|
Battle Of Lerin
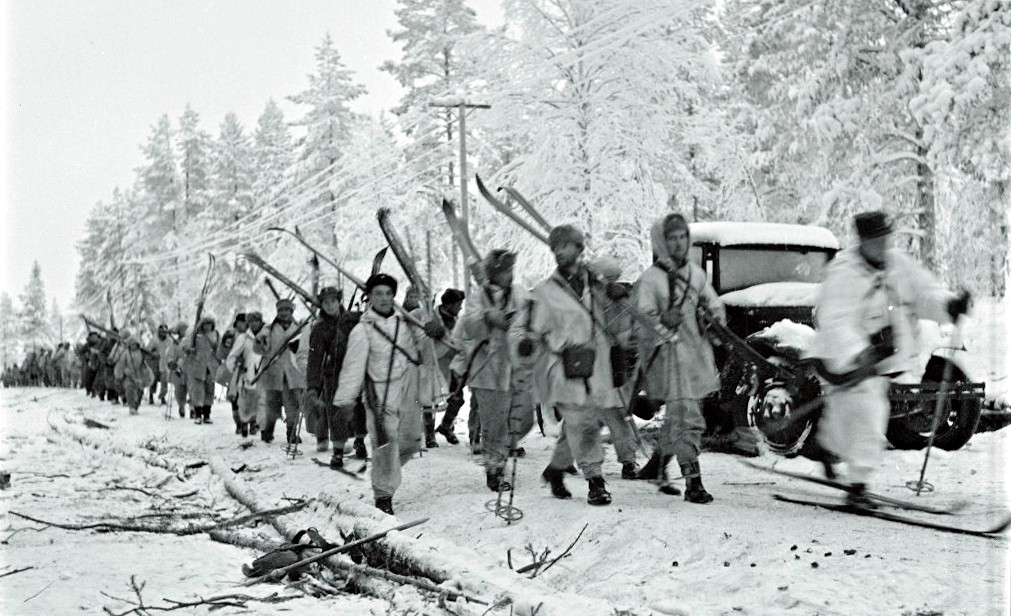
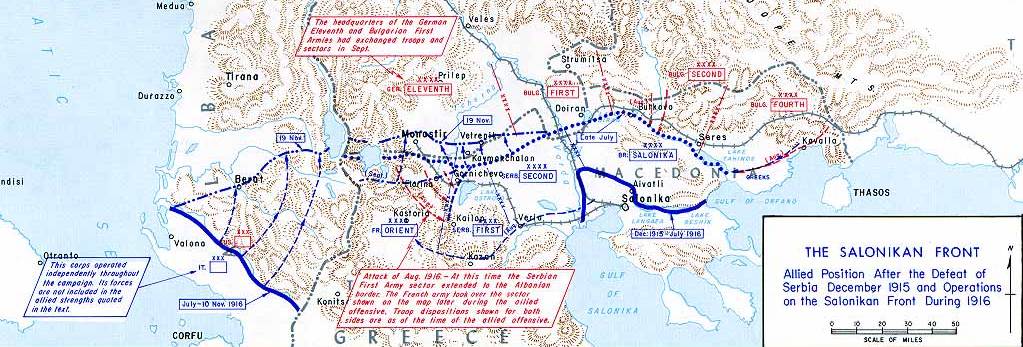
The Battle of Lerin or Battle of Florina or Chegan offensive was an offensive operation of the Bulgarian army during the First World War between 17–28 August 1916 in which they conquered the city of Florina (in present-day Greece but in Bulgaria known as ''Lerin''), but failed to take Chegan. Background In August 1916, Romania chose to join the war effort on the side of the Entente. The Allies planned a large offensive in the Macedonian front for the middle of August to support Romania's entry into the war and pin down as many Bulgarian forces as possible. The Bulgarian high command suspected an impending offensive, and the fighting around Doiran that erupted on 9 August only confirmed these suspicions. On their part, the Bulgarians had urged for an offensive in Macedonia since the beginning of the year, now planning a strike with the First Army and Second Army on both Allied flanks. The Struma operation on the eastern flank by the Bulgarian Second Army under general Tod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macedonian Front (World War I)
The Macedonian front, also known as the Salonica front (after Thessaloniki), was a military theatre of World War I formed as a result of an attempt by the Allied Powers to aid Serbia, in the autumn of 1915, against the combined attack of Germany, Austria-Hungary and Bulgaria. The expedition came too late and in insufficient force to prevent the fall of Serbia, and was complicated by the internal political crisis in Greece (the "National Schism"). Eventually, a stable front was established, running from the Albanian Adriatic coast to the Struma River, pitting a multinational Allied force against the Bulgarian Army, which was at various times bolstered with smaller units from the other Central Powers. The Macedonian front remained quite stable, despite local actions, until the great Allied offensive in September 1918, which resulted in the capitulation of Bulgaria and the liberation of Serbia. Background Following the assassination of the Crown Prince by a Bosnian Serb, Austria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vevi
Vevi ( el, Βεύη, before 1926: Μπάνιτσα - ''Banitsa'', before 1928: Μπάνιτσα - ''Banitsa''; Macedonian and bg, Баница, ''Banica'' or ''Banitsa'') is a village located in the municipal unit of Meliti in Florina regional unit, Macedonia, Greece. The village is passed by two national roads which lead to Thessaloniki, Florina, Amyntaio, and Kozani. Additionally, it has a railway station on the line between Florina and Thessaloniki. Economy It is mainly a farming community and is the site of the Achlada, the Vevi lignite mines from Upper Miocene. History The city dates back to Roman times. Archeological finds from this period, such as the marble torso of a male statue, are housed at the Archaeological Museum of Florina. The local church St. Nicolas was built and painted in 1460. There were 132 Christian households in the village in the first half of the 17th century. In 1845 the Russian slavist Victor Grigorovich recorded ''Banci'' as mainly Bulgarian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Involving France
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greece In World War I
At the outbreak of World War I in August 1914, the Kingdom of Greece remained neutral. Nonetheless, in October 1914, Greek forces once more occupied Northern Epirus, from where they had retreated after the end of the Balkan Wars. The disagreement between King Constantine, who favoured neutrality, and the pro-Allied Prime Minister Eleftherios Venizelos led to the National Schism, the division of the state between two rival governments. Finally, Greece united and joined the Allies in the summer of 1917. Background Greece had emerged victorious from the 1912–1913 Balkan Wars with her territory almost doubled, but found herself in a difficult international situation. The status of the Greek-occupied eastern Aegean islands was left undetermined and the Ottoman Empire continued to claim them, leading to a naval arms race and mass expulsions of ethnic Greeks from Anatolia. In the north, Bulgaria, defeated in the Second Balkan War, harbored plans for revenge against Greece a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbia In World War I
The Serbian campaign was a series of military expeditions launched in 1914 and 1915 by the Central Powers against the Kingdom of Serbia during the First World War. The first campaign began after Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia on 28 July 1914. The campaign to "punish" Serbia was under the command of Austrian Oskar Potiorek. It ended after three unsuccessful Austro-Hungarian invasion attempts were repelled by the Serbians and their Montenegrin allies. The victory of the Serbian Army at the battle of Cer is considered the first Allied victory in World War I, while the defeat of the Austro-Hungarian Army by Serbia has been called one of the great upsets of modern military history. The second campaign was launched, under German command, almost a year later, on 6 October 1915, when Bulgarian, Austro-Hungarian, and German forces, led by Field Marshal August von Mackensen, successfully invaded Serbia from three sides, pre-empting an Allied advance from Salonica to help S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Of World War I Involving Serbia
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Of World War I Involving Bulgaria
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Of The Balkans Theatre (World War I)
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monastir Offensive
Monastir offensive was an Allied military operation against the forces of the Central Powers during World War I, intended to break the deadlock on the Macedonian front by forcing the capitulation of Bulgaria and relieving the pressure on Romania. The offensive took the shape of a large battle and lasted for three months and ended with the capture of the town of Monastir. On an average depth of 50 kilometers, the Bulgarian First Army (from the end of September German Eleventh Army) gave battle on six occasions and was forced to retreat five times. Background In August 1916 Romania chose to join the war effort on the side of the Entente and concentrated most of its forces for an invasion of Transylvania, leaving its 3rd Army to guard the border with Bulgaria. The Russian and French proposals for a joint attack of the Romanian Army and the Allied Salonika Army against Bulgaria were no longer realistic. The Allies, however, still planned a large offensive in the Macedonian front fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maurice Sarrail
Maurice Paul Emmanuel Sarrail (6 April 1856 – 23 March 1929) was a French general of the First World War. Sarrail's openly socialist political connections made him a rarity amongst the Catholics, conservatism, conservatives and monarchism, monarchists who dominated the French Army officer corps under the French Third Republic, Third Republic before the war, and were the main reason why he was appointed to command at Salonika. At the start of the war, Sarrail commanded VI Corps then Third Army in the Ardennes and around Verdun, where his army played an important role in the final stages of the First Battle of the Marne and where he took the credit for holding Verdun (later the site of an Battle of Verdun, important battle in 1916). He was dismissed for poor leadership, amidst political uproar, in July 1915. The Salonika campaign – chosen out of several strategic options presented by Sarrail – was intended originally to support Serbia, with Bulgaria entering the war on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vegoritida
Vegoritida ( el, Βεγορίτιδα) is a former municipality in the Pella regional unit, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Edessa, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 289.987 km2. Population 3,635 (2011). The seat of the municipality was in Arnissa. The municipality was named after the Lake Vegoritida Lake Vegoritida ( el, Λίμνη Βεγορίτιδα, ''Limni Vegoritida''), also known in the past as Lake Ostrovo ( el, Λίμνη Οστρόβου, ''Limni Ostrovou''), is a large natural lake in western Macedonia, northern Greece. It is situa ..., and is situated on the northeastern shore of this lake. References Populated places in Pella (regional unit) Edessa, Greece {{CentralMacedonia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allies Of World War I
The Allies of World War I, Entente Powers, or Allied Powers were a coalition of countries led by France, the United Kingdom, Russia, Italy, Japan, and the United States against the Central Powers of Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, Bulgaria, and their colonies during the First World War (1914–1918). By the end of the first decade of the 20th century, the major European powers were divided between the Triple Entente and the Triple Alliance. The Triple Entente was made up of France, Britain, and Russia. The Triple Alliance was originally composed of Germany, Austria–Hungary, and Italy, but Italy remained neutral in 1914. As the war progressed, each coalition added new members. Japan joined the Entente in 1914 and after proclaiming its neutrality at the beginning of the war, Italy also joined the Entente in 1915. The term "Allies" became more widely used than "Entente", although France, Britain, Russia, and Italy were also referred to as the Quadruple Entente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


