|
Battle Of Viru Harbor
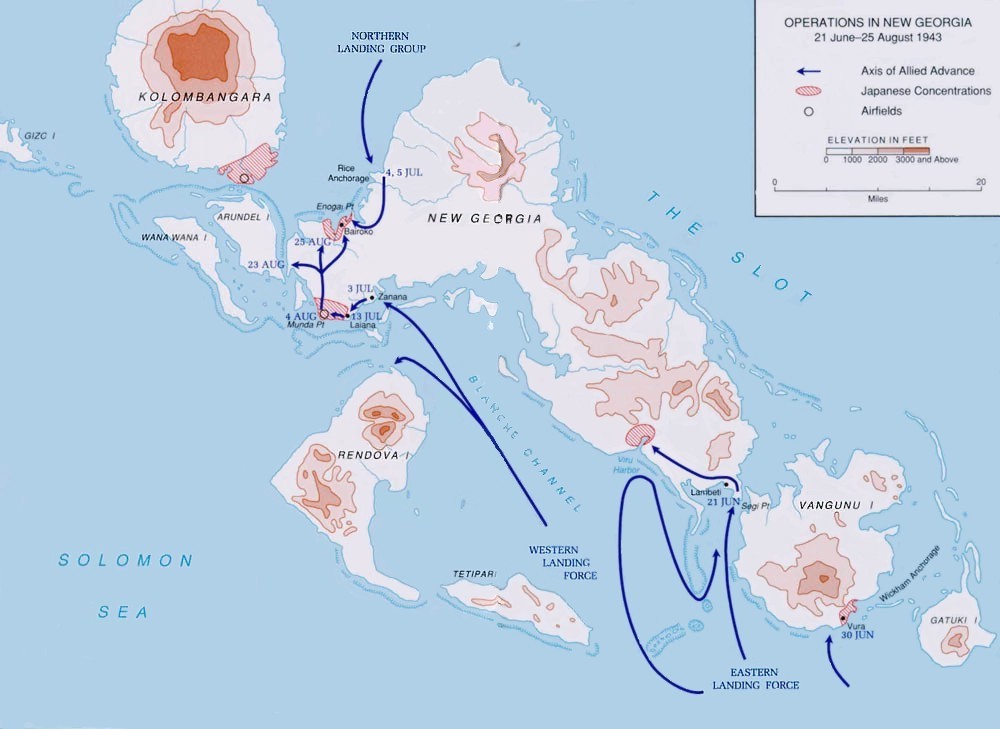
The Battle of Viru Harbor was a battle of the Pacific campaign of World War II that took place on New Georgia island during the New Georgia Campaign from 28 June – 1 July 1943. It was one of the first actions of the campaign and involved an overland advance by elements of a Marine Raider battalion, supported by a United States Army infantry company. Supported by airstrikes, the Marines carried out an enveloping attack on the Japanese defenders around the harbor and forced them to withdraw. The harbor was subsequently used by US forces to support further operations, although plans to build a PT boat base in the area were later canceled when the harbor was found to be unsuitable. Background The battle was one of the first actions of the New Georgia campaign. Located on the southeastern coast of New Georgia island, Viru Harbor lies along a key avenue of approach towards Rendova and Munda Point. In formulating their plans to secure the New Georgia islands, US planners assessed tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific War
The Pacific War, sometimes called the Asia–Pacific War, was the theater of World War II that was fought in Asia, the Pacific Ocean, the Indian Ocean, and Oceania. It was geographically the largest theater of the war, including the vast Pacific Ocean theater, the South West Pacific theater, the Second Sino-Japanese War, and the Soviet–Japanese War. The Second Sino-Japanese War between the Empire of Japan and the Republic of China had been in progress since 7 July 1937, with hostilities dating back as far as 19 September 1931 with the Japanese invasion of Manchuria. However, it is more widely accepted that the Pacific War itself began on 7 December (8 December Japanese time) 1941, when the Japanese simultaneously invaded Thailand, attacked the British colonies of Malaya, Singapore, and Hong Kong as well as the United States military and naval bases in Hawaii, Wake Island, Guam, and the Philippines. The Pacific War saw the Allies pitted against Japan, the latter ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Wickham Anchorage
The Battle of Wickham Anchorage took place during the New Georgia campaign in the Solomon Islands during the Pacific War from 30 June – 3 July 1943. During the operation US Marines and US Army troops landed by ship around Oleana Bay on Vangunu Island and advanced overland towards the anchorage where they attacked a garrison of Imperial Japanese Navy and Army troops. The purpose of the attack by the U.S. was to secure the lines of communication and supply between Allied forces involved in the New Georgia campaign and Allied bases in the southern Solomons. The U.S. forces were successful in driving the Japanese garrison from the area and securing the anchorage, which would later be used to stage landing craft for subsequent operations. Background The battle was one of the first actions of the New Georgia campaign. Located on the southern tip of Vangunu, Wickham Anchorage lies at the southern end of the New Georgia Islands archipelago between Vangunu and Gatukai. In formulating the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Kilty (DD-137)
USS ''Kilty'' (DD–137) was a ''Wickes''-class destroyer in the United States Navy. She was the first ship named for Admiral Augustus Kilty. ''Kilty'' was launched 25 April 1918 by the Mare Island Navy Yard, Vallejo, California; sponsored by Miss Elizabeth Harrison Shapley; and commissioned 17 December 1918. Service history After a Caribbean shakedown and a European cruise during the summer of 1919, ''Kilty'' returned to San Diego and operated there until she decommissioned 5 June 1922. World War II ''Kilty'' recommissioned 18 December 1939, and in April 1940 sailed on Neutrality Patrol out of San Diego. During the summer, she conducted reserve training cruises and resumed her patrols early in September. The destroyer continued these operations until the United States entered World War II. Then, ''Kilty'' intensified ASW patrols, trained armed-guard crews for merchantmen, and escorted coastal convoys throughout 1942. Reclassified APD-15 on 2 January 1943, ''Kilty'' cleared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Hopkins (DD-249)
USS ''Hopkins'' (DD-249/DMS-13) was a destroyer built in 1920 and in United States Navy service between 1921-1946. The third Navy ship named in honor of Commodore of the Continental Navy Esek Hopkins, she saw extensive action in the Pacific Theatre during World War II, emerging the most decorated ''Clemson''-class warship of that conflict. Construction and commissioning ''Hopkins'' was launched 26 June 1920 by the New York Shipbuilding Corporation, one of 156 destroyers built. She was sponsored by Miss Sarah Babbitt, a descendant of Commodore of the Continental Navy Esek Hopkins; and commissioned 21 March 1921 at Philadelphia. Service history After shakedown ''Hopkins'' arrived at Newport, Rhode Island, 31 May for battle practice training during the summer. In November, she was assigned to Destroyer Squadron 15 for tactical training with the Atlantic Fleet along the East Coast. ''Hopkins'' sailed from Hampton Roads 2 October 1922, and reached Constantinople 22 Oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Crosby (DD-164)
USS ''Crosby'' (DD–164) was a in the United States Navy during World War II, later reclassified as APD-17. She was named for Admiral Peirce Crosby. Construction and commissioning ''Crosby'' was launched on 28 September 1918 by Bethlehem Shipbuilding Corporation's Fore River Shipyard in Quincy, Massachusetts, sponsored by Mrs. C. Tittman. The ship was commissioned on 24 January 1919. Service history After commissioning, ''Crosby'' reported to the Atlantic Fleet. She joined in exercises in Guantanamo Bay until sailing for Trepassey Bay, Newfoundland in May 1919, to serve as plane guard during the historic flight of Navy seaplanes, the first aerial crossing of the Atlantic. On 1 July 1919, ''Crosby'' was assigned to the Pacific Fleet, and a week later she sailed from New York for San Diego, arriving on 7 August. She visited Portland, Oregon, and Seattle, Washington, then was placed in reserve status with reduced complement at San Diego on 30 January 1920. She continued ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Schley (DD-103)
USS ''Schley'' (DD-103) was a in the United States Navy during World War I and later designated, APD-14 in World War II. She was the first ship named in honor of Winfield Scott Schley. Construction and commissioning ''Schley'' was laid down on 29 October 1917 by Union Iron Works, San Francisco, California. The ship was launched on 28 March 1918, sponsored by Miss Eleanor Martin. The destroyer was commissioned on 20 September 1918, Commander Robert C. Giffen in command. Service history World War I ''Schley'' sailed from San Diego on 10 October 1918 for the east coast and, on 12 November, departed New York for the Mediterranean Sea. On 24 January 1919 at Taranto, Italy, she embarked Rear Admiral Mark L. Bristol, Senior American Naval Officer in Turkey, and transported him to Constantinople. ''Schley'' next assumed duty in the Adriatic Sea, acting as station ship at Pola, Italy, from 17 February to 15 April, and then visiting Italian and Yugoslav ports on the Adriatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
103rd Infantry Regiment (United States)
The 103rd Infantry Regiment was an infantry regiment of the United States Army that served in combat in the American Civil War, World War I, and World War II. It was an Army National Guard regiment from the states making up New England, but most of its soldiers came from Maine. It was a part of the 26th Infantry Division and the 43rd Infantry Division. The 103rd regiment fought in numerous battles before its deactivation after the Second World War. History American Civil War The 103rd Infantry Regiment was originally formed in 1861 as the 2nd Maine Volunteer Infantry Regiment. It served in the Union Army and was one of the first US regiments to see combat against the Confederates. It served in the First Battle of Bull Run, which was the first major battle of the Civil War and a decisive Union defeat. However, the 2nd Maine was one of the last regiments to retreat from the field. It served in the Peninsula Campaign and the Second Battle of Bull Run, both were also Union ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Waters (DD-115)
USS ''Waters'' (DD-115) was a in the United States Navy during World War I and World War II, later re-designated a high speed transport with the hull identification number APD-8. She was named in honor of Daniel Waters. Construction and commissioning ''Waters'' was laid down on 26 July 1917 at Philadelphia by William Cramp & Sons. The ship was launched on 3 March 1918, sponsored by Miss Mary Borland Thayer. The destroyer was commissioned at the Philadelphia Navy Yard on 8 August 1918. Service history World War I Although her active service began late in World War I, ''Waters'' still managed to get in two round-trip voyages to the British Isles and one to the Azores before the armistice in November 1918. On 11 August, she joined a convoy at Tompkinsville, New York, and put to sea for England. She escorted her charges safely into Devonport on 23 August and stood out again four days later in the screen for four ships headed home. The destroyer delivered the small convo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Dent
USS ''Dent'' (DD–116) was a ''Wickes''-class destroyer in the United States Navy during the World War I and later served as APD-9 in World War II. She was named for Captain John H. Dent. Construction and commissioning ''Dent'' was launched 23 March 1918 by William Cramp & Sons, Philadelphia; sponsored by Miss A. W. Collins, great-granddaughter of Captain Dent; and commissioned 9 September 1918. Service history ''Dent'' escorted a convoy to Ireland between 19 September and 8 November 1918, and then carried out training at Guantanamo Bay. On 1 May 1919 she got underway from New York to serve on station off Trepassey Harbor, Newfoundland, during the historic first aerial crossing of the Atlantic, a feat accomplished by a Navy seaplane. She returned to Newport on the 24th, and on 20 June she joined the escort for the yacht ''Imperator'', carrying the President of Brazil from New York to Newport. ''Dent'' arrived at San Pedro, California, 6 August 1919 to join the Pacifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Speed Transport
High-speed transports were converted destroyers and destroyer escorts used in US Navy amphibious operations in World War II and afterward. They received the US Hull classification symbol APD; "AP" for transport and "D" for destroyer. In 1969, the remaining ships were reclassified as "Fast Amphibious Transports", hull symbol LPR. APDs were intended to deliver small units such as Marine Raiders, Underwater Demolition Teams, and United States Army Rangers onto hostile shores. An APD could carry up to 200 troops - a company-size unit - and approximately 40 tons of cargo. It could also provide gunfire support if needed. was officially designated the Navy's first high-speed transport on 2 August 1940 when she became APD-1. Development Before the United States entered World War II, as newer and more modern destroyers joined the fleet, some older destroyers were refitted for other duties: as seaplane tenders, destroyer minelayers, or destroyer minesweepers, and in an innovation, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coastwatcher
The Coastwatchers, also known as the Coast Watch Organisation, Combined Field Intelligence Service or Section C, Allied Intelligence Bureau, were Allied military intelligence operatives stationed on remote Pacific islands during World War II to observe enemy movements and rescue stranded Allied personnel. They played a significant role in the Pacific Ocean theatre and South West Pacific theatre, particularly as an early warning network during the Guadalcanal campaign. Overview Captain Chapman James Clare, district naval officer of Western Australia, proposed a coastwatching programme in 1919. In 1922, the Australian Commonwealth Naval Board directed the Naval Intelligence Division of the Royal Australian Navy to organise a coastwatching service. Walter Brooksbank, a civil assistant to the Director of Naval Intelligence, worked in the 1920s and 1930s to organise a skeleton service of plantation owners and managers whose properties were in strategic locations in northern Austra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_off_Guadalcanal%2C_8_August_1942.jpg)
_underway_off_Mare_Island_in_October_1943.jpg)

_underway_on_31_October_1944.gif)
