|
Battle Of Campo Tenese
The Battle of Campo Tenese (9 March 1806) saw two divisions of the First French Empire, Imperial French Army of Naples led by Jean Reynier attack the left wing of the Royal Neapolitan Army under Roger de Damas. Though the defenders were protected by field fortifications, a French frontal attack combined with a turning movement rapidly overran the position and routed the Neapolitans with heavy losses. The action occurred at Campotenese, a little mountain village in the municipality of Morano Calabro in the north of Calabria. The battle was fought during the War of the Third Coalition, part of the Napoleonic Wars. Following the decision by King Ferdinand I of the Two Sicilies, Ferdinand IV of Naples to ally himself with the Austrian Empire, Russian Empire, and United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and Napoleon's decisive victory over the Allies at the Battle of Austerlitz, Napoleon declared Bourbon rule of southern Italy at an end. In the second week of February 1806 the Imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Third Coalition
The War of the Third Coalition) * In French historiography, it is known as the Austrian campaign of 1805 (french: Campagne d'Autriche de 1805) or the German campaign of 1805 (french: Campagne d'Allemagne de 1805) was a European conflict spanning the years 1805 to 1806. During the war, France and its client states under Napoleon I opposed an alliance, the Third Coalition, made up of the United Kingdom, the Holy Roman Empire, the Russian Empire, Naples, Sicily and Sweden. Prussia remained neutral during the war. Britain had already been at war with France following the breakdown of the Peace of Amiens and remained the only country still at war with France after the Treaty of Pressburg. From 1803 to 1805, Britain stood under constant threat of a French invasion. The Royal Navy, however, secured mastery of the seas and decisively destroyed a Franco-Spanish fleet at the Battle of Trafalgar in October 1805. The Third Coalition itself came to full fruition in 1804–05 as Napole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Italy
Southern Italy ( it, Sud Italia or ) also known as ''Meridione'' or ''Mezzogiorno'' (), is a macroregion of the Italian Republic consisting of its southern half. The term ''Mezzogiorno'' today refers to regions that are associated with the people, lands or culture of the historical and cultural region that was once politically under the administration of the former Kingdoms of Naples and Sicily (officially denominated as one entity ''Regnum Siciliae citra Pharum'' and ''ultra Pharum'', i.e. "Kingdom of Sicily on the other side of the Strait" and "across the Strait") and which later shared a common organization into Italy's largest pre-unitarian state, the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies. The island of Sardinia, which had neither been part of said region nor of the aforementioned polity and had been under the rule of the Alpine House of Savoy that would eventually annex the Bourbon-led and Southern Italian Kingdom altogether, is nonetheless often subsumed into the ''Mezzogiorno'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lieutenant General
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a three-star military rank (NATO code OF-8) used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in-command on the battlefield, who was normally subordinate to a captain general. In modern armies, lieutenant general normally ranks immediately below general and above major general; it is equivalent to the navy rank of vice admiral, and in air forces with a separate rank structure, it is equivalent to air marshal. A lieutenant general commands an army corps, made up of typically three army divisions, and consisting of around 60 000 to 70 000 soldiers (U.S.). The seeming incongruity that a lieutenant general outranks a major general (whereas a major outranks a lieutenant) is due to the derivation of major general from sergeant major general, which was a rank subordinate to lieutenant general (as a lieutenant outranks a sergeant major). In contrast, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maria Carolina Of Austria
Maria Carolina Louise Josepha Johanna Antonia (13 August 1752 – 8 September 1814) was List of consorts of Naples, Queen of Naples and List of Sicilian consorts, Sicily as the wife of King Ferdinand I of the Two Sicilies. As ''de facto'' ruler of her husband's kingdoms, Maria Carolina oversaw the promulgation of many reforms, including the revocation of the ban on Freemasonry, the enlargement of the navy under her favorite, Sir John Acton, 6th Baronet, Sir John Acton and the expulsion of Spanish influence. She was a proponent of enlightened absolutism until the advent of the French Revolution, when, in order to prevent its ideas gaining currency, she made Naples a police state. Born an archduchess of Austria, the thirteenth child of Empress Maria Theresa and Francis I, Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor Francis I, Maria Carolina married Ferdinand as part of an Austrian alliance with Spain, of which Charles III of Spain, Ferdinand's father was king. Following the birth of a male heir in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archduke Charles, Duke Of Teschen
Archduke Charles Louis John Joseph Laurentius of Austria, Duke of Teschen (german: link=no, Erzherzog Karl Ludwig Johann Josef Lorenz von Österreich, Herzog von Teschen; 5 September 177130 April 1847) was an Austrian field-marshal, the third son of Emperor Leopold II and his wife, Maria Luisa of Spain. He was also the younger brother of Francis II, Holy Roman Emperor. Despite being epileptic, Charles achieved respect both as a commander and as a reformer of the Austrian army. He was considered one of Napoleon's more formidable opponents and one of the greatest generals of the French Revolutionary Wars. He began his career fighting the revolutionary armies of France. Early in the wars of the First Coalition, he saw victory at Neerwinden in 1793, before being defeated at Wattignies 1793 and Fleurus 1794. In 1796, as chief of all Austrian forces on the Rhine, Charles defeated Jean-Baptiste Jourdan at Amberg, Würzburg and Limburg, and then won victories at Wetzlar, Emmendingen a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Italy (Napoleonic)
The Kingdom of Italy (1805–1814; it, Regno d'Italia; french: Royaume d'Italie) was a kingdom in Northern Italy (formerly the Italian Republic) in personal union with Napoleon I's French Empire. It was fully influenced by revolutionary France and ended with Napoleon's defeat and fall. Its government was assumed by Napoleon as King of Italy and the viceroyalty delegated to his stepson Eugène de Beauharnais. It covered some of Piedmont and the modern regions of Lombardy, Veneto, Emilia-Romagna, Friuli Venezia Giulia, Trentino, South Tyrol, and Marche. Napoleon I also ruled the rest of northern and central Italy in the form of Nice, Aosta, Piedmont, Liguria, Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio, but directly as part of the French Empire, rather than as part of a vassal state. Constitutional statutes The Kingdom of Italy was born on 17 March 1805, when the Italian Republic, whose president was Napoleon Bonaparte, became the Kingdom of Italy, with the same man (now styled Napoleon I) as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laurent Gouvion Saint-Cyr
Laurent de Gouvion Saint-Cyr, 1st Marquis of Gouvion-Saint-Cyr (; 13 April 1764 – 17 March 1830) was a French military commander in the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars who rose to the rank of Marshal of the Empire. He is regarded as Napoleon's finest commander in defensive warfare. Early life He was born Laurent Gouvion in Toul, Three Bishoprics (now Meurthe-et-Moselle), the eldest child of Jean-Baptiste Gouvion, a tanner, and his wife Anne-Marie Mercier. He adopted the name Saint-Cyr after his mother, who had abandoned him at an early age. He went to Rome when he was eighteen in order to study painting, but, although he continued his artistic studies after his return to Paris in 1784, he never adopted the profession of a painter. He married Anne Gouvion (Toul, 2 November 1775 - Paris, 18 June 1844) and had issue, including Laurent François, Marquis de Gouvion Saint-Cyr (30 December 1815 - 30 January 1904), married in Saint-Bouize on 17 August 1847 to Marie Ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Of Division
Divisional general is a general officer rank who commands an army division. The rank originates from the French (Revolutionary) System, and is used by a number of countries. The rank is above a brigade general, and normally below an army corps general. The rank is mostly used in countries where it is used as a modern alternative to a previous older rank of major-general or lieutenant-general. Specific countries Brazil The Brazilian rank ''general-de-divisão'' translates literally as "general of division", and is used by the army. This rank is equivalent to lieutenant-general. The air force equivalent is ''major-brigadeiro''(literally "major-brigadier"). The navy equivalent is ''vice-almirante'' (literally, vice-admiral) Chile The Chilean rank ''general de división'' translates literally as "general of division", and is used by the army. This rank is equivalent to lieutenant-general. The air force equivalent is ''general de aviación'' (literally "aviation general"). Thes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
André Masséna
André Masséna, Prince of Essling, Duke of Rivoli (born Andrea Massena; 6 May 1758 – 4 April 1817) was a French military commander during the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars.Donald D. Horward, ed., trans, annotated, The French Campaign in Portugal, An Account by Jean Jacques Pelet, 1810-1811 (Minneapolis, MN, 1973), 501. He was one of the original 18 Marshals of the Empire created by Napoleon I, with the nickname (the Dear Child of Victory). Many of Napoleon's generals were trained at the finest French and European military academies, however Masséna was among those who achieved greatness without the benefit of formal education. While those of noble rank acquired their education and promotions as a matter of privilege, Masséna rose from humble origins to such prominence that Napoleon referred to him as "the greatest name of my military empire". His military career is equaled by few commanders in European history. In addition to his battlefield successes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marshal Of France
Marshal of France (french: Maréchal de France, plural ') is a French military distinction, rather than a military rank, that is awarded to generals for exceptional achievements. The title has been awarded since 1185, though briefly abolished (1793–1804) and for a period dormant (1870–1916). It was one of the Great Officers of the Crown of France during the and Bourbon Restoration, and one of the Grand Dignitaries of the Empire during the First French Empire (when the title was Marshal of the Empire, not Marshal of France). A Marshal of France displays seven stars on each shoulder strap. A marshal also receives a baton: a blue cylinder with stars, formerly fleurs-de-lis during the monarchy and eagles during the First French Empire. The baton bears the Latin inscription of ', which means "terror in war, ornament in peace". Between the end of the 16th century and the middle of the 19th century, six Marshals of France were given the even more exalted rank of Marshal General ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Maida
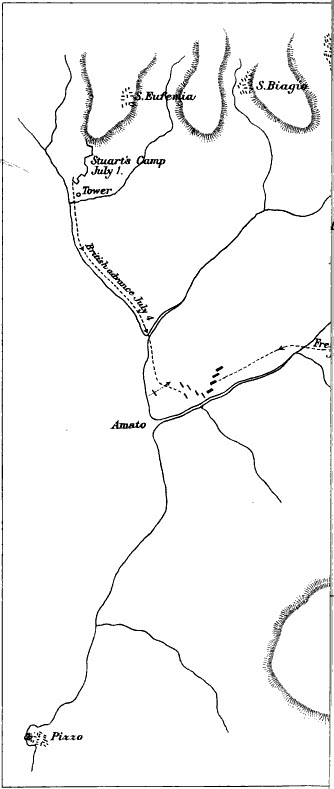
The Battle of Maida, fought on 4 July 1806 was a battle between the British expeditionary force and a French force outside the town of Maida in Calabria, Italy during the Napoleonic Wars. John Stuart led 5,236 Anglo-Sicilian troops to victory over about 5,400 Franco-Italian-Polish troops under the command of French general Jean Reynier, inflicting significant losses while incurring relatively few casualties. Maida is located in the toe of Italy, about west of Catanzaro. In early 1806, the French invaded and overran the Kingdom of Naples, forcing King Ferdinand I of the Two Sicilies and his government to flee to Sicily. The Calabrians revolted against their new conquerors and Stuart's expeditionary force tried to exploit the unrest by raiding the coast. While ashore, the British encountered Reynier's division and the two sides engaged in battle. The 19th-century historians presented the action as a typical fight between French columns and British lines. This view of the battle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Gaeta (1806)
The siege of Gaeta (26 February – 18 July 1806) saw the fortress city of Gaeta and its Neapolitan garrison under Louis of Hesse-Philippsthal besieged by an Imperial French corps led by André Masséna. After a prolonged defense in which Hesse was badly wounded, Gaeta surrendered and its garrison was granted generous terms by Masséna. The 1806 Invasion of Naples by Napoleon's forces was provoked when King Ferdinand I of Naples and Sicily joined the Third Coalition against Imperial France. The Kingdom of Naples was rapidly overrun by Imperial soldiers, but Hesse stubbornly held out at Gaeta. The garrison put up such fierce resistance that a large part of Masséna's ''Army of Naples'' was tied up in the siege for nearly five months. This prevented Masséna from sending reinforcements to quell an uprising that had started in Calabria as well as allowing the British to land an expeditionary force and score a victory at the Battle of Maida. However, because the British failed t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
.jpg)