|
Battle Of Yiling (208)
The Battle of Yiling was fought between the warlords Sun Quan and Cao Cao in 208 in the late Eastern Han dynasty. The battle was an integral part in the Red Cliffs campaign, as it was fought immediately after the major engagement at Wulin (烏林; in present-day Honghu, Hubei) during the Battle of Red Cliffs. The Battle of Yiling was also the prelude to the subsequent Battle of Jiangling. Background Immediately after Cao Cao's defeat at Wulin in the Battle of Red Cliffs, Zhou Yu led 30,000 troops into Nan Commandery in a move to capture Jing Province's capital city, Jiangling (江陵; in present-day Jingjiang 荆江, not to be confused with present-day Jiangling County, Hubei). Zhou Yu's army camped on the southern bank of the Yangtze River. Before engaging Cao Cao's general Cao Ren, Zhou Yu ordered Gan Ning to take Yiling (夷陵; present-day Yichang, Hubei) as a preemptive move to secure the entrance to Yi Province (covering present-day Sichuan and Chongqing). In addition, if ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Red Cliffs
The Battle of Red Cliffs, also known as the Battle of Chibi, was a decisive naval battle in the winter of AD 208–209 at the end of the Han dynasty, about twelve years prior to the beginning of the Three Kingdoms period in Chinese history. The battle was fought between the allied forces of the southern warlords Sun Quan, Liu Bei, and Liu Qi against the numerically-superior forces of the northern warlord Cao Cao. Liu Bei and Sun Quan frustrated Cao Cao's effort to conquer the land south of the Yangtze River and reunite the territory of the Eastern Han dynasty. The allied victory at Red Cliffs ensured the survival of Liu Bei and Sun Quan, gave them control of the Yangtze, and provided a line of defence that was the basis for the later creation of the two southern states of Shu Han and Eastern Wu. According to Norwich University, this was the largest naval battle in history in terms of the numbers involved. Descriptions of the battle differ widely and the site of the battle is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
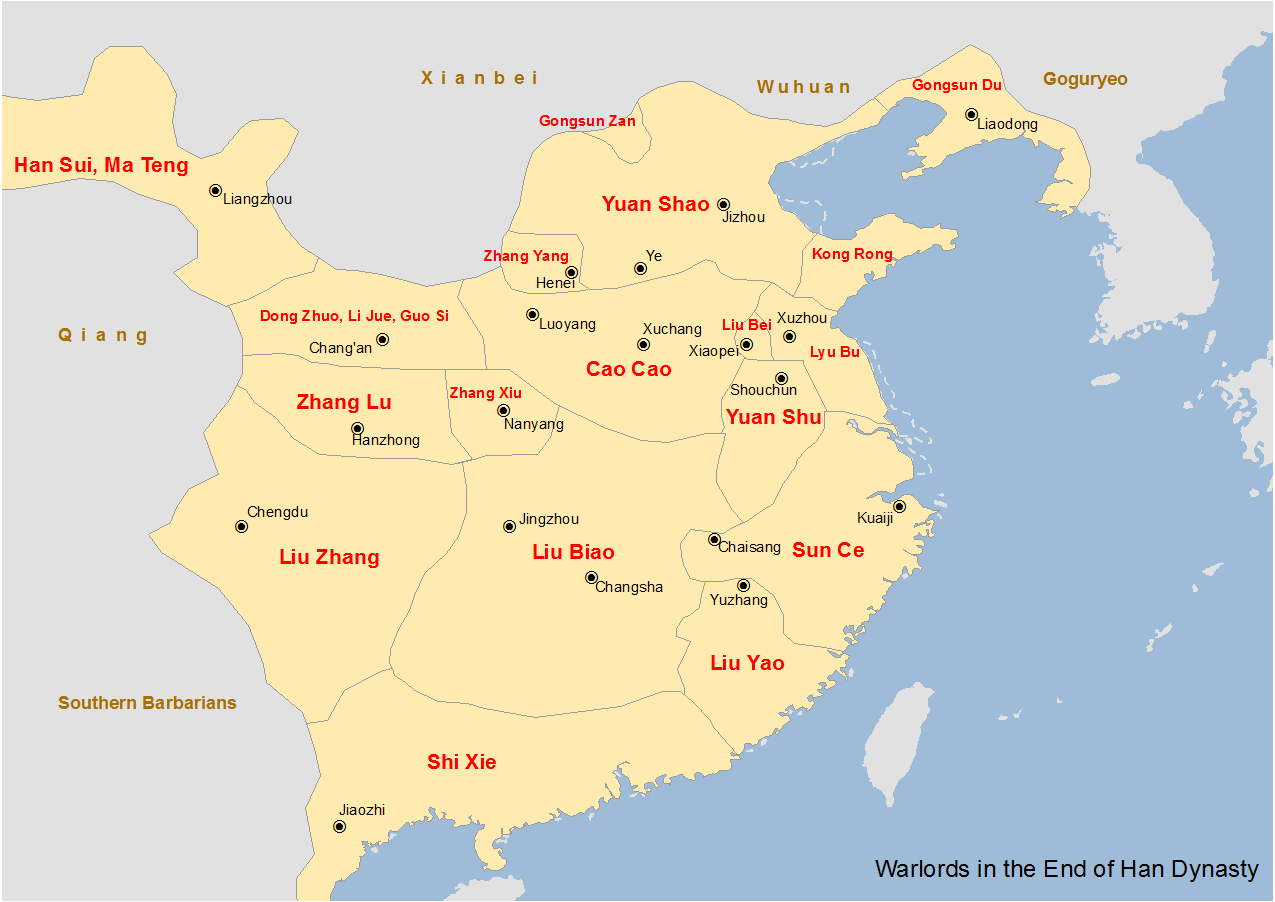
Liu Zhang (warlord)
Liu Zhang () ( 190s–210s), courtesy name Jiyu, was a Chinese politician and warlord who served as provincial governor who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He became the Governor of Yi Province (covering present-day Sichuan and Chongqing), succeeding his father Liu Yan and ruled the region until 214, when he surrendered to Liu Bei. Six years later, Liu Zhang again surrendered to Eastern Wu, and died shortly afterwards. Liu Zhang is often considered an incapable leader but is noted to have been the original lord of some of Shu Han's most famous generals and officials such as Fa Zheng, Meng Da, Yan Yan, Liu Ba, Huang Quan, Wu Yi, Li Yan, Dong He and others. Early life Liu Zhang was a descendant of Liu Yu, who was Prince of Lu in the early Han dynasty. The youngest son of Liu Yan, Liu Zhang spent his early career at the Han imperial court as an assistant to his two eldest brothers, Liu Fan and Liu Dan. They served at the court when it was controlled by the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zizhi Tongjian
''Zizhi Tongjian'' () is a pioneering reference work in Chinese historiography, published in 1084 AD during the Northern Song dynasty in the form of a chronicle recording Chinese history from 403 BC to 959 AD, covering 16 dynasties and spanning almost 1400 years. The main text is arranged into 294 scrolls (''juan'' , equivalent to a chapter) totaling about 3 million Chinese characters. In 1065 AD, Emperor Yingzong of Song commissioned his official Sima Guang (1019–1086 AD) to lead a project to compile a universal history of China, and granted him funding and the authority to appoint his own staff. His team took 19 years to complete the work and in 1084 AD it was presented to Emperor Yingzong's successor Emperor Shenzong of Song. It was well-received and has proved to be immensely influential among both scholars and the general public. Endymion Wilkinson regards it as reference quality: "It had an enormous influence on later Chinese historical wri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sima Guang
Sima Guang (17 November 1019 – 11 October 1086), courtesy name Junshi, was a Chinese historian, politician, and writer. He was a high-ranking Song dynasty scholar-official who authored the monumental history book ''Zizhi Tongjian''. Sima was a political conservative who opposed Wang Anshi's reforms. Early life Sima Guang was named after his birthplace Guāng Prefecture, where his father Sima Chi () served as a county magistrate in Guangshan County. The Simas were originally from Xia County in Shǎn Prefecture, and claimed descent from Cao Wei's official Sima Fu in the 3rd century. A famous anecdote relates how the young Sima Guang once saved a playmate who had fallen into an enormous vat full of water. As other children scattered in panic, Sima Guang calmly picked up a rock and smashed a hole in the base of the pot. Water leaked out, and his friend was saved from drowning. At age 6, Sima Guang once heard a lecture on the 4th-century BC history book '' Zuo Zhuan''. Fascinat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Records Of Three Kingdoms
The ''Records or History of the Three Kingdoms'', also known by its Chinese name as the Sanguo Zhi, is a Chinese historical text which covers the history of the late Eastern Han dynasty (c. 184–220 AD) and the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). It is widely regarded as the official and authoritative source historical text for that period. Written by Chen Shou in the third century, the work synthesizes the histories of the rival states of Cao Wei, Shu Han and Eastern Wu in the Three Kingdoms period into a single compiled text. The ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' is the main source of influence for the 14th century historical novel ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms,'' considered one of the great four novels of Chinese classical literature. Major chunks of the records have been translated into English, but the tome has yet to be fully translated. Origin and structure The ''Records of the Grand Historian'', ''Book of Han'' and ''Book of the Later Han'', and the ''Records ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chen Shou
Chen Shou (; 233–297), courtesy name Chengzuo (), was a Chinese historian, politician, and writer who lived during the Three Kingdoms period and Jin dynasty of China. Chen Shou is most known for his most celebrated work, the ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' (''Sanguozhi''), which records the history of the late Eastern Han dynasty and the Three Kingdoms period. Chen Shou wrote the Sanguozhi primarily in the form of biographies of notable persons of those eras. Today, Chen's ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' is part of the ''Twenty-Four Histories'' canon of ancient Chinese history. Historical sources on Chen Shou's life There are two biographies of Chen Shou. The first one is in the ''Chronicles of Huayang'', which was written by Chang Qu in the fourth century during the Eastern Jin dynasty. The second one is in the ''Book of Jin'', which was written by Fang Xuanling and others in the seventh century during the Tang dynasty. Life He started his career as an official in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhou Tai
Zhou Tai () (died 223), courtesy name Youping, was a military general serving under the warlord Sun Quan during the late Eastern Han dynasty and early Three Kingdoms period of China. He previously served under Sun Ce, Sun Quan's elder brother and predecessor. Service under Sun Ce Zhou Tai was from Xiacai County (), Jiujiang Commandery (), which is present-day Fengtai County, Anhui. Around the early 195, he and Jiang Qin came to serve Sun Ce, who was on a series of conquests in the Jiangdong region, where Zhou Tai helped Sun Ce to defeat Liu Yao and Wu Ju in this campaign. When Sun Ce occupied Kuaiji Commandery (present-day Shaoxing, Zhejiang) after the commandery's Administrator, Wang Lang, surrendered to him, he appointed Zhou Tai as a Major of Separate Command () and put him in command of some troops.(周泰字幼平,九江下蔡人也。 ... 與蔣欽隨孫策為左右,服事恭敬,數戰有功。策入會稽,署別部司馬,授兵。) ''Sanguozhi'' vol. 55. Sun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Dang
Han Dang (died 227), courtesy name Yigong, was a military general serving under the warlord Sun Quan during the late Eastern Han dynasty and early Three Kingdoms period of China. He previously served under Sun Quan's predecessors – Sun Jian (Sun Quan's father) and Sun Ce (Sun Quan's elder brother). Life Han Dang was from Lingzhi County (), Liaoxi Commandery (), which is in present-day Qian'an, Hebei. He possessed great physical strength and was highly skilled in archery and horse riding. The warlord Sun Jian recognised his abilities and recruited him. Han Dang accompanied Sun Jian on his military exploits throughout the 180s until 191, from the Yellow Turban Rebellion to the campaign against Dong Zhuo. He was hardworking and made many contributions in battle. However, even though he was serving in an army, he was actually more of a '' youxia'' or mercenary, so he was not awarded any titles for his achievements. He remained as a Major of Separate Command () under Sun Jian. After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huang Gai
Huang Gai () ( 180s–210s), courtesy name Gongfu, was a military general who served under the warlord Sun Quan during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He previously served under Sun Quan's predecessors – Sun Jian (Sun Quan's father) and Sun Ce (Sun Quan's elder brother). Early life Huang Gai was from Quanling County (), Lingling Commandery (), which is present-day Lingling District, Yongzhou, Hunan. He was a descendant of Huang Zilian (), a former Administrator of Nanyang Commandery. Huang Gai's grandfather moved from Nanyang to Lingling and had remained there since. Huang Gai was orphaned at a young age and he experienced hardships in his early days. However, he had high ambitions and, despite being poor, he worked hard and read books and studied military arts on his own. Early career and service under Sun Jian and Sun Ce Huang Gai later became a minor official in the local commandery office before he was nominated as a ''xiaolian'' and employed as an assistant in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheng Pu
Cheng Pu () (died after 210), courtesy name Demou, was a Chinese military general and politician serving under the warlord Sun Quan during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He previously served under Sun Quan's predecessors: Sun Jian (Sun Quan's father) and Sun Ce (Sun Quan's elder brother). Early career under Sun Jian Cheng Pu was from Tuyin County (), Youbeiping Commandery (), which is located east of present-day Fengrun District, Tangshan, Hebei. He initially served as a minor official in the local commandery office. He was good-looking, resourceful, and well versed in military strategy. Cheng Pu later came to serve Sun Jian and joined him in suppressing the Yellow Turban Rebellion in the 180s, defeating the rebels at Wan (宛; present-day Wancheng District, Nanyang, Henan) and Deng (鄧; present-day Dengzhou, Henan). In 190, he participated in the campaign against Dong Zhuo on Sun Jian's side, and defeated Dong Zhuo's forces at Yangren (陽人; believed to be near pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lu Su
Lu Su (172–217), courtesy name Zijing, was a Chinese military general and politician serving under the warlord Sun Quan during the late Eastern Han dynasty. In the year 200, when Sun Quan had just taken over the reins of power, his adviser Zhou Yu recommended Lu Su as a talent to Sun Quan. As one of Sun Quan's most important advisers in the warlord's early career, Lu Su is best known for making some significant contributions. Firstly, in 200 he drafted a long-term strategy for Sun Quan's power bloc to emerge as one of three major contending powers in China – a plan similar to Zhuge Liang's Longzhong Plan, which was proposed about seven years later. Secondly, before the Battle of Red Cliffs in late 208, he was the first person to persuade Sun Quan to ally with Liu Bei against Cao Cao. Thirdly, he succeeded Zhou Yu as the frontline commander of Sun Quan's forces in 210 after Zhou's death and maintained the Sun–Liu alliance. Fourthly, in 215, he represented Sun Quan at the neg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xu Huang
Xu Huang () (died 227), courtesy name Gongming, was a Chinese military general serving under the warlord Cao Cao in the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He later served in the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period under the first two rulers, Cao Pi and Cao Rui, before his death at the start of Cao Rui's reign. Xu Huang is best noted for breaking the siege at the Battle of Fancheng in 219 by routing the enemy commander Guan Yu on the field. Chen Shou, who wrote the third-century historical text ''Sanguozhi'', named Xu Huang as one of the Five Elite Generals of his time, alongside Yu Jin, Zhang He, Yue Jin and Zhang Liao. Early life and service under Yang Feng Xu Huang was born in Yang County (楊縣), Hedong Commandery, which is located southeast of present-day Hongtong County, Shanxi, in the late Eastern Han dynasty. He served as a minor official in the commandery office in his youth. Later, he became a subordinate of Yang Feng, a former White Wave Bandit who la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |