|
Battle Of Stromboli
The Battle of Stromboli, also known as the Second Battle of Stromboli or the Battle of Alicudi, took place on 8 January, 1676, during the Franco-Dutch War. The battle occurred between a French fleet of 20 ships under Abraham Duquesne and a combined fleet of 19 allied ships (18 Dutch and one Spanish ship) under Lieutenant-Admiral-General Michiel de Ruyter. It lasted eight hours and ended inconclusively. The fleets fought again several months later at the Battle of Augusta in April. Background At the end of the Franco-Spanish War, the Treaty of the Pyrenees in 1659 provided for Louis XIV to marry Maria Theresa, the eldest daughter of Philip IV of Spain, who was to bring a substantial dowry to Louis and who renounced her right to inherit the Spanish throne. The dowry was never paid. On the death of Philip IV in September 1665, his infant son Charles II of Spain the child of Philip's second wife Mariana of Austria was proclaimed king. Mariana's nearest male relative, the Emperor Leo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franco-Dutch War
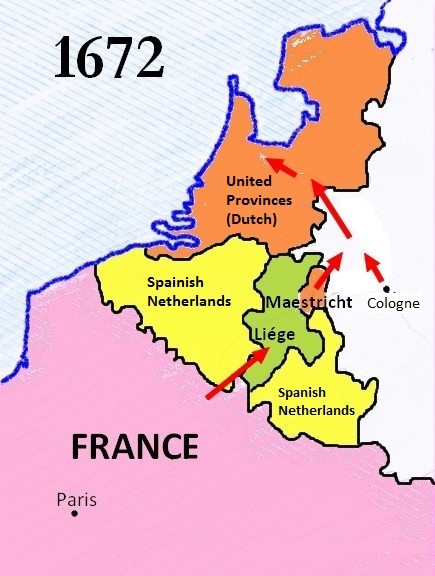
The Franco-Dutch War, also known as the Dutch War (french: Guerre de Hollande; nl, Hollandse Oorlog), was fought between France and the Dutch Republic, supported by its allies the Holy Roman Empire, Spain, Brandenburg-Prussia and Denmark-Norway. In its early stages, France was allied with Münster and Cologne, as well as England. The 1672 to 1674 Third Anglo-Dutch War and 1675 to 1679 Scanian War are considered related conflicts. The war began in May 1672 when France nearly overran the Dutch Republic, an event still known as the ''Rampjaar'' or "Disaster Year". Their advance was halted by the Dutch Water Line in June and by late July the Dutch position had stabilised. Concern over French gains led to a formal alliance in August 1673 between the Dutch, Emperor Leopold I, Spain and Brandenburg-Prussia. They were joined by Lorraine and Denmark, while England made peace in February 1674. Now facing a war on multiple fronts, the French withdrew from the Dutch Republic, retaining ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Anglo-Dutch War
The Second Anglo-Dutch War or the Second Dutch War (4 March 1665 – 31 July 1667; nl, Tweede Engelse Oorlog "Second English War") was a conflict between Kingdom of England, England and the Dutch Republic partly for control over the seas and trade routes, where England tried to end the Dutch domination of world trade during a period of intense European commercial rivalry, but also as a result of political tensions. After initial English successes, the war ended in a Dutch victory. It was the second of Anglo-Dutch Wars, a series of naval wars fought between the English and the Dutch in the 17th and 18th centuries. Background Anglo-Dutch relations Traditionally, many historians considered that the First Anglo-Dutch War, First and Second Anglo-Dutch Wars arose from commercial and maritime rivalry between England and the Netherlands. Although continuing commercial tensions formed the background to the second war, a group of ambitious English politicians and naval officers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strait Of Messina
The Strait of Messina ( it, Stretto di Messina, Sicilian: Strittu di Missina) is a narrow strait between the eastern tip of Sicily (Punta del Faro) and the western tip of Calabria ( Punta Pezzo) in Southern Italy. It connects the Tyrrhenian Sea to the north with the Ionian Sea to the south, within the central Mediterranean. At its narrowest point, between Torre Faro and Villa San Giovanni, it is wide. At the city of Messina, it is wide. The strait's maximum depth is about . The strait has strong tidal currents that create a unique marine ecosystem. A natural whirlpool in the northern portion of the strait has been linked to the Greek legend of Scylla and Charybdis. In some circumstances, the mirage of Fata Morgana can be observed when looking at Sicily from Calabria. With its bottleneck shape, it is also a compulsory point of transit in the migration of many bird species. In 1957, a 220 kV overhead power line was built across the Strait of Messina. Its pylons are amo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milazzo
Milazzo ( Sicilian: ''Milazzu''; la, Mylae; ) is a town (''comune'') in the Metropolitan City of Messina, Sicily, southern Italy; it is the largest commune in the Metropolitan City after Messina and Barcellona Pozzo di Gotto. The town has a population of around 31,500 inhabitants. History Several civilizations settled in Milazzo and left signs of their presence from the Neolithic age. In Homer's ''Odyssey'' Milazzo is presumably the place where Ulysses is shipwrecked and meets Polyphemus. Historically, the town originated as the ancient ''Mylae'' ( grc, Μύλαι), an outpost of Zancle, occupied before 648 BC, perhaps as early as 716 BC. It was taken by the Athenians in 426 BC. The people of Rhegium planted the exiles from Naxos and Catana in 395 BC as a counterpoise to Dionysius the Elder's foundation of Tyndaris; but Dionysius soon took it. In the bay Gaius Duilius won the first Roman naval victory over the Carthaginians (260 BC). In 36 BC the naval Battle of Mylae was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broadside (naval)
A broadside is the side of a ship, or more specifically the battery of cannon on one side of a warship or their coordinated fire in naval warfare, or a measurement of a warship's maximum simultaneous firepower which can be delivered upon a single target (because this concentration is usually obtained by firing a broadside). From the 16th century until the early decades of the steamship, vessels had rows of guns set in each side of the hull. Firing all guns on one side of the ship became known as a "broadside". The cannon of 18th-century men of war were accurate only at short range, and their penetrating power mediocre, which meant that the thick hulls of wooden ships could only be pierced at short ranges. These wooden ships sailed closer and closer towards each other until cannon fire would be effective. Each tried to be the first to fire a broadside, often giving one party a decisive headstart in the battle when it crippled the other ship.Platt (1993) p. 18 History Since anci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rear Admiral
Rear admiral is a senior naval flag officer rank, equivalent to a major general and air vice marshal and above that of a commodore and captain, but below that of a vice admiral. It is regarded as a two star "admiral" rank. It is often regarded as a two-star rank with a NATO code of OF-7. The term originated in the days of naval sailing squadrons and can trace its origins to the Royal Navy. Each naval squadron was assigned an admiral as its head, who commanded from the centre vessel and directed the squadron's activities. The admiral would in turn be assisted by a vice admiral, who commanded the lead ships that bore the brunt of a battle. In the rear of the squadron, a third admiral commanded the remaining ships and, as this section was considered to be in the least danger, the admiral in command of it was typically the most junior. This has continued into the modern age, with rear admiral the most junior admiralty of many navies. In most European navies, the equivalent rank i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chef D'escadre
''Chef d'escadre'' (; literally "squadron commander") was a rank in the French Navy during the Ancien Régime and until the French Revolution. The rank was changed to '' contre-amiral'' by a law passed on 15 May 1791. History The first chefs d'escadre were created by Louis XIII in 1627 - he had a "chef d'escadre of Normandy" commanding the port of Le Havre, a chef d'escadre of Brittany commanding Brest, and a chef d'escadre of Guyenne commanding Brouage. Each of these chefs d'escadres, as officiers d'épée, were flanked by a commissaire général, an officier de plume. Their numbers grew rapidly: in 1635 a chef d'escadre of Provence was created, then in 1647 a chef d'escadre for Flanders, in 1663 one for Poitou-Saintonge, in 1673 one for Picardy and one for Languedoc, in 1689 one for Aunis, in 1701 one for America, and in 1707 one for Roussillon. After 1715, there were more chefs d'escadre than there were coastal provinces, and so they started taking the title "chefs d'esc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jan Van Essen - Fleet Review Before Naples
Jan, JaN or JAN may refer to: Acronyms * Jackson, Mississippi (Amtrak station), US, Amtrak station code JAN * Jackson-Evers International Airport, Mississippi, US, IATA code * Jabhat al-Nusra (JaN), a Syrian militant group * Japanese Article Number, a barcode standard compatible with EAN * Japanese Accepted Name, a Japanese nonproprietary drug name * Job Accommodation Network, US, for people with disabilities * ''Joint Army-Navy'', US standards for electronic color codes, etc. * ''Journal of Advanced Nursing'' Personal name * Jan (name), male variant of ''John'', female shortened form of ''Janet'' and ''Janice'' * Jan (Persian name), Persian word meaning 'life', 'soul', 'dear'; also used as a name * Ran (surname), romanized from Mandarin as Jan in Wade–Giles * Ján, Slovak name Other uses * January, as an abbreviation for the first month of the year in the Gregorian calendar * Jan (cards), a term in some card games when a player loses without taking any tricks or scoring a mini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeolian Islands
The Aeolian Islands ( ; it, Isole Eolie ; scn, Ìsuli Eoli), sometimes referred to as the Lipari Islands or Lipari group ( , ) after their largest island, are a volcanic archipelago in the Tyrrhenian Sea north of Sicily, said to be named after Aeolus, the mythical ruler of the winds. The islands' inhabitants are known as Aeolians ( it, Eoliani, links=no). The islands had a permanent population of 14,224 at the 2011 census; the latest official estimate is 15,419 as of 1 January 2019. The Aeolian Islands are a popular tourist destination in the summer and attract up to 600,000 visitors annually. There are seven significant islands: Lipari, Vulcano, Salina, Stromboli, Filicudi, Alicudi and Panarea, and a set of minor islands and rocks. Geography The ''Lipari Islands'' are 30 km and 80 km off the north coast of Sicily in the Tyrrhenian Sea. Vulcano is located closest to the Sicilian coast. Lipari and Salina follow to the north, Filicudi and Alicudi to the west, and Pan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messina Revolt
The Messina revolt of 1672–78 began with a revolt against the patrician government of Messina on the island of Sicily by skilled workers in 1672. When the patricians regained control in 1674 they turned the movement into a revolt against Spanish rule. They obtained support from the French, and Messina was independent until the end of the Franco-Dutch War of 1672–78, when the Spanish regained control. Initial revolt The city of Messina had a population of 120,000 in the mid-17th century, with the city council dominated by a few patrician families. The Spanish government granted Messina a monopoly on the export of silk in 1663, but after loud protests from other ports of Sicily withdrew it the next year. There were no immediate disturbances, but the nobility and upper bourgeoisie of the city became hostile to the Spanish. The Spanish captain-general Luis de Hojo conceived the plan of turning the common people against the upper classes through a display of charity and devotion, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messina
Messina (, also , ) is a harbour city and the capital of the Italian Metropolitan City of Messina. It is the third largest city on the island of Sicily, and the 13th largest city in Italy, with a population of more than 219,000 inhabitants in the city proper and about 650,000 in the Metropolitan City. It is located near the northeast corner of Sicily, at the Strait of Messina and it is an important access terminal to Calabria region, Villa San Giovanni, Reggio Calabria on the mainland. According to Eurostat the FUA of the metropolitan area of Messina has, in 2014, 277,584 inhabitants. The city's main resources are its seaports (commercial and military shipyards), cruise tourism, commerce, and agriculture (wine production and cultivating lemons, oranges, mandarin oranges, and olives). The city has been a Roman Catholic Archdiocese and Archimandrite seat since 1548 and is home to a locally important international fair. The city has the University of Messina, founded in 1548 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_p280_Nr.11_-_LA_NOBILE_CITI_MESSINA.jpg)
