Wars
The Nicaean–Latin wars were a series of wars between the Latin Empire and the Empire of Nicaea, starting with the dissolution of the Byzantine Empire by the Fourth Crusade in 1204. The Latin Empire was aided by other Crusader states established on Byzantine territory after the Fourth Crusade, as well as the Republic of Venice, while the Empire of Nicaea was assisted occasionally by the Second Bulgarian Empire, and sought the aid of Venice's rival, the Republic of Genoa. The conflict also involved the Greek state of Epirus, which also claimed the Byzantine inheritance and opposed Nicaean hegemony. The Nicaean reconquest of Constantinople in 1261 AD and the restoration of the Byzantine Empire under the Palaiologos dynasty did not end the conflict, as the Byzantines launched on and off efforts to reconquer southern Greece (the Principality of Achaea and the Duchy of Athens) and the Aegean islands until the 15th century, while the Latin powers, led by the Angevin Kingdom of Naples, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
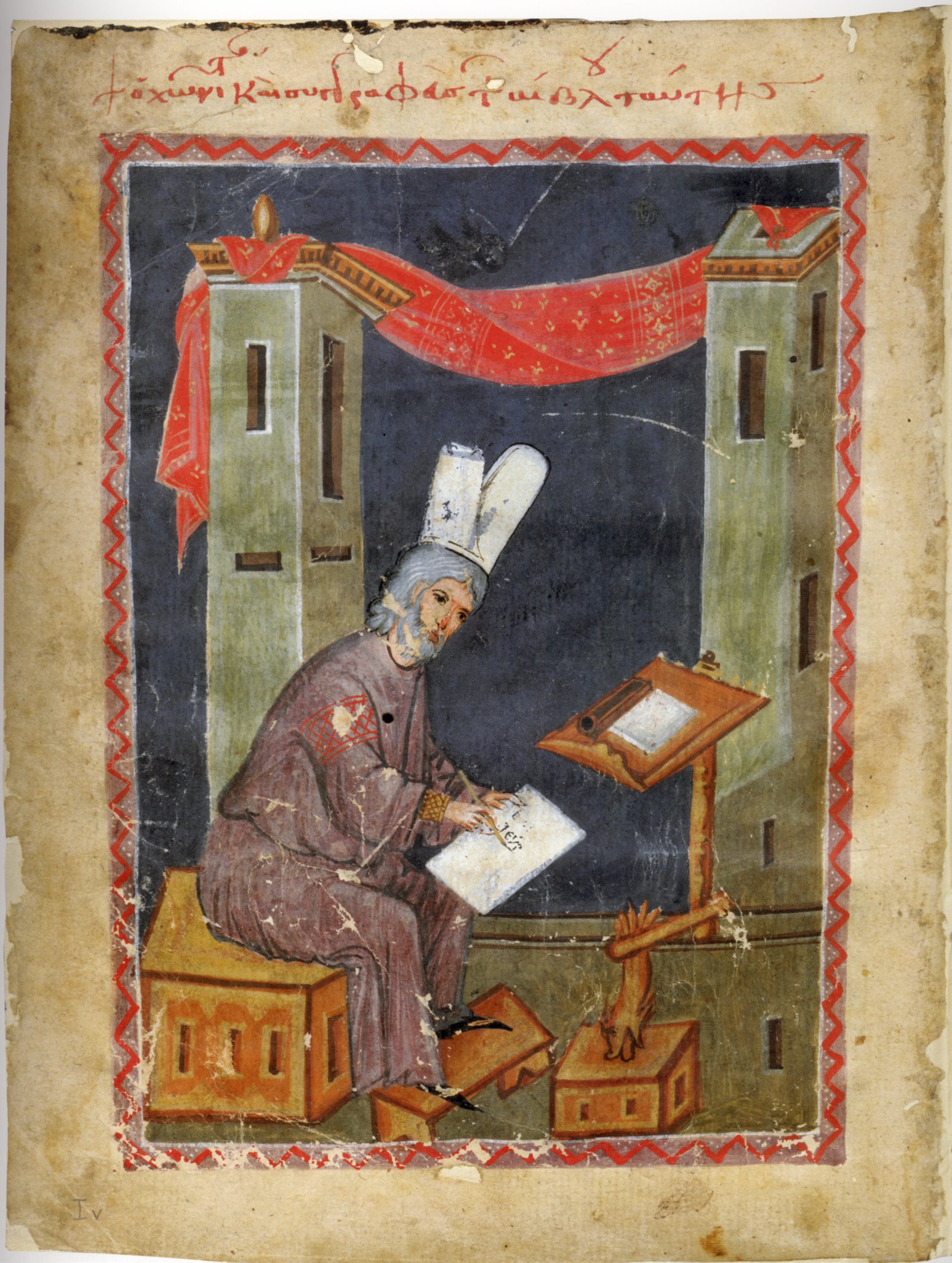
Nicetas Choniates
Niketas or Nicetas Choniates ( el, Νικήτας Χωνιάτης; c. 1155 – 1217), whose actual surname was Akominatos (Ἀκομινάτος), was a Byzantine Greek government official and historian – like his brother Michael Akominatos, whom he accompanied to Constantinople from their birthplace Chonae (from which came his nickname, "Choniates" meaning "person from Chonae"). Nicetas wrote a history of the Eastern Roman Empire from 1118 to 1207. Life Nicetas Akominatos was born to wealthy parents around or after 1150 in Phrygia in the city of Chonae (near the modern Honaz in Turkey). Bishop Nicetas of Chonae baptized and named the infant; later he was called "Choniates" after his birthplace. When he was nine, his father dispatched him with his brother Michael to Constantinople to receive an education. Niketas' older brother greatly influenced him during the early stages of his life. He initially secured a post in the civil service, and held important appointments under t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conflicts In 1205
Conflict may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Conflict'' (1921 film), an American silent film directed by Stuart Paton * ''Conflict'' (1936 film), an American boxing film starring John Wayne * ''Conflict'' (1937 film), a Swedish drama film directed by Per-Axel Branner * ''Conflict'' (1938 film), a French drama film directed by Léonide Moguy * ''Conflict'' (1945 film), an American suspense film starring Humphrey Bogart * ''Catholics: A Fable'' (1973 film), or ''The Conflict'', a film starring Martin Sheen * ''Judith'' (1966 film) or ''Conflict'', a film starring Sophia Loren * ''Samar'' (1999 film) or ''Conflict'', a 1999 Indian film by Shyam Benegal Games * ''Conflict'' (series), a 2002–2008 series of war games for the PS2, Xbox, and PC * ''Conflict'' (video game), a 1989 Nintendo Entertainment System war game * '' Conflict: Middle East Political Simulator'', a 1990 strategy computer game Literature and periodicals * ''Conflict'' (novel) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Involving The Empire Of Nicaea
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles In Medieval Anatolia
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Of The Fourth Crusade
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1205 In Europe
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaşehir
Alaşehir (), in Antiquity and the Middle Ages known as Philadelphia ( el, Φιλαδέλφεια, i.e., "the city of him who loves his brother"), is a town and district of Manisa Province in the Aegean region of Turkey. It is situated in the valley of the Kuzuçay ( Cogamus in antiquity), at the foot of the Bozdağ Mountain (Mount Tmolus in antiquity). The town is connected to İzmir by a railway. It stands on elevated ground commanding the extensive and fertile plain of the Gediz River (Hermus in antiquity), presenting an imposing appearance when seen from a distance. It has about 45 mosques. There are small industries and a fair trade. From one of the mineral springs comes a heavily charged water popular around Turkey. Within Turkey, the city's name is synonymous with the dried Sultana raisins, although cultivation for the fresh fruit market, less labour-intensive than the dried fruit, has gained prominence in recent decades. As Philadelphia, Alaşehir was a highly importan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niketas Choniates
Niketas or Nicetas Choniates ( el, Νικήτας Χωνιάτης; c. 1155 – 1217), whose actual surname was Akominatos (Ἀκομινάτος), was a Byzantine Greek government official and historian – like his brother Michael Akominatos, whom he accompanied to Constantinople from their birthplace Chonae (from which came his nickname, "Choniates" meaning "person from Chonae"). Nicetas wrote a history of the Eastern Roman Empire from 1118 to 1207. Life Nicetas Akominatos was born to wealthy parents around or after 1150 in Phrygia in the city of Chonae (near the modern Honaz in Turkey). Bishop Nicetas of Chonae baptized and named the infant; later he was called "Choniates" after his birthplace. When he was nine, his father dispatched him with his brother Michael to Constantinople to receive an education. Niketas' older brother greatly influenced him during the early stages of his life. He initially secured a post in the civil service, and held important appointments under t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodore I Laskaris
Theodore I Laskaris or Lascaris ( gr, Θεόδωρος Κομνηνὸς Λάσκαρις, Theodōros Komnēnos Laskaris; 1175November 1221) was the first emperor of Nicaea—a successor state of the Byzantine Empire—from 1205 to his death. Although he was born to an obscure aristocratic family, his mother was related to the imperial Komnenos clan. He married Anna, a younger daughter of Emperor Alexios III Angelos in 1200. He received the title of despot before 1203, demonstrating his right to succeed his father-in-law on the throne. The Fourth Crusade forced AlexiosIII to flee from Constantinople in 1203. Theodore was imprisoned by the crusaders (commonly referred to as " Latins" by the Byzantines), but he escaped. After crossing the Bosporus into Asia Minor (in present-day Turkey), he started to organise the local Greeks' resistance against the Latins in Bithynia in his father-in-law's name. He concluded an alliance with the Seljuq sultan of Rum, but he could ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abydos, Hellespont
Abydos ( grc, Ἄβυδος, la, Abydus) was an ancient city and bishopric in Mysia. It was located at the Nara Burnu promontory on the Asian coast of the Hellespont (the straits of Dardanelles), opposite the ancient city of Sestos, and near the city of Çanakkale in Turkey. Abydos was founded in c. 670 BC at the most narrow point in the straits, and thus was one of the main crossing points between Europe and Asia, until its replacement by the crossing between Lampsacus and Kallipolis in the 13th century, and the abandonment of Abydos in the early 14th century. In Greek mythology, Abydos is presented in the myth of Hero and Leander as the home of Leander. The city is also mentioned in ''Rodanthe and Dosikles'', a novel written by Theodore Prodromos, a 12th-century writer, in which Dosikles kidnaps Rodanthe at Abydos. Archaeology In 1675, the site of Abydos was first identified, and was subsequently visited by numerous classicists and travellers, such as Robert Wood, Richard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baldwin I Of Constantinople
Baldwin I ( nl, Boudewijn; french: Baudouin; July 1172 – ) was the first Emperor of the Latin Empire of Constantinople; Count of Flanders (as Baldwin IX) from 1194 to 1205 and Count of Hainaut (as Baldwin VI) from 1195-1205. Baldwin was one of the most prominent leaders of the Fourth Crusade, which resulted in the sack of Constantinople in 1204, the conquest of large parts of the Byzantine Empire, and the foundation of the Latin Empire. He lost his final battle to Kaloyan, the emperor of Bulgaria, and spent his last days as his prisoner. Early life and family history Baldwin was the son of Count Baldwin V of Hainaut and Countess Margaret I of Flanders.. When the childless Count Philip I of Flanders left on the last of his personal crusades in 1177, he designated Baldwin, his brother-in-law, as his heir. When Philip returned in 1179 after an unsuccessful siege of Harim during a joint campaign on behalf of the Principality of Antioch, he was designated as the chief advise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |