Abydos, Hellespont on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Abydos ( grc, Ἄβυδος, la, Abydus) was an ancient city and bishopric in
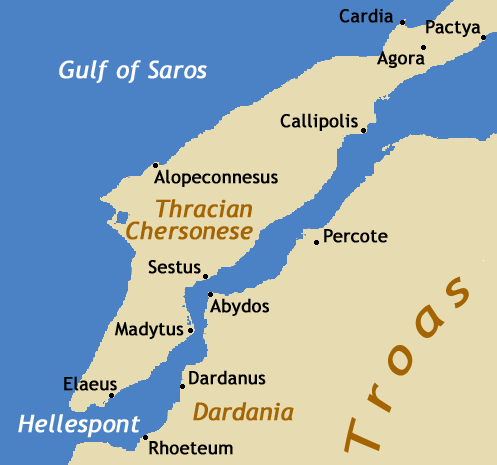 Abydos is mentioned in the ''
Abydos is mentioned in the '' During the
During the
Abydus
'. Brill Reference Online The city was conquered by During the
During the
Abydos
(C. Foss), pp. 8–9
Ports
(A. Kazhdan), pp. 1706–1707
Nikephoros I
(P. A. Hollingsworth), pp. 1476–1477 The city later also became part of the Aegean Sea (theme), theme of the Aegean Sea and was the seat of a ''tourmarches''. Abydos was sacked by an Abbasid Caliphate, Arab fleet led by Leo of Tripoli in 904 AD whilst en route to Constantinople.Kazhdan (1991)
Leo of Tripoli
(A. Kazhdan), p. 1216 The Rebellion of Bardas Phokas the Younger, revolt of Bardas Phokas the Younger, Bardas Phokas was defeated by Emperor Basil II at Abydos in 989 AD. In 992, the Republic of Venice, Venetians were granted reduced commercial tariffs at Abydos as a special privilege. In the early 11th century, Abydos became the seat of a separate command and the office of ''strategos'' (governor) of Abydos is first mentioned in 1004 with authority over the northern shore of the Hellespont and the islands of the Sea of Marmara. In 1024, a Rus' people, Rus' Battle of Lemnos (1024), raid led by a certain Chrysocheir defeated the local commander at Abydos and proceeded to travel south through the Hellespont. Following the Battle of Manzikert, Abydos was seized by the Seljuk Turks, but was recovered in 1086 AD, in which year Leo Kephalas was appointed ''katepano'' of Abydos. Abydos' population likely increased at this time as a result of the arrival of refugees from northwestern Anatolia who had fled the advance of the Turks. In 1092/1093, the city was attacked by Tzachas, a Turkish pirate.Kazhdan (1991)
Tzachas
(Ch. M. Brand), p. 2134 Emperor Manuel I Komnenos repaired Abydos' fortifications in the late 12th century. By the 13th century AD, the crossing from Lampsacus to Kallipolis had become more common and largely replaced the crossing from Abydos to Sestos.Kazhdan (1991)
Kallipolis
(A. Kazhdan), pp. 1094–1095 During the Fourth Crusade, in 1204, the Venetians seized Abydos, and, following the Sack of Constantinople (1204), Sack of Constantinople and the formation of the Latin Empire later that year, Baldwin I, Latin Emperor, Emperor Baldwin granted the land between Abydos and Adramyttium to his brother Henry of Flanders. Henry of Flanders passed through Abydos on 11 November 1204 and continued his march to Adramyttium. Abydos was seized by the Empire of Nicaea, a successor state of the Eastern Roman Empire, during its offensive in 1206–1207, but was reconquered by the Latin Empire in 1212–1213. The city was later recovered by Emperor John III Vatatzes. Abydos declined in the 13th century, and was eventually abandoned between 1304 and 1310/1318 due to the threat of Turkish tribes and disintegration of Roman control over the region.
Kyrillos of Abydos
'. The Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople In 1222, during the Latin occupation, the papal legate Giovanni Colonna (died 1245), Giovanni Colonna united the dioceses of Abydos and Madytos (Thrace), Madytos and placed the see under direct Papal authority.Leveniotis (2017), pp. 13-14 No longer a residential bishopric, Abydus is today listed by the Catholic Church as a titular see.
Mysia
Mysia (UK , US or ; el, Μυσία; lat, Mysia; tr, Misya) was a region in the northwest of ancient Asia Minor (Anatolia, Asian part of modern Turkey). It was located on the south coast of the Sea of Marmara. It was bounded by Bithynia on th ...
. It was located at the Nara Burnu Nara Burnu (Turkish language, Turkish "Cape Nara"), formerly Nağara Burnu, in English Nagara Point, and in older sources Point Pesquies, is a headland on the Anatolian side of the Dardanelles Straits, north of Çanakkale.
It is the narrowest and, ...
promontory on the Asian coast of the Hellespont (the straits of Dardanelles), opposite the ancient city of Sestos, and near the city of Çanakkale
Çanakkale (pronounced ), ancient ''Dardanellia'' (), is a city and seaport in Turkey in Çanakkale province on the southern shore of the Dardanelles at their narrowest point. The population of the city is 195,439 (2021 estimate).
Çanakkale is ...
in Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
. Abydos was founded in c. 670 BC at the most narrow point in the straits, and thus was one of the main crossing points between Europe and Asia, until its replacement by the crossing between Lampsacus
Lampsacus (; grc, Λάμψακος, translit=Lampsakos) was an ancient Greek city strategically located on the eastern side of the Hellespont in the northern Troad. An inhabitant of Lampsacus was called a Lampsacene. The name has been transmitt ...
and Kallipolis in the 13th century, and the abandonment of Abydos in the early 14th century.
In Greek mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the Cosmogony, origin and Cosmology#Metaphysical co ...
, Abydos is presented in the myth of Hero and Leander
Hero and Leander is the Greek myth relating the story of Hero ( grc, Ἡρώ, ''Hērṓ''; ), a priestess of Aphrodite (Venus in Roman mythology) who dwelt in a tower in Sestos on the European side of the Hellespont, and Leander ( grc, Λέ ...
as the home of Leander. The city is also mentioned in ''Rodanthe and Dosikles'', a novel written by Theodore Prodromos
Theodore Prodromos or Prodromus ( el, Θεόδωρος Πρόδρομος; c. 1100 – c. 1165/70), probably also the same person as the so-called Ptochoprodromos (Πτωχοπρόδρομος "Poor Prodromos"), was a Byzantine Greek writer, wel ...
, a 12th-century writer, in which Dosikles kidnaps Rodanthe at Abydos.
Archaeology
In 1675, the site of Abydos was first identified, and was subsequently visited by numerous classicists and travellers, such asRobert Wood Robert Wood may refer to:
Art
* Robert E. Wood (painter, born 1971), Canadian landscape artist
* Robert William Wood (1889–1979), American landscape artist
* Robert Wood (artist), accused and acquitted of the Camden Town murder
Military
* R ...
, Richard Chandler, and Lord Byron
George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron (22 January 1788 – 19 April 1824), known simply as Lord Byron, was an English romantic poet and Peerage of the United Kingdom, peer. He was one of the leading figures of the Romantic movement, and h ...
.Gunter (2015), p. 1 The city's acropolis is known in Turkish as Mal Tepe.
Following the city's abandonment, the ruins of Abydos were scavenged for building materials from the 14th to the 19th century, and remains of walls and buildings continued to be reported until at least the 19th century, however, little remains and the area was declared a restricted military zone in the early 20th century, thus little to no excavation has taken place.
History
Classical period
 Abydos is mentioned in the ''
Abydos is mentioned in the ''Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; grc, Ἰλιάς, Iliás, ; "a poem about Ilium") is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Odysse ...
'' as a Trojan
Trojan or Trojans may refer to:
* Of or from the ancient city of Troy
* Trojan language, the language of the historical Trojans
Arts and entertainment Music
* ''Les Troyens'' ('The Trojans'), an opera by Berlioz, premiered part 1863, part 189 ...
ally,Mitchell (2005) and, according to Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
, was occupied by Bebryces The Bebryces ( el, Βέβρυκες) were a tribe of people who lived in Bithynia. According to Strabo they were one of the many Thracian tribes that had crossed from Europe into Asia, although modern scholars have rather argued for a Celtic origin ...
and later Thracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. ...
after the Trojan War
In Greek mythology, the Trojan War was waged against the city of Troy by the Achaeans (Greeks) after Paris of Troy took Helen from her husband Menelaus, king of Sparta. The war is one of the most important events in Greek mythology and has ...
. It has been suggested that the city was originally a Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
n colony as there was a temple of Aphrodite
Aphrodite ( ; grc-gre, Ἀφροδίτη, Aphrodítē; , , ) is an ancient Greek goddess associated with love, lust, beauty, pleasure, passion, and procreation. She was syncretized with the Roman goddess . Aphrodite's major symbols include ...
Porne (Aphrodite the Harlot) within Abydos. Abydos was settled by Milesian colonists contemporaneously with the foundation of the cities of Priapos
In Greek mythology, Priapus (; grc, Πρίαπος, ) is a minor rustic fertility god, protector of livestock, fruit plants, gardens and male genitalia. Priapus is marked by his oversized, permanent erection, which gave rise to the medical term ...
and Prokonnesos
Marmara Island ( ) is a Turkish island in the Sea of Marmara. With an area of it is the largest island in the Sea of Marmara and is the second largest island of Turkey after Gökçeada (older name in Turkish: ; el, Ίμβρος, links=no ''I ...
in .Hansen & Nielsen (2004), p. 993 Strabo related that Gyges, King of Lydia
Lydia (Lydian language, Lydian: 𐤮𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣𐤠, ''Śfarda''; Aramaic: ''Lydia''; el, Λυδία, ''Lȳdíā''; tr, Lidya) was an Iron Age Monarchy, kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the mod ...
, granted his consent to the Milesians to settle Abydos;Bean (1976), p. 5 it is argued that this was carried out by Milesian mercenaries to act as a garrison to prevent Thracian raids into Asia Minor. The city became a thriving centre for tuna exportation as a result of the high yield of tuna in the Hellespont.
Abydos was ruled by Daphnis, a pro-Persian tyrant
A tyrant (), in the modern English usage of the word, is an absolute ruler who is unrestrained by law, or one who has usurped a legitimate ruler's sovereignty. Often portrayed as cruel, tyrants may defend their positions by resorting to rep ...
, in the 520s BC,Hansen & Nielsen (2004), p. 1003 but was occupied by the Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, wikt:𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎶, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an History of Iran#Classical antiquity, ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Bas ...
in 514. Darius I
Darius I ( peo, 𐎭𐎠𐎼𐎹𐎺𐎢𐏁 ; grc-gre, Δαρεῖος ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was a Persian ruler who served as the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his ...
destroyed the city following his Scythian campaign in 512. Abydos participated in the Ionian Revolt
The Ionian Revolt, and associated revolts in Aeolis, Doris, Cyprus and Caria, were military rebellions by several Greek regions of Asia Minor against Persian rule, lasting from 499 BC to 493 BC. At the heart of the rebellion was the dissatisf ...
in the early 5th century BC, however, the city returned briefly to Persian control as, in 480, at the onset of the Second Persian invasion of Greece
The second Persian invasion of Greece (480–479 BC) occurred during the Greco-Persian Wars, as King Xerxes I of Persia sought to conquer all of Greece. The invasion was a direct, if delayed, response to the defeat of the first Persian invasion ...
, Xerxes I
Xerxes I ( peo, 𐎧𐏁𐎹𐎠𐎼𐏁𐎠 ; grc-gre, Ξέρξης ; – August 465 BC), commonly known as Xerxes the Great, was the fourth King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, ruling from 486 to 465 BC. He was the son and successor of ...
and the Persian army passed through Abydos on their march to Greece crossing the Hellespont on Xerxes' Pontoon Bridges
Xerxes' Pontoon Bridges were constructed in 480 BC during the second Persian invasion of Greece upon the order of Xerxes I of Persia for the purpose of Xerxes’ army to traverse the Hellespont (the present-day Dardanelles) from Asia into Thra ...
. After the failed Persian invasion, Abydos became a member of the Athenian
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
-led Delian League
The Delian League, founded in 478 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Pl ...
, and was part of the Hellespontine district. Ostensibly an ally, Abydos was hostile to Athens throughout this time, and contributed a ''phoros
In Ancient Greece, phoros ( el, φόρος) was the name for the membership dues paid to Athens by the members of the Delian League, formed to offer protection from Persian forces. It could be paid in military equipment (such as triremes) or money, ...
'' of 4-6 talents. Xenophon
Xenophon of Athens (; grc, wikt:Ξενοφῶν, Ξενοφῶν ; – probably 355 or 354 BC) was a Greek military leader, philosopher, and historian, born in Athens. At the age of 30, Xenophon was elected commander of one of the biggest Anci ...
documented that Abydos possessed gold mines at Astyra or Kremaste at the time of his writing.
 During the
During the Second Peloponnesian War
The Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC) was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world. The war remained undecided for a long time until the decisive intervention of t ...
, a Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referre ...
n expedition led by Dercylidas Dercylidas (Greek: Δερκυλίδας) was a Spartan commander during the 5th and 4th century BC. For his cunning and inventiveness, he was nicknamed Sisyphus. In 411 BC he was appointed harmost at Abydos. In 399 BC, he was advised by Antisthen ...
arrived at Abydos in early May 411 BC and successfully convinced the city to defect from the Delian League and fight against Athens, at which time he was made harmost
Harmost ( el, , "joiner" or "adaptor") was a Spartan term for a military governor. The Spartan general Lysander instituted several harmosts during the period of Spartan hegemony after the end of the Peloponnesian War in 404 BC. They were sent int ...
(commander/governor) of Abydos.Hodkinson (2005) A Spartan fleet was defeated
Defeated may refer to:
* "Defeated" (Breaking Benjamin song)
* "Defeated" (Anastacia song)
*"Defeated", a song by Snoop Dogg from the album ''Bible of Love''
*Defeated, Tennessee, an unincorporated community
*''The Defeated
''The Defeated'', al ...
by Athens at Abydos in the autumn of 411 BC. Abydos was attacked by the Athenians in the winter of 409/408 BC, but was repelled by a Persian force led by Pharnabazus, satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires.
The satrap served as viceroy to the king, though with consid ...
(governor) of Hellespontine Phrygia
Hellespontine Phrygia ( grc, Ἑλλησποντιακὴ Φρυγία, Hellēspontiakē Phrygia) or Lesser Phrygia ( grc, μικρᾶ Φρυγία, mikra Phrygia) was a Persian satrapy (province) in northwestern Anatolia, directly southeast of t ...
. Dercylidas held the office of harmost of Abydos until at least . According to Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of phil ...
, Abydos had an oligarchic
Oligarchy (; ) is a conceptual form of power structure in which power rests with a small number of people. These people may or may not be distinguished by one or several characteristics, such as nobility, fame, wealth, education, or corporate, r ...
constitution at this time. At the beginning of the Corinthian War
The Corinthian War (395–387 BC) was a conflict in ancient Greece which pitted Sparta against a coalition of city-states comprising Thebes, Athens, Corinth and Argos, backed by the Achaemenid Empire. The war was caused by dissatisfaction with ...
in 394 BC, Agesilaus II
Agesilaus II (; grc-gre, Ἀγησίλαος ; c. 442 – 358 BC) was king of Sparta from c. 399 to 358 BC. Generally considered the most important king in the history of Sparta, Agesilaus was the main actor during the period of Spartan hegemony ...
, King of Sparta, passed through Abydos into Thrace. Abydos remained an ally of Sparta throughout the war and Dercylidas served as harmost of the city from 394 until he was replaced by Anaxibius in ; the latter was killed in an ambush near Abydos by the Athenian general Iphicrates
Iphicrates ( grc-gre, Ιφικράτης; c. 418 BC – c. 353 BC) was an Athenian general, who flourished in the earlier half of the 4th century BC. He is credited with important infantry reforms that revolutionized ancient Greek warfare by ...
in .Phang et al. (2016), p. 57 At the conclusion of the Corinthian War, under the terms of the Peace of Antalcidas
The King's Peace (387 BC) was a peace treaty guaranteed by the Persian King Artaxerxes II that ended the Corinthian War in ancient Greece. The treaty is also known as the Peace of Antalcidas, after Antalcidas, the Spartan diplomat who traveled t ...
in 387 BC, Abydos was annexed to the Persian Empire. Within the Persian Empire, Abydos was administered as part of the satrapy of Hellespontine Phrygia, and was ruled by the tyrant Philiscus in 368. In , the city came under the control of the tyrant Iphiades.
Hellenistic period
Abydos remained under Persian control until it was seized by a Macedonian army led byParmenion
Parmenion (also Parmenio; grc-gre, Παρμενίων; c. 400 – 330 BC), son of Philotas, was a Macedonian general in the service of Philip II of Macedon and Alexander the Great. A nobleman, Parmenion rose to become Philip's chief milita ...
, a general of Philip II Philip II may refer to:
* Philip II of Macedon (382–336 BC)
* Philip II (emperor) (238–249), Roman emperor
* Philip II, Prince of Taranto (1329–1374)
* Philip II, Duke of Burgundy (1342–1404)
* Philip II, Duke of Savoy (1438-1497)
* Philip ...
, in the spring of 336 BC.Ashley (2004), p. 187 In 335, whilst Parmenion besieged the city of Pitane, Abydos was besieged by a Persian army led by Memnon of Rhodes
Memnon of Rhodes (Greek: Μέμνων ὁ Ῥόδιος; c. 380 – 333 BC) was a prominent Rhodian Greek commander in the service of the Persian Achaemenid Empire. Related to the Persian aristocracy by the marriage of his sister to the satr ...
, forcing Parmenion to abandon his siege of Pitane and march north to relieve Abydos. Alexander ferried across from Sestos to Abydos in 334 and travelled south to the city of Troy, after which he returned to Abydos. The following day, Alexander left Abydos and led his army north to Percote
Percote or Perkote ( grc, Περκώτη) was a town or city of ancient Mysia on the southern (Asian) side of the Hellespont, to the northeast of Troy. Percote is mentioned a few times in Greek mythology, where it plays a very minor role each time. ...
. Alexander later established a royal mint at Abydos, as well as at other cities in Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
.
After the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC, Abydos, as part of the satrapy of Hellespontine Phrygia, came under the control of Leonnatus
Leonnatus ( el, Λεοννάτος; 356 BC – 322 BC) was a Macedonian officer of Alexander the Great and one of the ''diadochi.''
He was a member of the royal house of Lyncestis, a small Greek kingdom that had been included in Macedonia by King ...
as a result of the Partition of Babylon. At the Partition of Triparadisus
The Partition of Triparadisus was a power-sharing agreement passed at Triparadisus in 321 BC between the generals (''Diadochi'') of Alexander the Great, in which they named a new regent and arranged the repartition of the satrapies of Alexander's e ...
in 321 BC, Arrhidaeus
Arrhidaeus or Arrhidaios ( el, Ἀρριδαῖoς lived 4th century BC), one of Alexander the Great's generals, was entrusted by Ptolemy to bring Alexander's body to Egypt in 323 BC, contrary to the wishes of Perdiccas who wanted the body sent ...
succeeded Leonnatus as satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia.
In 302, during the Fourth War of the Diadochi
The Wars of the Diadochi ( grc, Πόλεμοι τῶν Διαδόχων, '), or Wars of Alexander's Successors, were a series of conflicts that were fought between the generals of Alexander the Great, known as the Diadochi, over who would rule h ...
, Lysimachus
Lysimachus (; Greek: Λυσίμαχος, ''Lysimachos''; c. 360 BC – 281 BC) was a Thessalian officer and successor of Alexander the Great, who in 306 BC, became King of Thrace, Asia Minor and Macedon.
Early life and career
Lysimachus was b ...
, King of Thrace, crossed over into Asia Minor and invaded the kingdom of Antigonus I.Magie (2015), p. 89 Unlike the neighbouring cities of Parium
Parium (or Parion; el, Πάριον) was a Greek city of Adrasteia in Mysia on the Hellespont. Its bishopric was a suffragan of Cyzicus, the metropolitan see of the Roman province of Hellespontus.
History
Founded in 709 B.C., the ancient ci ...
and Lampsacus which surrendered, Abydos resisted Lysimachus and was besieged. Lysimachus was forced to abandon the siege, however, after the arrival of a relief force sent by Demetrius
Demetrius is the Latinized form of the Ancient Greek male given name ''Dēmḗtrios'' (), meaning “Demetris” - "devoted to goddess Demeter".
Alternate forms include Demetrios, Dimitrios, Dimitris, Dmytro, Dimitri, Dimitrie, Dimitar, Dumit ...
, son of King Antigonus I. According to Polybius
Polybius (; grc-gre, Πολύβιος, ; ) was a Greek historian of the Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , which covered the period of 264–146 BC and the Punic Wars in detail.
Polybius is important for his analysis of the mixed ...
, by the third century BC, the neighbouring city of Arisbe had become subordinate to Abydos. The city of Dardanus also came under the control of Abydos at some point in the Hellenistic period.Mackay (1976), p. 258 Abydos became part of the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
after 281 BC.Abydus
'. Brill Reference Online The city was conquered by
Ptolemy III Euergetes
, predecessor = Ptolemy II
, successor = Ptolemy IV
, nebty = ''ḳn nḏtj-nṯrw jnb-mnḫ-n-tꜢmrj'Qen nedjtinetjeru inebmenekhentamery''The brave one who has protected the gods, a potent wall for The Beloved Land
, nebty_hiero ...
, King of Egypt, in 245 BC, and remained under Ptolemaic control until at least 241, as Abydos had become part of the Kingdom of Pergamon
The Kingdom of Pergamon or Attalid kingdom was a Greek state during the Hellenistic period that ruled much of the Western part of Asia Minor from its capital city of Pergamon. It was ruled by the Attalid dynasty (; grc-x-koine, Δυναστ ...
by c. 200 BC.
 During the
During the Second Macedonian War
The Second Macedonian War (200–197 BC) was fought between Macedon, led by Philip V of Macedon, and Rome, allied with Pergamon and Rhodes. Philip was defeated and was forced to abandon all possessions in southern Greece, Thrace and Asia Min ...
, Abydos was besieged by Philip V Philip V may refer to:
* Philip V of Macedon (221–179 BC)
* Philip V of France (1293–1322)
* Philip II of Spain, also Philip V, Duke of Burgundy (1526–1598)
* Philip V of Spain
Philip V ( es, Felipe; 19 December 1683 – 9 July 1746) was ...
, King of Macedonia, in 200 BC,Jaques (2007), p. 4 during which many of its citizens chose to commit suicide rather than surrender. Marcus Aemilius Lepidus met with Philip V during the siege to deliver an ultimatum on behalf of the Roman senate
The Roman Senate ( la, Senātus Rōmānus) was a governing and advisory assembly in ancient Rome. It was one of the most enduring institutions in Roman history, being established in the first days of the city of Rome (traditionally founded in ...
. Ultimately, the city was forced to surrender to Philip V due to a lack of reinforcements. The Macedonian occupation ended after the Peace of Flamininus at the end of the war in 196 BC. At this time, Abydos was substantially depopulated and partially ruined as a result of the Macedonian occupation.
In the spring of 196 BC, Abydos was seized by Antiochus III
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the res ...
, '' Megas Basileus'' of the Seleucid Empire, who refortified the city in 192/191 BC. Antiochus III later withdrew from Abydos during the Roman-Seleucid War, thus allowing for the transportation of the Roman army into Asia Minor by October 190 BC. Dardanus was subsequently liberated from Abydene control, and the Treaty of Apamea
The Treaty of Apamea was a peace treaty conducted in 188 BC between the Roman Republic and Antiochus III, ruler of the Seleucid Empire. It ended the Roman–Seleucid War. The treaty took place after Roman victories at the Battle of Thermopylae ...
of 188 BC returned Abydos to the Kingdom of Pergamon. A gymnasium was active at Abydos in the 2nd century BC.
Roman period
Attalus III
Attalus III ( el, Ἄτταλος Γ΄) Philometor Euergetes ( – 133 BC) was the last Attalid king of Pergamon, ruling from 138 BC to 133 BC.
Biography
Attalus III was the son of king Eumenes II and his queen Stratonice of Pergamon, and h ...
, King of Pergamon, bequeathed his kingdom to Rome upon his death in 133 BC, and thus Abydos became part of the province of Asia. The gold mines of Abydos at Astyra or Kremaste were near exhaustion at the time was Strabo was writing. The city was counted amongst the ''telonia'' (custom houses) of the province of Asia in the ''lex portorii Asiae'' of 62 AD, and formed part of the ''conventus iuridicus
In Ancient Rome territorial organization, a ''conventus iuridicus'' was the capital city of a subdivision of some provinces (Dalmatia, Hispania, Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either consi ...
Adramytteum''. Abydos is mentioned in the ''Tabula Peutingeriana
' (Latin for "The Peutinger Map"), also referred to as Peutinger's Tabula or Peutinger Table, is an illustrated ' (ancient Roman road map) showing the layout of the '' cursus publicus'', the road network of the Roman Empire.
The map is a 13th-ce ...
'' and Antonine Itinerary. The mint of Abydos ceased to function in the mid-3rd century AD.Leveniotis (2017), p. 8
It is believed that Abydos, with Sestos and Lampsacus, is referred to as one of the "three large capital cities" of the Roman Empire in ''Weilüe
The ''Weilüe'' () was a Chinese historical text written by Yu Huan between 239 and 265. Yu Huan was an official in the state of Cao Wei (220–265) during the Three Kingdoms period (220–280). Although not a formal historian, Yu Huan has been h ...
'', a 3rd-century AD Chinese text. The city was the centre for customs collection at the southern entrance of the Sea of Marmara
The Sea of Marmara,; grc, Προποντίς, Προποντίδα, Propontís, Propontída also known as the Marmara Sea, is an inland sea located entirely within the borders of Turkey. It connects the Black Sea to the Aegean Sea via the ...
, and was administered by a ''komes ton Stenon'' (count of the Straits) or an ''archon
''Archon'' ( gr, ἄρχων, árchōn, plural: ἄρχοντες, ''árchontes'') is a Greek word that means "ruler", frequently used as the title of a specific public office. It is the masculine present participle of the verb stem αρχ-, mean ...
'' from the 3rd century to the 5th century AD.Leveniotis (2017), p. 12 In the 6th century AD, Emperor Justinian I
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovat ...
introduced the office of ''komes Abydou'' with responsibility for collecting customs duty in Abydos.Kazhdan (1991)Abydos
(C. Foss), pp. 8–9
Medieval period
Pope Martin I
Pope Martin I ( la, Martinus I, el, Πάπας Μαρτίνος; between 590 and 600 – 16 September 655), also known as Martin the Confessor, was the bishop of Rome from 21 July 649 to his death 16 September 655. He served as Pope Theodore I's ...
rested at Abydos in the summer of 653 whilst en route to Constantinople. As a result of the administrative reforms of the 7th century, Abydos came to be administered as part of the theme
Theme or themes may refer to:
* Theme (arts), the unifying subject or idea of the type of visual work
* Theme (Byzantine district), an administrative district in the Byzantine Empire governed by a Strategos
* Theme (computing), a custom graphical ...
of Opsikion
The Opsician Theme ( gr, θέμα Ὀψικίου, ''thema Opsikiou'') or simply Opsikion (Greek: , from la, Obsequium) was a Byzantine Empire, Byzantine Theme (country subdivision), theme (a military-civilian province) located in northwestern As ...
. The office of ''kommerkiarios The ''kommerkiarios'' (Greek: κομμερκιάριος) was a fiscal official of the Byzantine Empire charged with the collection of the imperial sales tax or ''kommerkion''.
History and functions
The ''kommerkiarios'' was perhaps the successor o ...
'' of Abydos is first attested in the mid-7th century, and was later sometimes combined with the office of '' paraphylax'', the military governor of the fort, introduced in the 8th century, at which time the office of ''komes ton stenon'' is last mentioned.Nesbitt & Oikonomides (1996), pp. 73-74
After the 7th century AD, Abydos became a major seaport.Kazhdan (1991)Ports
(A. Kazhdan), pp. 1706–1707
Maslama ibn Abd al-Malik
Maslama ibn ʿAbd al-Malik ( ar, مسلمة بن عبد الملك, in Greek sources , ''Masalmas''; – 24 December 738) was an Umayyad prince and one of the most prominent Arab generals of the early decades of the 8th century, leading severa ...
, during his Siege of Constantinople (717–718), campaign against Constantinople, crossed over into Thrace at Abydos in July 717. The office of ''archon'' at Abydos was restored in the late 8th century and endured until the early 9th century. In 801, Empress Irene of Athens, Irene reduced commercial tariffs collected at Abydos. Emperor Nikephoros I, Irene's successor, introduced a tax on slaves purchased beyond the city.Kazhdan (1991)Nikephoros I
(P. A. Hollingsworth), pp. 1476–1477 The city later also became part of the Aegean Sea (theme), theme of the Aegean Sea and was the seat of a ''tourmarches''. Abydos was sacked by an Abbasid Caliphate, Arab fleet led by Leo of Tripoli in 904 AD whilst en route to Constantinople.Kazhdan (1991)
Leo of Tripoli
(A. Kazhdan), p. 1216 The Rebellion of Bardas Phokas the Younger, revolt of Bardas Phokas the Younger, Bardas Phokas was defeated by Emperor Basil II at Abydos in 989 AD. In 992, the Republic of Venice, Venetians were granted reduced commercial tariffs at Abydos as a special privilege. In the early 11th century, Abydos became the seat of a separate command and the office of ''strategos'' (governor) of Abydos is first mentioned in 1004 with authority over the northern shore of the Hellespont and the islands of the Sea of Marmara. In 1024, a Rus' people, Rus' Battle of Lemnos (1024), raid led by a certain Chrysocheir defeated the local commander at Abydos and proceeded to travel south through the Hellespont. Following the Battle of Manzikert, Abydos was seized by the Seljuk Turks, but was recovered in 1086 AD, in which year Leo Kephalas was appointed ''katepano'' of Abydos. Abydos' population likely increased at this time as a result of the arrival of refugees from northwestern Anatolia who had fled the advance of the Turks. In 1092/1093, the city was attacked by Tzachas, a Turkish pirate.Kazhdan (1991)
Tzachas
(Ch. M. Brand), p. 2134 Emperor Manuel I Komnenos repaired Abydos' fortifications in the late 12th century. By the 13th century AD, the crossing from Lampsacus to Kallipolis had become more common and largely replaced the crossing from Abydos to Sestos.Kazhdan (1991)
Kallipolis
(A. Kazhdan), pp. 1094–1095 During the Fourth Crusade, in 1204, the Venetians seized Abydos, and, following the Sack of Constantinople (1204), Sack of Constantinople and the formation of the Latin Empire later that year, Baldwin I, Latin Emperor, Emperor Baldwin granted the land between Abydos and Adramyttium to his brother Henry of Flanders. Henry of Flanders passed through Abydos on 11 November 1204 and continued his march to Adramyttium. Abydos was seized by the Empire of Nicaea, a successor state of the Eastern Roman Empire, during its offensive in 1206–1207, but was reconquered by the Latin Empire in 1212–1213. The city was later recovered by Emperor John III Vatatzes. Abydos declined in the 13th century, and was eventually abandoned between 1304 and 1310/1318 due to the threat of Turkish tribes and disintegration of Roman control over the region.
Ecclesiastical history
The bishopric of Abydus appears in all the ''Notitiae Episcopatuum'' of the Patriarchate of Constantinople from the mid-7th century until the time of Andronikos III Palaiologos (1341), first as a suffragan of Cyzicus and then from 1084 as a metropolitan see without suffragans. The earliest bishop mentioned in extant documents is Marcian, who signed the joint letter of the bishops of Hellespontus to Emperor Leo I (emperor), Leo I in 458, protesting about the murder of Proterius of Alexandria. A letter of Peter the Fuller (471–488) mentions a bishop of Abydus called Pamphilus. Ammonius signed the decretal letter of the Council of Constantinople in 518 against Severus of Antioch and others. Isidore was at the Third Council of Constantinople (680–681), John at the Trullan Council (692), Theodore at the Second Council of Nicaea (787). An unnamed bishop of Abydus was a counsellor of Emperor Nikephoros II in 969. Seals attest Theodosius as bishop of Abydos in the 11th century, and John as metropolitan bishop of Abydos in the 11/12th century. Abydos remained a metropolitan see until the city fell to the Turks in the 14th century. The diocese is currently a titular see of the Patriarchate of Constantinople, and Gerasimos Papadopoulos was titular Bishop of Abydos from 1962 until his death in 1995. Simeon Kruzhkov was bishop of Abydos from May to September 1998. Kyrillos Katerelos was consecrated bishop of Abydos in 2008.Kyrillos of Abydos
'. The Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople In 1222, during the Latin occupation, the papal legate Giovanni Colonna (died 1245), Giovanni Colonna united the dioceses of Abydos and Madytos (Thrace), Madytos and placed the see under direct Papal authority.Leveniotis (2017), pp. 13-14 No longer a residential bishopric, Abydus is today listed by the Catholic Church as a titular see.
See also
* List of ancient Greek citiesReferences
Notes CitationsBibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
{{Commons category-inline, Abydos (Hellespont) Ancient Greek archaeological sites in Turkey Former populated places in Turkey Greek colonies in Mysia Milesian colonies Members of the Delian League Populated places established in the 7th century BC Populated places of the Byzantine Empire Roman towns and cities in Turkey Populated places in ancient Mysia