|
Battle Of The Philippines (1941-42)
Battle of the Philippines may refer to several wars, military campaigns, and major battles which have been fought in the Philippine Islands, including: *Spanish conquest **Battle of Bangkusay Channel **1582 Cagayan battles ** Tondo Conspiracy ** Bankaw revolt **Battle of Puerto de Cavite * Philippine revolts against Spain *The Philippine Revolution (1896–98), called the "Tagalog War" by the Spanish, a military conflict between the people of the Philippines and the Spanish colonial authorities ** Battle of San Mateo and Montalban ** Battle of San Francisco de Malabon ** Battle of San Juan del Monte ** Kawit revolt ** Battle of Sambat **Battle of Pateros **Battle of Camalig ** Battles of Batangas **Battle of Talisay ** Battle of Pasong Tamo ** Battle of Imus ** Battle of Binakayan-Dalahican ** Battle of Kakarong de Sili ** Battle of Perez Dasmariñas ** Cry of Tarlac **Battle of Zapote Bridge (1897) **Battle of Calamba **Battle of Tayabas **Battle of Tres de Abril ** Siege of Zamb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Bangkusay Channel
The Battle of Bangkusay ( fil, Labanan sa Ilog Bangkusay; es, Batalla de Bangkusay), on June 3, 1571, was a naval engagement that marked the last resistance by locals to the Spanish Empire's occupation and colonization of the Pasig River delta, which had been the site of the indigenous polities of Rajahnate of Maynila and Tondo. Tarik Sulayman, the chief of Macabebes, refused to ally with the Spanish and decided to mount an attack at Bangkusay Channel on Spanish forces, led by Miguel López de Legazpi. Sulayman's forces were defeated, and Sulayman himself was killed. The Spanish victory in Bangkusay and Legazpi's alliance with Lakandula of Tondo, enabled the Spaniards to establish themselves throughout the city and its neighboring towns. Historical Account Background Miguel López de Legazpi was searching for a suitable place to establish the Spanish colonial capital after being forced to leave first Cebu and then Iloilo by Portuguese pirates. In 1570, Martin de Go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Imus
The Battle of Imus ( fil, Labanan sa Imus, es, Batalla de Imus), or the siege of Imus ( fil, Pagkubkob sa Imus, es, El Cerco de Imus), was the first major battle of the Philippine revolution against the Spanish colonial government in the province of Cavite. It was fought between September 1–3, 1896 at Imus, Cavite province in the Philippines, right after Bonifacio's ill-fated attack on the gunpowder magazine at the Battle of San Juan del Monte in Manila.Spencer, Tucker C. (2009)"The Encyclopedia of the Spanish-American and Philippine-American Wars - Battle of Imus River" pg. 303. ABC_CLIO, LLC, Santa Barbara. . The resulting victory for the Filipino revolutionaries in Imus very much alarmed the Spanish government in the country. Following the conflict, they attempted to subdue the revolutionaries in Cavite province with the twin battles in Binakayan and Dalahican weeks after the battle in Imus. Background The revolution began in Cavite province shortly after it joined th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
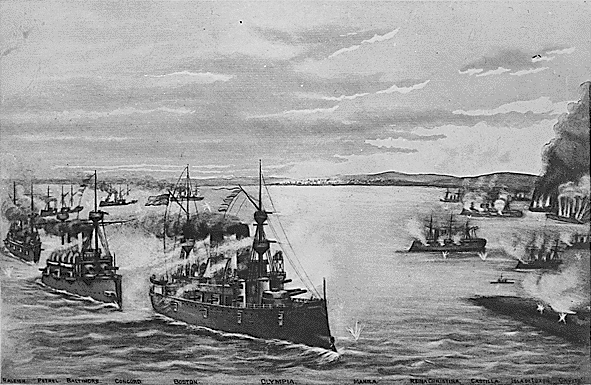
Battle Of Manila Bay
The Battle of Manila Bay ( fil, Labanan sa Look ng Maynila; es, Batalla de Bahía de Manila), also known as the Battle of Cavite, took place on 1 May 1898, during the Spanish–American War. The American Asiatic Squadron under Commodore George Dewey engaged and destroyed the Spanish Pacific Squadron under ''Contraalmirante'' (Rear admiral) Patricio Montojo. The battle took place in Manila Bay in the Philippines, and was the first major engagement of the Spanish–American War. The battle was one of the most decisive naval battles in history and marked the end of the Spanish colonial period in Philippine history. Tensions between Spain and the United States worsened over the Spanish conduct during their efforts to quell the Cuban War of Independence, with many Americans being agitated by largely falsified reports of Spanish atrocities against the Cuban population. In January 1898, fearing the fate of American interests in Cuba due to the war, the cruiser USS ''Main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Manila (other)
Battle of Manila may refer to: Land battles * Battle of Manila (1570), Spanish forces from Mexico vs. Muslims from Brunei * Battle of Manila (1574), Chinese Pirate Warlord "Limahong" vs. the Spanish * Battle of Manila (1762), British take Manila during the Seven Years' War * Raid on Manila (1798), British reconnaissance operation during French Revolutionary Wars * Battle of Manila (1896), Filipino Revolutionaries vs. the Spanish during the Philippine Revolution * Battle of Manila (1898), United States and Filipino Revolutionaries vs. the Spanish during the Spanish–American War * Battle of Manila (1899), Filipino forces vs. the United States during the Philippine–American War * Battle of Manila (1945), Liberation of Manila from Japan during World War II Naval battles * Battle of Manila Bay (1898) See also * Battle of Bangkusay Channel (1571) * Battles of La Naval de Manila (1646) * Battle of the Philippines (other) * Philippine revolts against Spain Durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negros Revolution
The Negros Revolution ( fil, Himagsikang Negrense; ceb, Rebolusyong Negrense; es, Revolución negrense), commemorated and popularly known as the Fifth of November ( es, links=no, Cinco de noviembre) or Negros Day ( hil, Adlaw sang Negros; ceb, links=no, Adlaw sa Negros; es, links=no, Día de Negros), was a political movement that in 1898 created a government on Negros Island in the Philippines, ending Spanish control of the island and paving the way for a republican government run by the Negrense natives. The newly established Negros Republic (; ceb, links=no, Republika sa Negros; es, links=no, República de Negros) lasted for approximately three months. American forces landed on the island unopposed on February 2, 1899, ending the island's independence. Negros was then annexed to the Philippine Islands on 20 April 1901. Prelude to revolution It has been stipulated that the Spanish civil and religious authorities in Negros did not initially suspect that the sugar barons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Alapan
The Battle of Alapan ( fil, Labanan sa Alapan, es, Batalla de Alapan) was fought on May 28, 1898, and was the first military victory of the Filipino Revolutionaries led by Emilio Aguinaldo after his return to the Philippines from Hong Kong. After the American naval victory in the Battle of Manila Bay, Aguinaldo returned from exile in Hong Kong, reconstituted the Philippine Revolutionary Army, and fought against the Spanish troops in a garrison in Alapan, Imus, Cavite. The battle lasted for five hours, from 10:00 A.M. to 3:00 P.M. After the victory at Alapan, Aguinaldo unfurled the Philippine flag for the first time, and hoisted it at the Teatro Caviteño in Cavite Nuevo (present-day Cavite City) in front of Filipino revolutionaries and more than 270 captured Spanish troops. A group of American sailors of the US Asiatic Squadron also witnessed the unfurling. Flag Day is celebrated every May 28 in honor of this battle. This day also marks the start of the national Independence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Zamboanga
The siege of Fort Pilar was fought between April and May 1898 on then-town of Zamboanga in Mindanao as a part of the Philippine Revolution. One of the only few actions against Spanish colonials forces in Mindanao, the victory brought about by the Zamboangueño Ethnolinguistic Nation, after their capture of Fort Pilar several weeks later, paved way for the foundation of the short-lived Republic of Zamboanga. Background When the Philippine Revolution spread to Mindanao, General Vicente Alvarez organized an army of Christian Filipinos, Tribal warriors, and Muslim Krismen and fought the Spaniards for freedom’s sake. Alvarez initiated the revolution in Zamboanga, in March 1898. He was able to take control of the peninsula, except the port of Zamboanga and Fort Pilar, which were fortified by the Spanish forces. He then organized the Zamboangueño Revolutionary Government along with his aides-de-camp Felipe Ramos and Melanio Calixto. Calixto was promoted to Major, Ramos as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Tres De Abril
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Tayabas
The siege of Tayabas ( fil, Pagkubkob sa Tayabas, es, Sitio de Tayabas) was a 2-month campaign of the Philippine Revolution that saw intense guerrilla warfare and bloodshed for the province. The battle occurred shortly after Aguinaldo's return from Hong Kong in May of the same year. Tayabas was just one of the many triumphs for the revolutionaries in that year, leading up to Philippine independence. Background On December 14, 1897, Emilio Aguinaldo and Gov. Gen. Primo de Rivera signed the Pact of Biak-na-Bato ending the first phase of the Philippine revolution. However, many Generals of the revolution, Like Paciano Rizal and Miguel Malvar, rejected the pact and continued the fight against Spain. Malvar took command of the disoriented and disillusioned forces of the southern provinces of Batangas, Tayabas and Laguna together with Rizal, but in the end, he rounded up his followers and left for Hong Kong together with other key revolutionaries. In mid-May, 1898, Aguinaldo r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Calamba
The Battle of Calamba ( fil, Labanan sa Calamba, es, Batalla de Calamba) was a battle fought between Filipino Revolutionaries in Laguna in the Philippines and the colonial forces of the Spanish Empire. Background Emilio Aguinaldo had returned from exile in Hong Kong and was amassing a large force to drive out the Spanish from Cavite. General Leopoldo Garcia Peña, the Spanish military commander at Cavite, was hard-pressed with roughly 3,000 Spanish troops scattered in various detachments in Cavite. The combined forces of Generals Luciano San Miguel, Mariano Noriel, Artemio Ricarte and Juan Cailles, having with them about 6,000–8,000 troops, who began attacking and decimating Peña's units one by one. With the war of liberation once again in full swing, Laguna was soon also subsumed by waves of revolutionary fervor, and surely enough rebel armies were quickly formed in an effort to liberate the province from Spanish control. One of such forces was led by General Paciano Riz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Zapote Bridge (1897)
The Battle of Zapote Bridge was fought on February 17, 1897, as part of the Philippine Revolution. Filipino revolutionary forces led by General Emilio Aguinaldo defeated Spanish forces under the command of Governor-General Camilo de Polavieja. In this battle, General Edilberto Evangelista (a Filipino civil engineer, trench builder and member of the Katipunan) was killed. Background With the loss of the revolutionary battle and the opening of the second phase of the war, the Spaniards began their campaign to recapture territories. This campaign was in Filipino hands in the early phase of the revolution after the decisive battles of Binakayan and Dalahican in 1896. Governor-General Camilo de Polavieja now fully aware that the mainweight of the revolution is in Cavite, decided to launch a two-pronged assault which will defeat the revolutionaries led by Aguinaldo. He ordered General José de Lachambre with a much bigger force to march against Silang to take on the ''Katipun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cry Of Tarlac
{{Campaignbox Philippine Revolution The Cry of Tarlac ( fil, Sigaw sa Tarlac, es, Gritos de Tarlac) was an uprising led by General Francisco Macabulos in La Paz, Tarlac in January 1897. Although the province of Tarlac was already classified to be in a state of rebellion even before the uprising, major hostilities unfolded after the cry. Background The previous year, eight provinces were put under martial law by the Spanish government in Manila. The eight rays of the Sun on the Philippine flag represent these eight provinces including the province of Tarlac, which had a revolutionary chapter of the Katipunan established by Ladislao Diwa. After the Cry of Pugad Lawin and the later Cry of Nueva Ecija in September, the Spanish government began sending troops to the revolted provinces and local militias from the Visayan islands helped quell the insurrection in central Luzon, however, the main revolutionaries from the area, Mariano Llanera and Manuel Tinio continued a guerilla w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |