|
Battle Of Thiepval Ridge
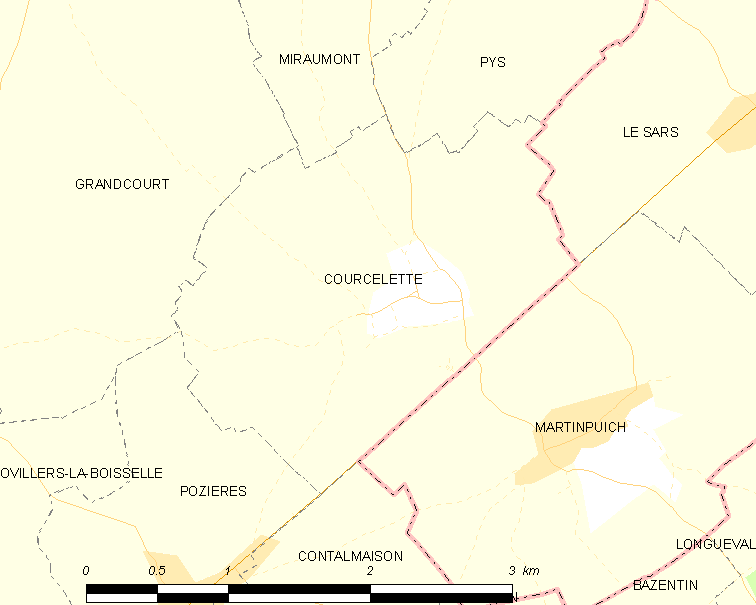
The Battle of Thiepval Ridge was the first large offensive of the Reserve Army (Lieutenant General Hubert Gough), during the Battle of the Somme on the Western Front during the First World War. The attack was intended to benefit from the Fourth Army attack in the Battle of Morval, by starting afterwards. The battle was fought on a front from Courcelette in the east, near the Albert–Bapaume road, to Thiepval and the Schwaben Redoubt () in the west, which overlooked the German defences further north in the Ancre valley, the rising ground towards Beaumont-Hamel and Serre beyond. Thiepval Ridge was well fortified and the German defenders fought with great determination, while the British co-ordination of infantry and artillery declined after the first day, due to the confused nature of the fighting in the mazes of trenches, dugouts and shell-craters. The final British objectives were not reached until a reorganisation of the Reserve Army and the Battle of the Ancre Heights (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Somme
The Battle of the Somme (French: Bataille de la Somme), also known as the Somme offensive, was a battle of the First World War fought by the armies of the British Empire and French Third Republic against the German Empire. It took place between 1 July and 18 November 1916 on both sides of the upper reaches of the Somme, a river in France. The battle was intended to hasten a victory for the Allies. More than three million men fought in the battle of whom one million were wounded or killed, making it one of the deadliest battles in human history. The French and British had committed themselves to an offensive on the Somme during the Chantilly Conference in December 1915. The Allies agreed upon a strategy of combined offensives against the Central Powers in 1916 by the French, Russian, British and Italian armies, with the Somme offensive as the Franco-British contribution. Initial plans called for the French army to undertake the main part of the Somme offensive, supported ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Great War
The ''History of the Great War Based on Official Documents by Direction of the Committee of Imperial Defence'' (abbreviated to ''History of the Great War'' or ''British Official History'') is a series of concerning the war effort of the British state during the First World War. It was produced by the Historical Section of the Committee of Imperial Defence from 1915 to 1949; after 1919 Brigadier-General Sir James Edmonds was Director. Edmonds wrote many of the army volumes and influenced the choice of historians for the navy, air force, medical and veterinary volumes. Work had begun on the series in 1915 and in 1920, the first volumes of ''Naval Operations'' and ''Seaborne Trade'', were published. The first "army" publication, ''Military Operations: France and Belgium 1914'' Part I and a separate map case were published in 1922 and the final volume, ''The Occupation of Constantinople'' were published in 2010. The ''History of the Great War'' Military Operations volumes were or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battalion
A battalion is a military unit, typically consisting of 300 to 1,200 soldiers commanded by a lieutenant colonel, and subdivided into a number of companies (usually each commanded by a major or a captain). In some countries, battalions are exclusively infantry, while in others battalions are unit-level organizations. The word battalion came into the English language in the 16th century from the French language (French: ''bataillon'' meaning "battle squadron"; Italian: ''battaglione'' meaning the same thing; derived from the Vulgar Latin word ''battalia'' meaning "battle" and from the Latin word ''bauttere'' meaning "to beat" or "to strike"). The first use of the word in English was in the 1580s. Description A battalion comprises two or more primary mission companies which are often of a common type (e.g., infantry, tank, or maintenance), although there are exceptions such as combined arms battalions in the U.S. Army. In addition to the primary mission companies, a battal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Company (military Unit)
A company is a military unit, typically consisting of 80–250 soldiers and usually commanded by a major or a captain. Most companies are formed of three to seven platoons, although the exact number may vary by country, unit type, and structure. Usually several companies are grouped as a battalion or regiment, the latter of which is sometimes formed by several battalions. Occasionally, ''independent'' or ''separate'' companies are organized for special purposes, such as the 1st Air Naval Gunfire Liaison Company or the 3rd Force Reconnaissance Company. These companies are not organic to a battalion or regiment, but rather report directly to a higher level organization such as a Marine Expeditionary Force headquarters (i.e., a corps-level command). Historical background The modern military company became popularized during the reorganization of the Swedish Army in 1631 under King Gustav II Adolph. For administrative purposes, the infantry was divided into companies consisti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Army (United Kingdom)
The Third Army was a field army of the British Army during World War I that saw active service on the Western Front throughout the war. First World War The Third Army was part of the British Army during World War I and was formed in France on 13 July 1915, under the command of Lieutenant-General Charles Monro. During August 1915 the Third Army took over trench line south of the French Tenth Army, which had to keep in position for the forthcoming autumn offensive. This made the Third Army geographically separate from the other British Armies for the time being. This remained the case until March 1916, when the French Tenth Army was redeployed because of French losses at Verdun and the British Fourth Army was formed in preparation for the Battle of the Somme. The battles it took part in on the Western Front included: * Battle of the Somme * Battle of Cambrai * Second Battle of Arras (April 1917) * Battle of Passchendaele * Battle of Amiens (August 1918) * Hundred Days Offen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivor Maxse
General Sir Frederick Ivor Maxse, (22 December 1862 – 28 January 1958) was a senior British Army officer who fought during the First World War, best known for his innovative and effective training methods. Early life Ivor Maxse was the eldest of four children born to Admiral Frederick Maxse and Cecilia Steel. His siblings were Olive Hermione Maxse, and editors Violet Milner, Viscountess Milner, and Leopold Maxse. His maternal grandmother was Lady Caroline FitzHardinge, daughter of Frederick Berkeley, 5th Earl of Berkeley. He was a nephew of Sir Henry Berkeley Fitzhardinge Maxse He was educated at Mr. Lake's Preparatory School in Caterham, Surrey from 1875 to 1877; Rugby School from 1877 to 1880 and Sandhurst from 1881 to 1882.Correlli Barnett, �Maxse, Sir (Frederick) Ivor (1862–1958)��, rev. Roger T. Stearn, ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, 2004; online edn, May 2008, accessed 5 June 2011. Early military career Maxse was commis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major-general (United Kingdom)
Major general (Maj Gen) is a "two-star" rank in the British Army and Royal Marines. The rank was also briefly used by the Royal Air Force for a year and a half, from its creation to August 1919. In the British Army, a major general is the customary rank for the appointment of division commander. In the Royal Marines, the rank of major general is held by the Commandant General. A Major General is senior to a Brigadier but subordinate to lieutenant general. The rank is OF-7 on the NATO rank scale, equivalent to a rear admiral in the Royal Navy or an air vice-marshal in the Royal Air Force and the air forces of many Commonwealth countries. The rank insignia is the star (or 'pip') of the Order of the Bath, over a crossed sword and baton. In terms of orthography, compound ranks were invariably hyphenated, prior to about 1980. Nowadays the rank is almost equally invariably non-hyphenated. When written as a title, especially before a person's name, both words of the rank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th (Eastern) Division
The 18th (Eastern) Division was an infantry division of the British Army formed in September 1914 during the First World War as part of the K2 Army Group, part of Lord Kitchener's New Armies. From its creation the division trained in England until 25 May 1915 when it landed in France and spent the duration of the First World War in action on the Western Front, becoming one of the elite divisions of the British Army. During the Battle of the Somme in the latter half of 1916, the 18th Division was commanded by Major General Ivor Maxse. Formation history The division was formed in September 1914 during the First World War as part of the K2 Army Group, part of Lord Kitchener's New Armies. It was formed in the Colchester area but re-located to Salisbury Plain in May 1915. Major-General Ivor Maxse took command in October 1914. Order of battle The following units served in the division. ; 53rd Brigade : * 10th (Service) Battalion, Essex Regiment * 8th (Service) Battalion, Norfol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claud Jacob
Field Marshal Sir Claud William Jacob, (21 November 1863 – 2 June 1948) was a British Indian Army officer. He served in the First World War as commander of the Dehra Dun Brigade, as General Officer Commanding 21st Division and as General Officer Commanding II Corps in the Fifth Army. During the Battle of the Somme, his corps undertook the British attack during the Battle of Thiepval Ridge in September 1916 and the subsequent assault on St Pierre Divion during the Battle of the Ancre in November 1916. He remained in command of II Corps for the Battle of Passchendaele in Autumn 1917. After the War he commanded a corps of the British Army of the Rhine during the occupation there and then served as Chief of the General Staff in India. He went on to be General Officer Commanding Northern Command in India before temporarily becoming Commander-in-Chief, India and then taking over as Military Secretary to the India Office. Military career Jacob was born on 21 November 1863, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lieutenant-general (United Kingdom)
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen), formerly more commonly lieutenant-general, is a senior rank in the British Army and the Royal Marines. It is the equivalent of a multinational three-star rank; some British lieutenant generals sometimes wear three-star insignia, in addition to their standard insignia, when on multinational operations. Lieutenant general is a superior rank to major general, but subordinate to a (full) general. The rank has a NATO rank code of OF-8, equivalent to a vice-admiral in the Royal Navy and an air marshal in the Royal Air Force (RAF) and the air forces of many Commonwealth countries. The rank insignia for both the Army and the Royal Marines is a crown over a crossed sabre and baton. Since the coronation of Queen Elizabeth II, the St Edward's Crown, commonly known as the Queen's Crown, has been depicted. Before 1953, the Tudor Crown, commonly known as the King's Crown, was used. British Army usage Ordinarily, lieutenant general is the rank held by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
II Corps (United Kingdom)
The II Corps was an army corps of the British Army formed in both the First World War and the Second World War. There had also been a short-lived II Corps during the Waterloo Campaign. Napoleonic precursor Assembling an army in the Southern Netherlands to fight Napoleon's resurgent forces in the spring of 1815, the Duke of Wellington formed it into army corps, deliberately mixing units from the Anglo-Hanoverian, Dutch and German contingents so that the weaker elements would be stiffened by more experienced or reliable troops. As he put it: ‘It was necessary to organize these troops in brigades, divisions, and corps d’armee with those better disciplined and more accustomed to war’. He placed II Corps under the command of Lord Hill. However, Wellington did not use the corps as tactical entities, and continued his accustomed practice of issuing orders directly to divisional and lower commanders. When he drew up his army on the ridge at Waterloo, elements of the various co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Ancre Heights
The Battle of the Ancre Heights (1 October – 11 November 1916), is the name given to the continuation of British attacks after the Battle of Thiepval Ridge from during the Battle of the Somme. The battle was conducted by the Reserve Army (renamed Fifth Army on 29 October) from Courcelette near the Albert–Bapaume road, west to Thiepval on Bazentin Ridge. British possession of the heights would deprive the German 1st Army of observation towards Albert to the south-west and give the British observation north over the Ancre valley to the German positions around Beaumont-Hamel, Serre and Beaucourt. The Reserve Army conducted large attacks on and from Many smaller attacks were made in the intervening periods, amid interruptions caused by frequent heavy rain, which turned the ground and roads into rivers of mud and grounded aircraft. German forces in footholds on the ridge, at the east end of ( Regina Trench) and in the remaining parts of ( Schwaben Redoubt) to the north and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |