|
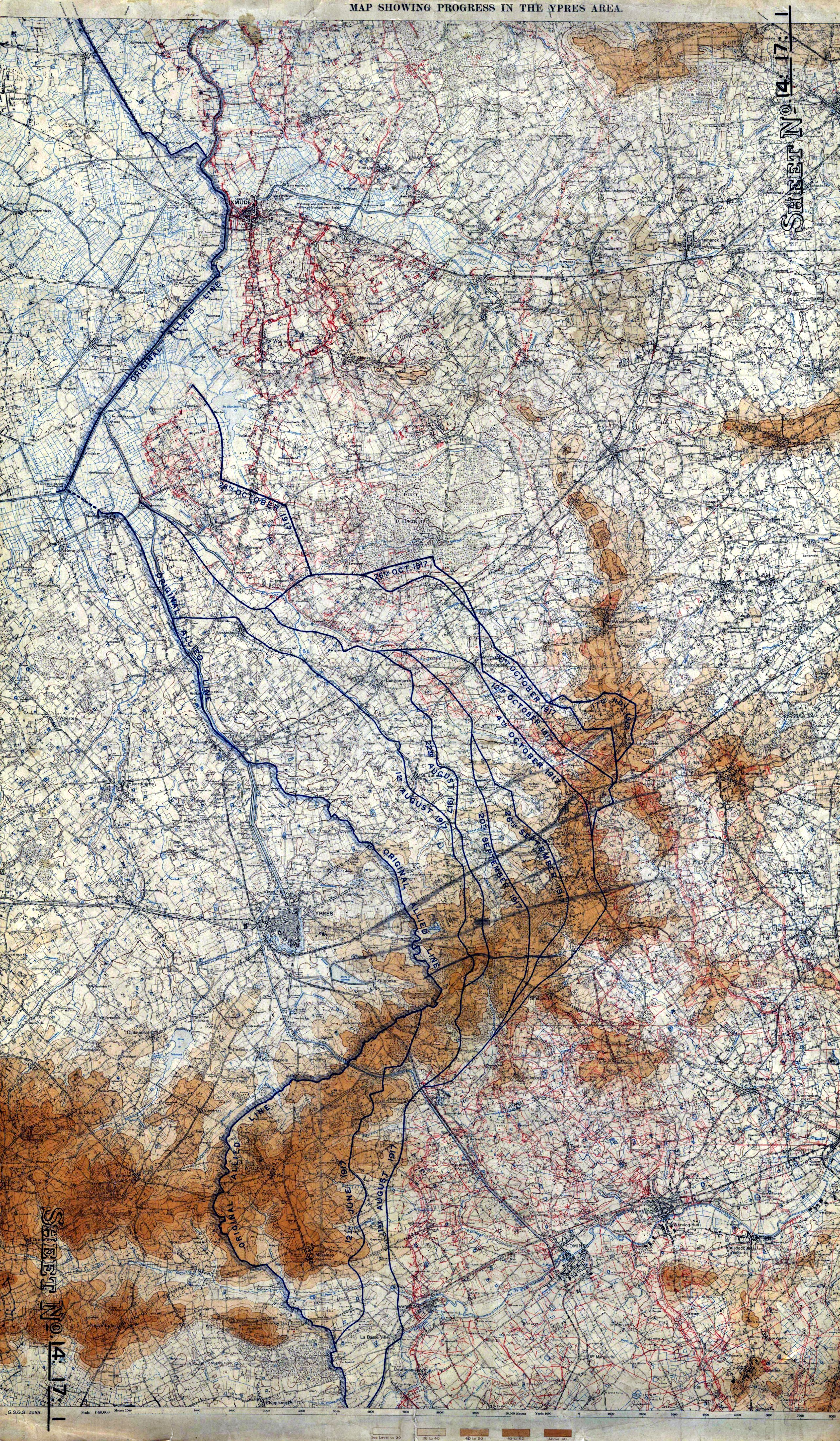
Battle Of The Peaks Of Flanders
The Fifth Battle of Ypres, also called the Advance in Flanders and the Battle of the Peaks of Flanders (french: Bataille des Crêtes de Flandres) is an informal name used to identify a series of World War I battles in northern France and southern Belgium (Flanders) from late September to October 1918. Background After the German spring offensive of 1918 failed to achieve a decisive victory, German morale waned and the increasing numbers of American soldiers arriving on the Western Front gave the Allies a growing numerical advantage over the western armies of the German Empire. To take advantage of this Marshal of France Ferdinand Foch developed a strategy which became known as the Grand Offensive, in which attacks were made on the German lines over as wide a front as possible. Belgian, British and French forces around the Ypres Salient were to form the northern pincer of an offensive towards the Belgian city of Liège. The British Second Army had followed up some minor with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Front (World War I)
The Western Front was one of the main theatres of war during the First World War. Following the outbreak of war in August 1914, the German Army opened the Western Front by invading Luxembourg and Belgium, then gaining military control of important industrial regions in France. The German advance was halted with the Battle of the Marne. Following the Race to the Sea, both sides dug in along a meandering line of fortified trenches, stretching from the North Sea to the Swiss frontier with France, which changed little except during early 1917 and in 1918. Between 1915 and 1917 there were several offensives along this front. The attacks employed massive artillery bombardments and massed infantry advances. Entrenchments, machine gun emplacements, barbed wire and artillery repeatedly inflicted severe casualties during attacks and counter-attacks and no significant advances were made. Among the most costly of these offensives were the Battle of Verdun, in 1916, with a combined 700,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Net Income
In business and accounting, net income (also total comprehensive income, net earnings, net profit, bottom line, sales profit, or credit sales) is an entity's income minus cost of goods sold, expenses, depreciation and amortization, interest, and taxes for an accounting period. It is computed as the residual of all revenues and gains less all expenses and losses for the period,Stickney, et al. (2009) Financial Accounting: An Introduction to Concepts, Methods, and Uses. Cengage Learning and has also been defined as the net increase in shareholders' equity that results from a company's operations.Needles, et al. (2010) Financial Accounting. Cengage Learning. It is different from gross income, which only deducts the cost of goods sold from revenue. For households and individuals, net income refers to the (gross) income minus taxes and other deductions (e.g. mandatory pension contributions). Definition Net income can be distributed among holders of common stock as a dividend or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leie
The Lys () or Leie () is a river in France and Belgium, and a left-bank tributary of the Scheldt. Its source is in Pas-de-Calais, France, and it flows into the river Scheldt in Ghent, Belgium. Its total length is . Historically a very polluted river from the high population density and industrialisation in both Northern France and Belgium, it has seen substantial improvements in recent years, partly due to the decline of the principal industry, the spinning and weaving of flax. The region of the Leie (between Deinze and Ghent) was known as a favourite place for numerous painters in the first half of the 20th century. The source of the Lys is in a village, Lisbourg, east of Fruges, in the Pas-de-Calais department of France. It flows generally northeast through the following departments of France, provinces of Belgium and towns and municipalities: *Pas-de-Calais (F): Thérouanne, Aire-sur-la-Lys * Nord (F): Merville, Armentières, Halluin *Hainaut (province), Hainaut (B): Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sixth Army (France)
The Sixth Army (french: 6eme Armée) was a field army of the French Army during World War I and World War II. World War I The Sixth Army was formed 26 August 1914, composed of troops from various disparate French armies: two active army corps, the ( 4th and 7th respectively detached from the Third Army and First Army, the 5th and 6th groups of reserve divisions, the 45th and 37th Infantry Divisions, a native brigade and a cavalry corps. After Alexander von Kluck rotated his German First Army away from Paris to reinforce Karl von Bülow's German Second Army, Joseph Gallieni ordered the Sixth Army to attack von Kluck's forces. Although the German First Army counterattacked, this allowed John French's British Expeditionary Force to occupy a twenty-mile salient between the two armies beginning the First Battle of the Marne. France would end up contributing three corps to the opening attack of the Battle of the Somme (the 20th Army Corps, I Colonial and 35th Corps of the Sixth Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Action At Outtersteene Ridge
Action may refer to: * Action (narrative), a literary mode * Action fiction, a type of genre fiction * Action game, a genre of video game Film * Action film, a genre of film * ''Action'' (1921 film), a film by John Ford * ''Action'' (1980 film), a film by Tinto Brass * ''Action 3D'', a 2013 Telugu language film * ''Action'' (2019 film), a Kollywood film. Music * Action (music), a characteristic of a stringed instrument * Action (piano), the mechanism which drops the hammer on the string when a key is pressed * The Action, a 1960s band Albums * ''Action'' (B'z album) (2007) * ''Action!'' (Desmond Dekker album) (1968) * ''Action Action Action'' or ''Action'', a 1965 album by Jackie McLean * ''Action!'' (Oh My God album) (2002) * ''Action'' (Oscar Peterson album) (1968) * ''Action'' (Punchline album) (2004) * ''Action'' (Question Mark & the Mysterians album) (1967) * ''Action'' (Uppermost album) (2011) * ''Action'' (EP), a 2012 EP by NU'EST * ''Action'', a 1984 albu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Army (United Kingdom)
The British Second Army was a field army active during the First and Second World Wars. During the First World War the army was active on the Western Front throughout most of the war and later active in Italy. During the Second World War the army was the main British contribution to the Normandy landings on 6 June 1944 and advance across Europe. First World War The Second Army was part of the British Army formed on 26 December 1914, when the British Expeditionary Force was split in two due to becoming too big to control its subordinate formations. The army controlled both III Corps and IV Corps. Second Army spent most of the war positioned around the Ypres salient, but was redeployed to Italy as part of the Italian Expeditionary Force between November 1917 and March 1918. In 1919 it was reconstituted as the British Army of the Rhine.Edmonds (1987) Commanders * 1914–1915 General Sir Horace Smith-Dorrien * 1915–1917 General Sir Herbert Plumer * 1917–1918 General Sir Henr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liège
Liège ( , , ; wa, Lîdje ; nl, Luik ; german: Lüttich ) is a major city and municipality of Wallonia and the capital of the Belgian province of Liège. The city is situated in the valley of the Meuse, in the east of Belgium, not far from borders with the Netherlands (Maastricht is about to the north) and with Germany (Aachen is about north-east). In Liège, the Meuse meets the river Ourthe. The city is part of the '' sillon industriel'', the former industrial backbone of Wallonia. It still is the principal economic and cultural centre of the region. The municipality consists of the following districts: Angleur, , Chênée, , Grivegnée, Jupille-sur-Meuse, Liège, Rocourt, and Wandre. In November 2012, Liège had 198,280 inhabitants. The metropolitan area, including the outer commuter zone, covers an area of 1,879 km2 (725 sq mi) and had a total population of 749,110 on 1 January 2008. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ypres Salient
The Ypres Salient around Ypres in Belgium was the scene of several battles and an extremely important part of the Western front during the First World War. Ypres district Ypres lies at the junction of the Ypres–Comines Canal and the Ieperlee. The city is overlooked by Kemmel Hill in the south-west and from the east by low hills running south-west to north-east with Wytschaete (Wijtschate), Hill 60 to the east of Verbrandenmolen, Hooge, Polygon Wood and Passchendaele (Passendale). The high point of the ridge is at Wytschaete, from Ypres, while at Hollebeke the ridge is distant and recedes to at Polygon Wood. Wytschaete is about above the plain; on the Ypres–Menin road at Hooge, the elevation is about and at Passchendaele. The rises are slight, apart from the vicinity of Zonnebeke, which has a From Hooge and to the east, the slope is near Hollebeke, it is heights are subtle but have the character of a saucer lip around Ypres. The main ridge has spurs sloping east an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Offensive
The Hundred Days Offensive (8 August to 11 November 1918) was a series of massive Allied offensives that ended the First World War. Beginning with the Battle of Amiens (8–12 August) on the Western Front, the Allies pushed the Central Powers back, undoing their gains from the German spring offensive. The Germans retreated to the Hindenburg Line, but the Allies broke through the line with a series of victories, starting with the Battle of St Quentin Canal on 29 September. The offensive, together with a revolution breaking out in Germany, led to the Armistice of 11 November 1918 which ended the war with an Allied victory. The term "Hundred Days Offensive" does not refer to a battle or strategy, but rather the rapid series of Allied victories against which the German Army had no reply. Background The German spring offensive of the German Army on the Western Front had begun on 21 March 1918 with Operation Michael and had petered out by July. The Germans had advanced to the Riv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand Foch
Ferdinand Foch ( , ; 2 October 1851 – 20 March 1929) was a French general and military theorist who served as the Supreme Allied Commander during the First World War. An aggressive, even reckless commander at the First Marne, Flanders and Artois campaigns of 1914–1916, Foch became the Allied Commander-in-Chief in late March 1918 in the face of the all-out German spring offensive, which pushed the Allies back using fresh soldiers and new tactics that trenches could not withstand. He successfully coordinated the French, British and American efforts into a coherent whole, deftly handling his strategic reserves. He stopped the German offensive and launched a war-winning counterattack. In November 1918, Marshal Foch accepted the German cessation of hostilities and was present at the Armistice of 11 November 1918. At the outbreak of war in August 1914, Foch's XX Corps participated in the brief invasion of Germany before retreating in the face of a German counter-attack and succ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marshal Of France
Marshal of France (french: Maréchal de France, plural ') is a French military distinction, rather than a military rank, that is awarded to generals for exceptional achievements. The title has been awarded since 1185, though briefly abolished (1793–1804) and for a period dormant (1870–1916). It was one of the Great Officers of the Crown of France during the and Bourbon Restoration, and one of the Grand Dignitaries of the Empire during the First French Empire (when the title was Marshal of the Empire, not Marshal of France). A Marshal of France displays seven stars on each shoulder strap. A marshal also receives a baton: a blue cylinder with stars, formerly fleurs-de-lis during the monarchy and eagles during the First French Empire. The baton bears the Latin inscription of ', which means "terror in war, ornament in peace". Between the end of the 16th century and the middle of the 19th century, six Marshals of France were given the even more exalted rank of Marshal General ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |