|
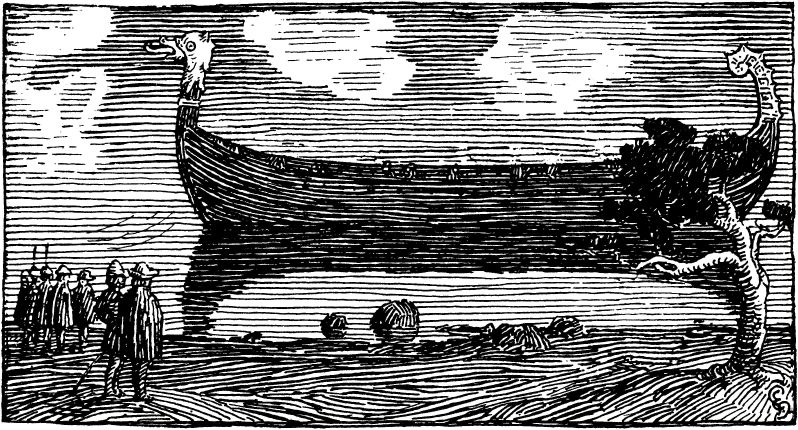
Battle Of Svolder
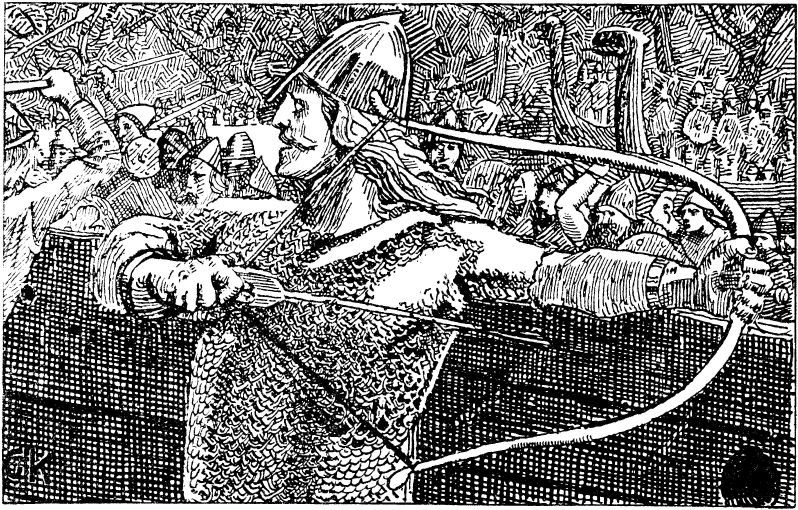
The Battle of Svolder (''Svold'' or ''Swold'') was a large naval battle during the Viking age, fought in September 999 or 1000 in the western Baltic Sea between King Olaf of Norway and an alliance of the Kings of Denmark and Sweden and Olaf's enemies in Norway. The backdrop of the battle was the unification of Norway into a single independent state after longstanding Danish efforts to control the country, combined with the spread of Christianity in Scandinavia. King Olaf Tryggvason was sailing to, or home from, an expedition in Wendland (Pomerania), when he was ambushed by an alliance of Svein Forkbeard, King of Denmark, Olof Skötkonung (also known as Olaf Eiríksson or Olaf the Swede), King of Sweden, and Eirik Hákonarson, Jarl of Lade. According to the Saga of King Olaf I Tryggvason, he had 60 warships plus the contribution of 11 warships from the Jomvikingsbr> His ships were captured one by one, last of all the '' Ormen Lange (longship), Ormen Lange'', which Jarl Eirik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Sinding
Otto Ludvig Sinding (20 December 1842 – 22 November 1909) was a Norwegian painter, illustrator, poet and dramatist. Sinding drew on motives from Norwegian nature, folk life and history. Personal life Otto Sinding was born in Kongsberg as a son of mine superintendent Matthias Wilhelm Sinding (1811–1860) and Cecilie Marie Mejdell (1817–86). He was the older brother of the sculptor Stephan Sinding and the composer Christian Sinding. He was a nephew of Nicolai Mejdell (1822–1899) and Thorvald Mejdell (1824–1908), and through the former a first cousin of Glør Thorvald Mejdell, who married Otto's sister Thora Cathrine Sinding. Otto Sinding was also a first cousin of Alfred Sinding-Larsen and the three siblings Ernst Anton Henrik Sinding, Elisabeth Sinding and Gustav Adolf Sinding. In April 1874 in Karlsruhe Otto Sinding married Anna Christine Nielsen (1855–1914), an adoptive daughter of Hans Gude and Betsy Anker. Their son Sigmund Sinding became a notable painter. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianization Of Scandinavia
The Christianization of Scandinavia, as well as other Nordic countries and the Baltic countries, took place between the 8th and the 12th centuries. The realms of Denmark, Norway and Sweden established their own Archdioceses, responsible directly to the Pope, in 1104, 1154 and 1164, respectively. The conversion to Christianity of the Scandinavian people required more time, since it took additional efforts to establish a network of churches. The earliest signs of Christianization were in the 830s with Ansgar's construction of churches in Birka and Hedeby in the 830s. The conversion of Scandinavian kings occurred over the period 960–1020. Subsequently, Scandinavian kings sought to establish churches, dioceses and Christian kingship, as well as destroy pagan temples. Denmark was the first Scandinavian country to Christianize, as Harald Bluetooth declared this around AD 975, and raised the larger of the two Jelling Stones. According to historian Anders Winroth, Christianity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
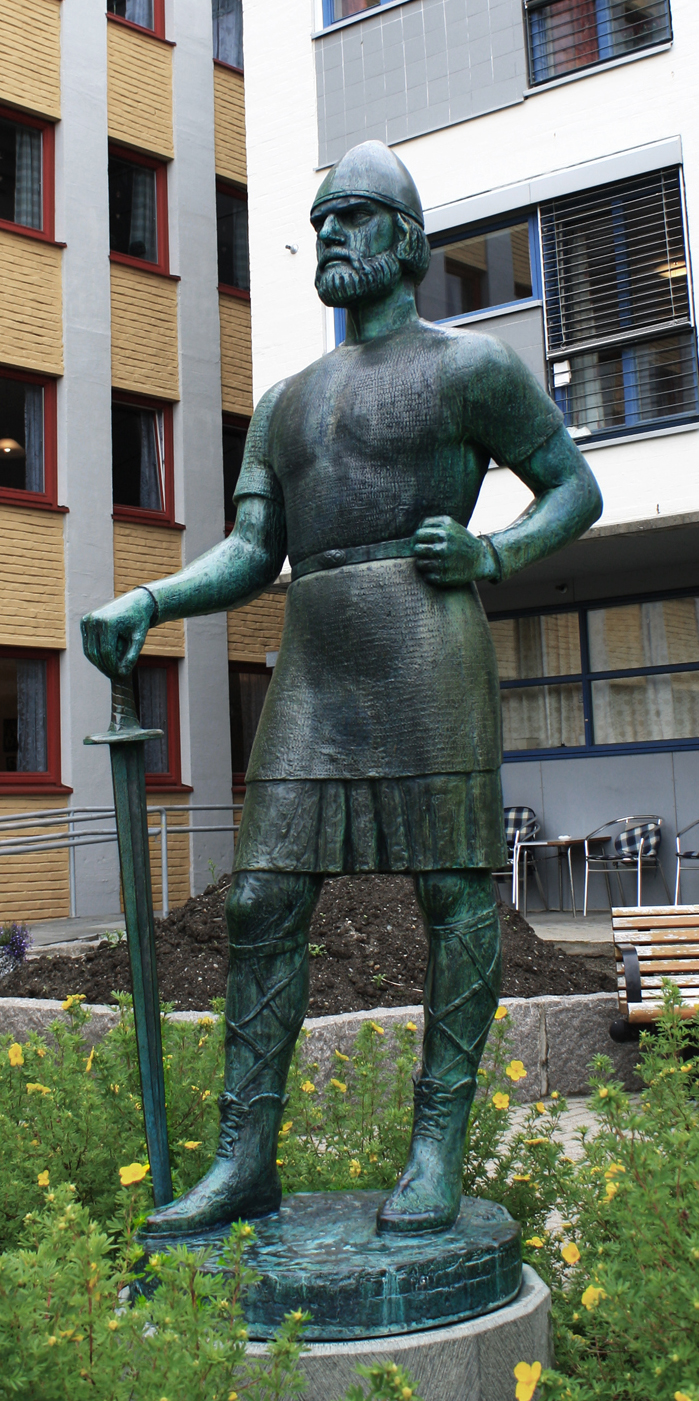
Harald Fairhair
Harald Fairhair no, Harald hårfagreModern Icelandic: ( – ) was a Norwegian king. According to traditions current in Norway and Iceland in the eleventh and twelfth centuries, he reigned from 872 to 930 and was the first King of Norway. Supposedly, two of his sons, Eric Bloodaxe and Haakon the Good, succeeded Harald to become kings after his death. Much of Harald's biography is uncertain. A couple of praise poems by his court poet Þorbjörn Hornklofi survive in fragments, but the extant accounts of his life come from sagas set down in writing around three centuries after his lifetime. His life is described in several of the Kings' sagas, none of them older than the twelfth century. Their accounts of Harald and his life differ on many points, but it is clear that in the twelfth and thirteenth centuries Harald was regarded as having unified Norway into one kingdom. Since the nineteenth century, when Norway was in a personal union with Sweden, Harald has become ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petty Kingdom
A petty kingdom is a kingdom described as minor or "petty" (from the French 'petit' meaning small) by contrast to an empire or unified kingdom that either preceded or succeeded it (e.g. the numerous kingdoms of Anglo-Saxon England unified into the Kingdom of England in the 10th century, or the numerous Gaelic kingdoms of Ireland as the Kingdom of Ireland in the 16th century). Alternatively, a petty kingdom would be a minor kingdom in the immediate vicinity of larger kingdoms, such as the medieval Kingdom of Mann and the Isles relative to the kingdoms of Scotland or England or the Viking kingdoms of Scandinavia. In the context of the Early Middle Ages or the prehistoric Iron Age, many minor kingdoms are also known as tribal kingdoms. In the parallel Southeast Asian political model, petty kingdoms were known as Mueang. By the European High Middle Ages, many post-Roman Early Middle Ages petty kingdoms had evolved into principalities, grand duchies, or duchies. By the Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heimskringla
''Heimskringla'' () is the best known of the Old Norse kings' sagas. It was written in Old Norse in Iceland by the poet and historian Snorre Sturlason (1178/79–1241) 1230. The name ''Heimskringla'' was first used in the 17th century, derived from the first two words of one of the manuscripts (''kringla heimsins'', "the circle of the world"). ''Heimskringla'' is a collection of sagas about Swedish and Norwegian kings, beginning with the saga of the legendary Swedish dynasty of the Ynglings, followed by accounts of historical Norwegian rulers from Harald Fairhair of the 9th century up to the death of the pretender Eystein Meyla in 1177. The exact sources of the Snorri's work are disputed, but they include earlier kings' sagas, such as Morkinskinna, Fagrskinna and the 12th-century Norwegian synoptic histories and oral traditions, notably many skaldic poems. He explicitly names the now lost work '' Hryggjarstykki'' as his source for the events of the mid-12th century. Alth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snorri Sturluson
Snorri Sturluson ( ; ; 1179 – 22 September 1241) was an Icelandic historian, poet, and politician. He was elected twice as lawspeaker of the Icelandic parliament, the Althing. He is commonly thought to have authored or compiled portions of the '' Prose Edda'', which is a major source for what is today known as Norse mythology, and '' Heimskringla'', a history of the Norwegian kings that begins with legendary material in '' Ynglinga saga'' and moves through to early medieval Scandinavian history. For stylistic and methodological reasons, Snorri is often taken to be the author of '' Egil's saga''. He was assassinated in 1241 by men claiming to be agents of the King of Norway. Biography Early life Snorri Sturluson was born in (commonly transliterated as Hvamm or Hvammr) as a member of the wealthy and powerful Sturlungar clan of the Icelandic Commonwealth, in AD 1179. His parents were ''Sturla Þórðarson the Elder'' of ''Hvammur'' and his second wife, ''Guðný Böðvarsdó ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Einarr Þambarskelfir
Einar Eindridesson Thambarskelfir (c. 980–c. 1050) ( Old Norse: ''Einarr Þambarskelfir'', Modern Norwegian: ''Einar Tambarskjelve'') was an influential Norwegian noble and politician during the 11th century. He headed the feudal lords in their opposition to Olaf Haraldsson. Several references are made to him in Snorri Sturluson's Heimskringla. His cognomen, ''Thambarskelfir'', has two strongly differing explanations. One is that it is derived from ', meaning "shaking bowstring". Thus, the name suggests a master of the longbow. The other is that it is derived from ', meaning "belly", and that it translates to "wobbly belly", surely an unflattering reflection of his physical build. Or it could be the “belly” of the bow. Background Einarr Thambarskelfir was the son of Eindride, a rich and influential farmer at the Viking Age political center of Melhus. Einar Thambarskelfir was a jarl and chieftain at Husaby, a farm in Skaun municipality, and a powerful warlord with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigrid The Haughty
Sigrid the Haughty (Old Norse:''Sigríðr (hin) stórráða''), also known as ''Sigrid Storråda'' (Swedish), is a Scandinavian queen appearing in Norse sagas. Sigrid is named in several late and sometimes contradictory Icelandic sagas composed generations after the events they describe, but there is no reliable historical evidence correlating to her story as they describe her. She is reported by '' Heimskringla'' to have been wife of Eric the Victorious of Sweden, sought as wife by Olaf Tryggvasson, then married to Sweyn Forkbeard of Denmark, but elsewhere author Snorri Sturluson says that Sweyn was married to a different woman. It is unclear if the figure of Sigrid was a real person. Some recent scholars identify her with a documented Polish wife of Eric and perhaps Sweyn mentioned by medieval chroniclers and referred to as ' Świętosława' by some modern historians, but the potential husbands attributed to Sigrid lived over a wide date range and other modern scholars believe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kings' Sagas
Kings' sagas ( is, konungasögur, nn, kongesoger, -sogor, nb, kongesagaer) are Old Norse sagas which principally tell of the lives of semi-legendary and legendary (mythological, fictional) Nordic kings, also known as saga kings. They were composed during the twelfth through the fourteenth centuries, primarily in Iceland, but with some written in Norway. Kings' sagas frequently contain episodic stories known in scholarship as '' þættir'', such as the '' Íslendingaþættir'' (about Icelanders), '' Styrbjarnar þáttr Svíakappa'', '' Hróa þáttr heimska'', and ''Eymundar þáttr hrings'' (about people from elsewhere). List of Kings' sagas Including works in Latin, and in approximate order of composition (though many dates could be off by decades) *A Latin work by Sæmundr fróði, c. 1120, lost. *The older version of '' Íslendingabók'' by Ari fróði, c. 1125, lost. *'' Hryggjarstykki'' by Eiríkr Oddsson, c. 1150, lost. *'' Historia Norvegiæ'', c. 1170. *''Historia d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam Of Bremen
Adam of Bremen ( la, Adamus Bremensis; german: Adam von Bremen) (before 1050 – 12 October 1081/1085) was a German medieval chronicler. He lived and worked in the second half of the eleventh century. Adam is most famous for his chronicle '' Gesta Hammaburgensis ecclesiae pontificum'' (''Deeds of Bishops of the Hamburg Church''). He was "one of the foremost historians and early ethnographers of the medieval period". In his chronicle, he included a chapter mentioning the Norse outpost of Vinland, and was thus the first European to write about the New World. Life Little is known of his life other than hints from his own chronicles. He is believed to have come from Meissen, then its own margravate. The dates of his birth and death are uncertain, but he was probably born before 1050 and died on 12 October of an unknown year (possibly 1081, at the latest 1085). From his chronicles, it is apparent that he was familiar with a number of authors. The honorary name of ''Magister Adam'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earls Of Lade
The Earls of Lade ( no, ladejarler) were a dynasty of Norse '' jarls'' from Lade (Old Norse: ''Hlaðir''), who ruled what is now Trøndelag and Hålogaland from the 9th century to the 11th century. The seat of the Earls of Lade was at Lade Gaard, now located in the eastern parts of the city of Trondheim. The site is near the seaside of the Trondheimsfjord, which was an important waterway in the Viking Age. According to Snorri, King Harald I of Norway was a great commander but lacked a fleet. For that he was assisted by Håkon Grjotgardsson. In gratitude Harald made him the first earl of Lade. Notable Earls of Lade * Hákon Grjótgarðsson (c. 860–870 – c. 900–920), an ally and father-in-law of Harald Fairhair * Sigurðr Hákonarson (died 962), friend and advisor of Hákon the Good * Hákon Sigurðarson (c. 937–995), ruler of Norway from about 975 to 995 * Eiríkr Hákonarson (960s – 1020s), governor of the majority of Norway under Svein Forkbeard * Sve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ormen Lange (longship)
Ormrinn Langi in Old Norse (''The Long Serpent'') ''Ormen Lange'' in Norwegian, ''Ormurin Langi'' in Faroese was one of the most famous of the Viking longships. It was built for the Norwegian King Olav Tryggvason, and was the largest and most powerful longship of its day. In the late 990s King Olav was on a "Crusade" around the country to bring Christianity to Norway. When he was traveling north to Hålogaland he came to a petty kingdom in today's Skjerstad, where the king named Raud the Strong refused to convert to Christianity. A battle ensued, during which Saltstraum, a maelstrom that prevented reinforcements to the king's men, forced King Olav to flee. He continued up north but returned some weeks later when the maelstrom had subsided. Olav won the battle, captured Raud, and gave him two choices: die or convert. The Sagas say that Olav tried to convert him but Raud cursed the name of Jesus, and the King became so enraged that he stuck a ''kvanstilk'' (a stalk of ''Angelica' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |