|
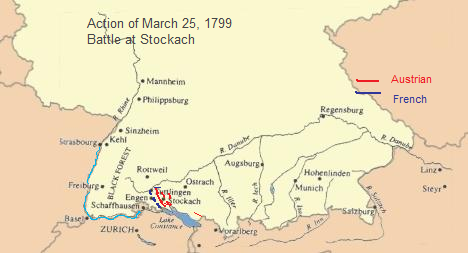
Battle Of Stockach (1799)
The Battle of Stockach occurred on 25 March 1799, when French and Austrian armies fought for control of the geographically strategic Hegau region in present-day Baden-Württemberg.There was a second battle the following year—see Second Battle of Stockach. Some older English sources refer to this as the Battle of Stochach and some French chronicles as Battle of Liptingen (or Leibtengen). In the broader military context, this battle constitutes a keystone in the first campaign in southwestern Germany during the Wars of the Second Coalition, part of the French Revolutionary Wars. It was the second battle between the French Army of the Danube, commanded by Jean-Baptiste Jourdan, and the Habsburg Army under Archduke Charles; the armies had met a few days earlier, 20–22 March, on the marshy fields southeast of Ostrach and the Pfullendorf heights. The Austrian Army's superior strength, almost three-to-one, forced the French to withdraw. At Stockach, the French concentrated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
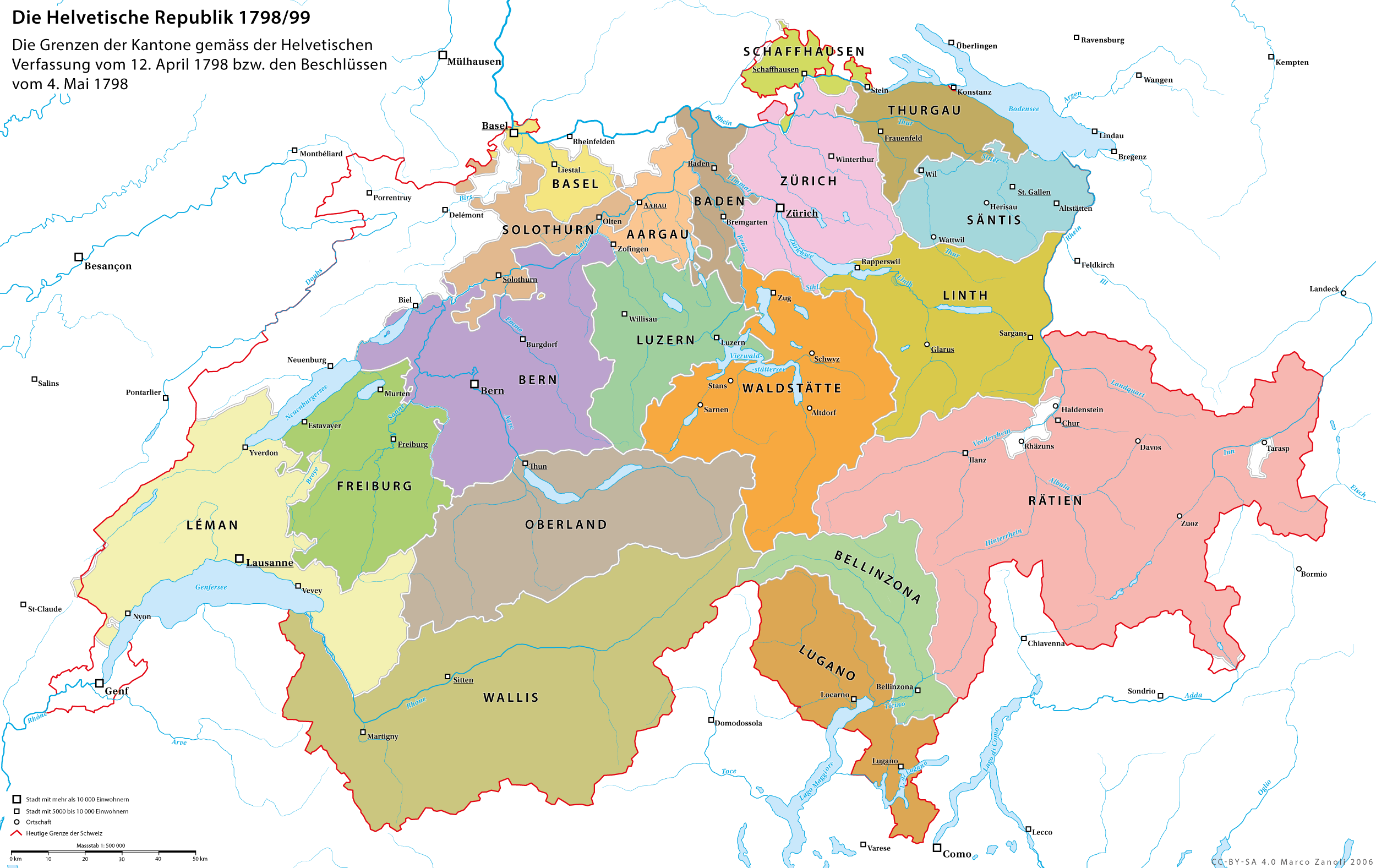
War Of The Second Coalition
The War of the Second Coalition (1798/9 – 1801/2, depending on periodisation) was the second war on revolutionary France by most of the European monarchies, led by Britain, Austria and Russia, and including the Ottoman Empire, Portugal, Naples and various German monarchies. Prussia did not join this coalition, and Spain supported France. The overall goal of Britain and Russia was to contain the expansion of the French Republic and restore the monarchy in France, whereas Austria, still weakened and in deep financial debt from the War of the First Coalition, primarily sought to recover its position and come out of the war stronger than it entered. Due in important part to this difference in strategy among the three major allied powers, the Second Coalition failed to overthrow the revolutionary regime, and French territorial gains since 1793 were confirmed. In the Franco–Austrian Treaty of Lunéville in February 1801, France held all its previous gains and obtained new land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Wiesloch (1799)
The Battle of Wiesloch (german: Schlacht bei Wiesloch) occurred on 3 December 1799, during the War of the Second Coalition, part of the French Revolutionary Wars. Lieutenant Field Marshal Anton Count Sztáray de Nagy-Mihaly Anton may refer to: People *Anton (given name), including a list of people with the given name *Anton (surname) Places *Anton Municipality, Bulgaria **Anton, Sofia Province, a village *Antón District, Panama **Antón, a town and capital of th ... commanded the far right wing protecting the main Austrian army in Swabia, under the command of Archduke Charles, Duke of Teschen. With the victory at Wiesloch (on 3 December), Sztáray's force drove the French from the right bank of the Rhine and relieved the fortress at Philippsburg. References External linksWiesloch [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Gotthard Pass
The Battle of Gotthard Pass or Battle of St. Gotthard Pass (24–26 September 1799) saw an Imperial Russian army commanded by Field Marshal Alexander Suvorov supported by two Austrian brigades attack a French division under General of Division Claude Lecourbe. The Austro-Russian army successfully captured the Gotthard Pass after stiff fighting on the first day. Suvorov's main body was assisted by a Russian flanking column led by Lieutenant General Andrei Rosenberg and a smaller Austrian flanking column under General-major Franz Xaver von Auffenberg. The next day, Suvorov's army fought its way north along the upper Reuss River valley past the ''Teufelsbrücke'' (Devil's Bridge) in Schöllenen Gorge. By 26 September the army reached Altdorf near Lake Lucerne. The term summarises a total of five battles or engagements between Airolo and Altdorf fought against the retreating French troops over the course of three days. The main engagement of 25 September is also known as the Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Mannheim (1799)
The Battle of Mannheim (18 September 1799) was fought between an Austrian army commanded by Archduke Charles, Duke of Teschen and a French army under Jacques Léonard Muller. Most of the French '' Army of the Rhine'' had retreated to the west bank of the Rhine River, leaving the division of Antoine Laroche Dubouscat to hold Mannheim on the east bank. Despite assistance by Michel Ney, Laroche's division was beaten and driven out of the city when attacked by Charles and a much superior force. The War of the Second Coalition action occurred in the city of Mannheim, located in the state of Baden-Württemberg in southwest Germany about south of Frankfurt. In the summer of 1799, Muller's 18,000-man army had the mission of drawing Charles' Austrian army away from Switzerland, the central and western portions of which were held by André Masséna's army. Moving south from Mannheim, the ''Army of the Rhine'' laid siege to Philippsburg. Provoked by this threat to his strategic rear, Char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Amsteg
The Battle of Amsteg (14–16 August 1799) saw a Republican French division under General of Division Claude Lecourbe face a brigade of Habsburg Austrian soldiers led by General-major Joseph Anton von Simbschen. Lecourbe's offensive began on 14 August when six columns of French infantry advanced on the upper Reuss valley from the north and east. By 16 August, Lecourbe's forces had driven Simbschen's Austrians from the valley and seized control of the strategic Gotthard Pass between Italy and Switzerland. On 4 June, the First Battle of Zurich was fought between André Masséna's French Army of Helvetia and an Austrian army led by Archduke Charles, Duke of Teschen. After the battle, Massena relinquished Zürich and retreated to a strong defensive position to the west of the city. At about the same time, the French commander ordered Lecourbe to abandon the Gotthard Pass and pull back to Lucerne. In August, Masséna had second thoughts and wanted Lecourbe to recapture the Gottha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Battle Of Zurich
The Second Battle of Zurich (25–26 September 1799) was a key victory by the Republican French army in Switzerland led by André Masséna over an Austrian and Russian force commanded by Alexander Korsakov near Zürich. It broke the stalemate that had resulted from the First Battle of Zurich three months earlier and led to the withdrawal of Russia from the Second Coalition. Most of the fighting took place on both banks of the river Limmat up to the gates of Zürich, and within the city itself. Background After the First Battle of Zurich Masséna had consolidated to a defensive line behind the lower reaches of the Aare River. At this time his entire army in Switzerland consisted of around 77,000 combatants, positioned as: * 1st Division ( Tharreau) in the Upper Valais and the Simplon Pass. * 2nd Division ( Lecourbe) in the St Gotthard and the valley of the Reuss. * 3rd Division ( Soult) Right wing near Glarus, centre on the left bank of the Linth, the left near Adlisw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Battle Of Zurich
The First Battle of Zurich, from 4 to 7 June 1799, forced French General André Masséna to yield the city of Zurich to the Austrians, under Archduke Charles, and to retreat beyond the Limmat, where he managed to fortify his positions, which resulted in a stalemate. The Helvetic Republic in 1798 became a battlefield of the French Revolutionary Wars. During the summer, Russian troops, under General Alexander Korsakov, replaced the Austrian troops, and at the Second Battle of Zurich, the French regained control of the city, along with the rest of Switzerland. Background Political and diplomatic situation Initially, the rulers of Europe viewed the revolution in France as an event between the French king and his subjects, and not something in which they should interfere. As revolutionary rhetoric grew more strident, they declared the interest of the monarchs of Europe as one with the interests of Louis and his family; this Declaration of Pillnitz threatened ambiguous, but q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Winterthur
The Battle of Winterthur (27 May 1799) was an important action between elements of the Army of the Danube and elements of the Habsburg army, commanded by Friedrich Freiherr von Hotze, during the War of the Second Coalition, part of the French Revolutionary Wars. The small town of Winterthur lies northeast of Zürich, in Switzerland. Because of its position at the junction of seven roads, the army that held the town controlled access to most of Switzerland and points crossing the Rhine into southern Germany. Although the forces involved were small, the ability of the Austrians to sustain their 11-hour assault on the French line resulted in the consolidation of three Austrian forces on the plateau north of Zürich, leading to the French defeat a few days later. By mid-May 1799, the Austrians had wrested control of parts of Switzerland from the French as forces under the command of Hotze and Count Heinrich von Bellegarde pushed them out of the Grisons. After defeating Jean-Bapt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Frauenfeld
The Battle of Frauenfeld was a military encounter during the War of the Second Coalition (1799-1802). It took place on 25 May 1799 between Austrian and French troops. The battle ended in the evening with the retreat of the Austrians, but on the following day the French withdrew. Background The Swiss Old Confederacy was occupied by the French Empire in 1798 and the French-supported Helvetic Republic was established on its territory. Thus, at the beginning of the War of the Second Coalition, French troops under General André Masséna (1758–1817) were operating on Swiss soil. After defeats in the Battle of Feldkirch and the Battle of Stockach, the French had to pull back and abandon eastern Switzerland. Two Austrian armies under General Friedrich von Hotze (1739–1799) and Archduke Charles (1771–1847) pursued them. They sought to unite these two armies as quickly as possible. On 22 May 1799, the vanguard of the Archduke's army reached Frauenfeld, where they stopped in or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Stockach (1800)
The Battles of Stockach and Engen were fought on 3 May 1800 between the army of the First French Republic under Jean Victor Marie Moreau and the army of the Habsburg monarchy led by Paul Kray. The fighting near Engen resulted in a stalemate. However, while the two main armies were engaged at Engen, Claude Lecourbe captured Stockach from its Austrian defenders (the latter commanded by Joseph, Prince of Lorraine-Vaudemont). The loss of his main supply base at Stockach compelled Kray to order a retreat. Stockach is located near the northwestern end of Lake Constance while Engen is west of Stockach. The action occurred during the War of the Second Coalition, part of the French Revolutionary Wars. Background ''See the Messkirch 1800 Order of Battle for details of the French and Austrian armies in the campaign.'' Plans At the beginning of 1800 the armies of France and the Habsburgs faced each other across the Rhine. Feldzeugmeister Paul Kray led approximately 120,000 troops. Besid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Feldkirch
The Battle of Feldkirch (23 March 1799) saw some French corps led by André Masséna attack a weaker Austrian force under Franz Jellacic. Defending fortified positions, the Austrians repulsed all of the French columns, though the struggle lasted until nightfall. This and other French setbacks in southern Germany soon caused Masséna to go on the defensive. The War of the Second Coalition combat occurred at the Austrian town of Feldkirch, Vorarlberg, located west of Innsbruck. On a flimsy pretext, a French army invaded Switzerland in January 1798 and forced the country into an uneasy alliance marked by occasional revolts. By the start of hostilities with Austria in early 1799, Masséna was in command of the '' Army of Helvetia''. Going on the offensive, the French inflicted defeats on the Austrians at Maienfeld, Chur and Feldkirch on 6 and 7 March. Ordered to attack Feldkirch in late March by his superior Jean-Baptiste Jourdan, Masséna attacked with troops under Nicolas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)