|
Battle Of Cuautla (1911)
The Battle of Cuautla was a battle between the forces of Emiliano Zapata and the federal army of the Mexican government that took place in the state of Morelos from May 11–19, 1911, during the Mexican Revolution. It has sometimes been described as "six of the most terrible days of battle in the whole Revolution".. Eventually, the remains of the defending "Golden Fifth" regiment, the Fifth Cavalry Regiment of the Federal Army, withdrew and Zapata took control of the town. The ''Zapatista'' victory convinced Porfirio Díaz to come to terms with Francisco Madero, agree to the Treaty of Ciudad Juárez and resign as president. While the Zapatistas enjoyed numerical supremacy, the federal troops held strong defensive positions, were better armed and trained, and unlike the rebels, had artillery with them.. Political background In late 1910 and early 1911 armed insurrections against the regime of Porfirio Díaz broke out throughout Mexico. The two main centers of opposition were loca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexican Revolution
The Mexican Revolution ( es, Revolución Mexicana) was an extended sequence of armed regional conflicts in Mexico from approximately 1910 to 1920. It has been called "the defining event of modern Mexican history". It resulted in the destruction of the Federal Army and its replacement by a revolutionary army, and the transformation of Mexican culture and Federal government of Mexico, government. The northern Constitutionalists in the Mexican Revolution, Constitutionalist faction prevailed on the battlefield and drafted the present-day Constitution of Mexico, which aimed to create a strong central government. Revolutionary generals held power from 1920 to 1940. The revolutionary conflict was primarily a civil war, but foreign powers, having important economic and strategic interests in Mexico, figured in the outcome of Mexico's power struggles. The United States involvement in the Mexican Revolution, United States played an especially significant role. Although the decades-long r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambrosio Figueroa
Ambrosio may refer to: People *Alessandra Ambrosio (born 1981), a Brazilian model *Arturo Ambrosio (1870–1960), an Italian film producer *Fabrisia Ambrosio, Brazilian-born physical therapist and academic *Franco Ambrosio (1932–2009), an Italian businessman *Giovanni Ambrosio (1420–1484), Italian dancer and writer on dance (Guglielmo Ebreo da Pesaro) *Luigi Ambrosio (born 1963), an Italian mathematician *Thomas Ambrosio (born 1971), American political scientist *Vittorio Ambrosio (1879–1958), an Italian general from World War I and World War II Other * Ambrosio (horse), a racehorse * Ambrosio Film, an Italian film production company that existed from 1906 to 1924 See also *D'Ambrosio D'Ambrosio or d'Ambrosio is an Italian surname. It also may refer to: * Alfredo D'Ambrosio (1871–1914), Italian violinist and composer * Antonino D'Ambrosio (born 1971), Italian-American author, filmmaker, producer, and visual artist * Brian An ... * Ambrosiano (other) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuernavaca
Cuernavaca (; nci-IPA, Cuauhnāhuac, kʷawˈnaːwak "near the woods", ) is the capital and largest city of the state of Morelos in Mexico. The city is located around a 90-minute drive south of Mexico City using the Federal Highway 95D. The name ''Cuernavaca'' is a euphonism derived from the Nahuatl toponym and means 'surrounded by or close to trees'. The name was Hispanicized to ''Cuernavaca''; Hernán Cortés called it ''Coadnabaced'' in his letters to Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, and Bernal Díaz del Castillo used the name ''Cuautlavaca'' in his chronicles. The coat-of-arms of the municipality is based on the pre-Columbian pictograph emblem of the city which depicts a tree trunk () with three branches, with foliage, and four roots colored red. There is a cut in the trunk in the form of a mouth, from which emerges a speech scroll, probably representing the language Nahuatl and by extension the locative suffix , meaning 'near'. Cuernavaca has long been a favorite escape fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
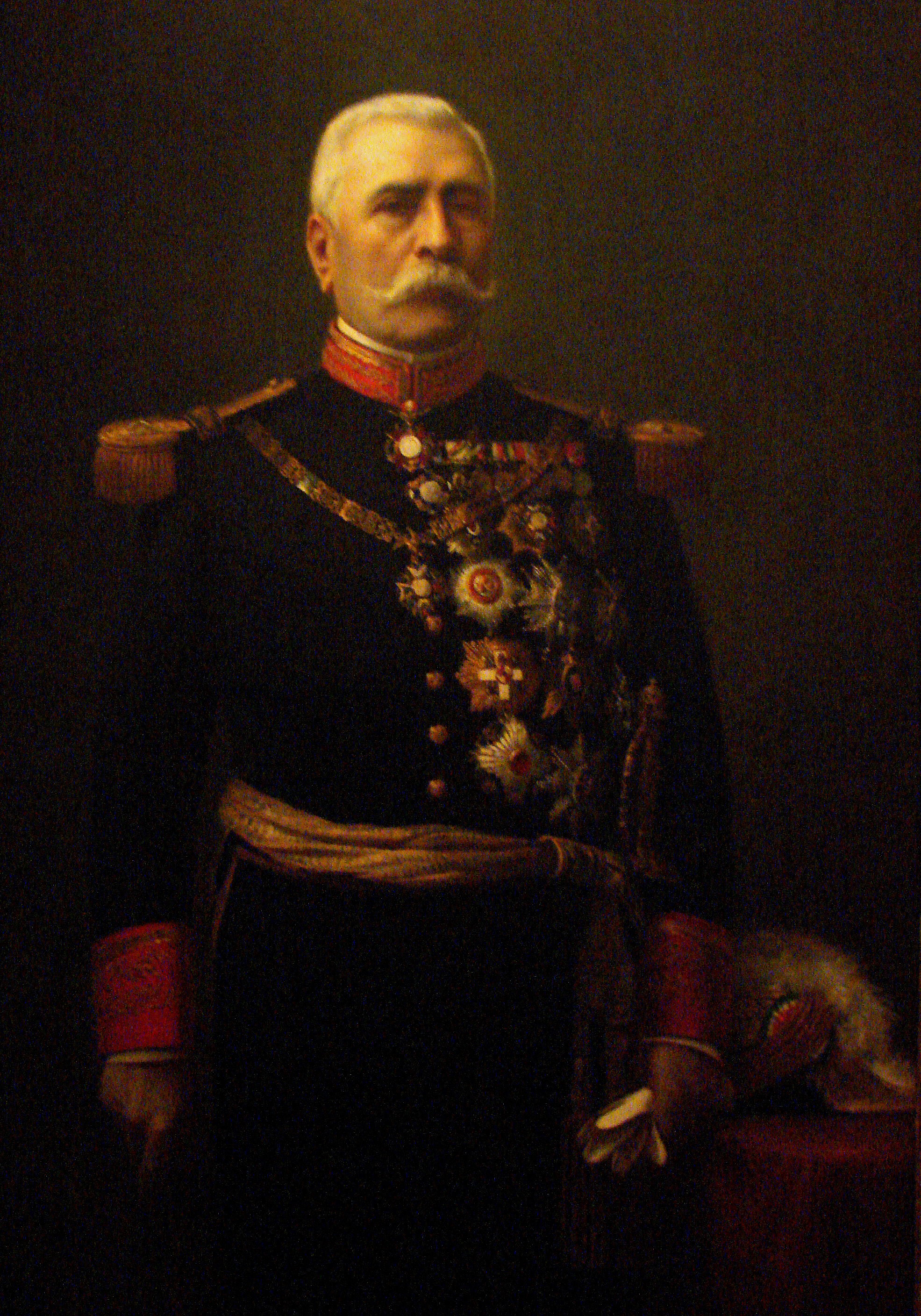
Victoriano Huerta
José Victoriano Huerta Márquez (; 22 December 1854 – 13 January 1916) was a general in the Mexican Federal Army and 39th President of Mexico, who came to power by coup against the democratically elected government of Francisco I. Madero with the aid of other Mexican generals and the U.S. Ambassador to Mexico. His violent seizure of power set off a new wave of armed conflict in the Mexican Revolution. After a military career under President Porfirio Díaz and Interim President Francisco León de la Barra, Huerta became a high-ranking officer during the presidency of Madero during the first phase of the Mexican Revolution (1911–13). In February 1913 Huerta joined a conspiracy against Madero, who entrusted him to control a revolt in Mexico City. The Ten Tragic Days – actually fifteen days – saw the forced resignation of Madero and his vice president and their murders. The coup was backed by the nascent German Empire as well as the United States under the Taft administrati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Gun
A machine gun is a fully automatic, rifled autoloading firearm designed for sustained direct fire with rifle cartridges. Other automatic firearms such as automatic shotguns and automatic rifles (including assault rifles and battle rifles) are typically designed more for firing short bursts rather than continuous firepower, and are not considered true machine guns. As a class of military kinetic projectile weapon, machine guns are designed to be mainly used as infantry support weapons and generally used when attached to a bipod or tripod, a fixed mount or a heavy weapons platform for stability against recoils. Many machine guns also use belt feeding and open bolt operation, features not normally found on other infantry firearms. Machine guns can be further categorized as light machine guns, medium machine guns, heavy machine guns, general purpose machine guns and squad automatic weapons. Similar automatic firearms of caliber or more are classified as autocannons, rat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bunker
A bunker is a defensive military fortification designed to protect people and valued materials from falling bombs, artillery, or other attacks. Bunkers are almost always underground, in contrast to blockhouses which are mostly above ground. They were used extensively in World War I, World War II, and the Cold War for weapons facilities, command and control centers, and storage facilities. Bunkers can also be used as protection from tornadoes. Trench bunkers are small concrete structures, partly dug into the ground. Many artillery installations, especially for coastal artillery, have historically been protected by extensive bunker systems. Typical industrial bunkers include mining sites, food storage areas, dumps for materials, data storage, and sometimes living quarters. When a house is purpose-built with a bunker, the normal location is a reinforced below-ground bathroom with fiber-reinforced plastic shells. Bunkers deflect the blast wave from nearby explosions to prevent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aqueduct (water Supply)
An aqueduct is a watercourse constructed to carry water from a source to a distribution point far away. In modern engineering, the term ''aqueduct'' is used for any system of pipes, ditches, canals, tunnels, and other structures used for this purpose. The term ''aqueduct'' also often refers specifically to a bridge carrying an artificial watercourse. Aqueducts were used in ancient Greece, ancient Egypt, and ancient Rome. The simplest aqueducts are small ditches cut into the earth. Much larger channels may be used in modern aqueducts. Aqueducts sometimes run for some or all of their path through tunnels constructed underground. Modern aqueducts may also use pipelines. Historically, agricultural societies have constructed aqueducts to irrigate crops and supply large cities with drinking water. Etymology The word ''aqueduct'' is derived from the Latin words (''water'') and (''led'' or ''guided''). Ancient aqueducts Although particularly associated with the Romans, aqueducts we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jonacatepec
Jonacatepec de Leondro Valle is a city in the Mexican state of Morelos. The city serves as the municipal seat for the surrounding municipality of the same name. The municipality reported 15,690 inhabitants in the year 2015 census. The name ''Jonacatepec'' comes from Nahuatl language and was written ''Xonakatepek ''. Its etymological roots come from ''Xonaka-tl'' (onion), ''Tepe-tl'' (hill), ''k apócope'' from the adverb ''ko'' (place) and means "on the hill where there are onions". Leondro Valle is in reference to a supporter of the Plan de Ayutla of 1857 which opposed the dictatorship of Antonio López de Santa Anna. Leondro Valle was from the town of Jonacatepec. Jonacatepec has 98 km2 (38 sq. miles), which represents 1.97% of the total area of the state. It is 1,290 meters (3,967 feet) above sea level. History Prehispanic Era During the Prehispanic era, the first settlers of Morelos were the Olmec (1500-900 BCE), subject to Chalcatzingo who flourished in the Archaic pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yautepec De Zaragoza
Yautepec is a municipality located in the north-central part of the Mexican state of Morelos. The municipal seat is the city of Yautepec de Zaragoza. It stands at . The city serves as the municipal seat for the surrounding municipality of Yautepec. In the 2020 census the municipality had a population of 105,780, the fifth-largest community in the state in population (after Cuernavaca, Jiutepec, Cuautla, and Temixco). The municipality, which has an area of 203 km² (78.4 sq mi) reported 102,690 inhabitants in the 2015 census. Yautepec de Zaragoza had 44,353 inhabitants in 2020. Other large towns in the municipality are La Joya (population 14,126), Cocoyoc (population 10,178), Oaxtepec (population 7,097), Los Arcos (San Carlos) (population 5,736), Oacalco (population 2,543), Lázaro Cárdenas (El Empalme) (population 1,503), Itzamatitlán (population 1,366), Corral Grande (population 1,189), San Isidro (population 1,153), Ignacio Bastida (Santa Catarina Tlayca) (population 1, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlixco
Atlixco () is a city and a municipality in the Mexican state of Puebla. It is a regional industrial and commercial center but economically it is much better known for its production of ornamental plants and cut flowers. The city was founded early in the colonial period, originally under the jurisdiction of Huejotzingo, but eventually separated to become an independent municipality. The municipality has a number of notable cultural events, the most important of which is the ''El Huey Atlixcayotl'', a modern adaptation of an old indigenous celebration. This event brings anywhere from 800 to 1,500 participants from all over the state of Puebla to create music, dance, and other cultural and artistic performances. Atlixco joined the UNESCO Global Network of Learning Cities in 2018. History The name "Atlixco" comes from a Nahuatl phrase which can be interpreted as either "water in the valley" or "water on the ground." Its main economic activity has earned the city the suffix of "de las f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metepec, State Of Mexico
Metepec () is a municipality in the State of Mexico in Mexico and is located directly to the east of the state capital, Toluca, at an altitude of above sea level. The center of Mexico City lies some 50 km further to the east. The city of Metepec also form part of the Greater Toluca. The name Metepec comes from Náhuatl meaning ''hill of the agave plants''. However, it is also known in the Matlatzinca language as "Nepinta-Tuhi" meaning 'people of corn land' and in the Otomi language as "Ntaguada". The city The city center lies at the foot of the hill that gives the city and municipality its name. There has been a community here since the Otomis and Matlatzincas settled in this part of the Valley of Toluca: the Matlatzincas reached their cultural peak between AD 1120 and 1450 as part of the Teotihuacan culture. The Aztecs conquered this community, along with the rest of the area by AD 1470 by the tlatoani (chief) named Axáyacatl. The Spanish arrived here in AD 1526 obli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |