|
Battle Of Bryansk (1941)
The Battle of Bryansk (2–21 October 1941) was a twenty-day battle during World War II conducted in the Bryansk Oblast as a part of the overall Moscow campaign. Returning from the Kiev operation, Heinz Guderian attacked in an unexpected direction capturing Bryansk and Oryol with few casualties thereby encircling two Soviet formations, the 13th Army and 3rd Army. A third Soviet formation, the 50th Army was encircled by infantry of the German 2nd Army north of Bryansk. However the encircled Red Army units continued fighting, delaying the drive on Moscow for two weeks. This delay, as well as the casualties taken by the Wehrmacht liquidating the pockets contributed to the German collapse at the gates of Moscow. See also: Vyazma and Bryansk pockets. As a result of this battle, the Germans occupied Bryansk until they were expelled by the Red Army on 17 September 1943 as a part of the Smolensk campaign. Background and planning After the successful encirclement of the reconst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Front (World War II)
The Eastern Front of World War II was a Theater (warfare), theatre of conflict between the European Axis powers against the Soviet Union (USSR), Polish Armed Forces in the East, Poland and other Allies of World War II, Allies, which encompassed Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Northern Europe, Northeast Europe (Baltic states, Baltics), and Southeast Europe (Balkans) from 22 June 1941 to 9 May 1945. It was known as the Great Patriotic War (term), Great Patriotic War in the Soviet Union – and still is in some of its successor states, while almost everywhere else it has been called the ''Eastern Front''. In present-day German and Ukrainian historiography the name German-Soviet War is typically used. The battles on the Eastern Front of the Second World War constituted the largest military confrontation in history. They were characterised by unprecedented ferocity and brutality, wholesale destruction, mass deportations, and immense loss of life due to combat, starvation, expos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bryansk Oblast
Bryansk Oblast (russian: Бря́нская о́бласть, ''Bryanskaya oblast''), also known as Bryanshchina (russian: Брянщина, ) is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is the types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Bryansk. As of the Russian Census (2021), 2021 Census, its population was 1,169,161. Geography Bryansk Oblast lies in western European Russia in the central to western parts of the East European Plain, on the divide between the Desna River, Desna and Volga River, Volga drainage basin, basins. The oblast borders with Smolensk Oblast in the north, Kaluga Oblast in the northeast, Oryol Oblast in the east, Kursk Oblast in the southeast, Chernihiv Oblast, Chernihiv and Sumy Oblasts of Ukraine in the south, and with Gomel Region, Gomel and Mogilev Region, Mogilev Oblasts of Belarus in the west. The relief is a typical East European Plain landscape, with alternating rolling hills and shallo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3rd Panzer Army
The 3rd Panzer Army (german: 3. Panzerarmee) was a German armoured formation during World War II, formed from the 3rd Panzer Group on 1 January 1942. 3rd Panzer Group The 3rd Panzer Group (german: Panzergruppe 3) was formed on 16 November 1940. It was a constituent part of Army Group Centre and participated in Operation Barbarossa and fought in the Battle of Moscow in late 1941 and early 1942. Later it served in Operation Typhoon, where it was placed under operational control of the Ninth Army. ''Panzergruppe 3'' was retitled the 3rd Panzer Army on 1 January 1942. Orders of battle At the start of Operation Barbarossa the Group consisted of the XXXIX and LVII Army Corps (mot.). 2 October 1941 Part of Army Group Centre. * Commander: Colonel General Hermann Hoth * Chief of Staff: Colonel Walther von Hünersdorff * XLI Motorized Corps under General of Panzer Troops Georg-Hans Reinhardt ** 1.Panzer-Division under Lieutenant General Friedrich Kirchner ** 36.Infant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Group South
Army Group South (german: Heeresgruppe Süd) was the name of three German Army Groups during World War II. It was first used in the 1939 September Campaign, along with Army Group North to invade Poland. In the invasion of Poland Army Group South was led by Gerd von Rundstedt and his chief of staff Erich von Manstein. Two years later, Army Group South became one of three army groups into which Germany organised their forces for Operation Barbarossa. Army Group South's principal objective was to capture Soviet Ukraine and its capital Kiev. In September 1944, the Army Group South Ukraine was renamed Army Group South in Eastern Hungary. It fought in Western Hungary until March 1945 and retired to Austria at the end of the Second World War, where it was renamed Army Group Ostmark on 2 April 1945. Operation Barbarossa Ukraine was a major center of Soviet industry and mining and had the good farmland required for Hitler's plans for ''Lebensraum'' ('living space'). Army Group South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Leningrad
The siege of Leningrad (russian: links=no, translit=Blokada Leningrada, Блокада Ленинграда; german: links=no, Leningrader Blockade; ) was a prolonged military blockade undertaken by the Axis powers against the Soviet city of Leningrad (present-day Saint Petersburg) on the Eastern Front of World War II. Germany's Army Group North advanced from the south, while the German-allied Finnish army invaded from the north and completed the ring around the city. The siege began on 8 September 1941, when the Wehrmacht severed the last road to the city. Although Soviet forces managed to open a narrow land corridor to the city on 18 January 1943, the Red Army did not lift the siege until 27 January 1944, 872 days after it began. The blockade became one of the longest and most destructive sieges in history, and it was possibly the costliest siege in history due to the number of casualties which were suffered throughout its duration. While not classed as a war crime at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Group North
Army Group North (german: Heeresgruppe Nord) was a German strategic formation, commanding a grouping of field armies during World War II. The German Army Group was subordinated to the ''Oberkommando des Heeres'' (OKH), the German army high command, and coordinated the operations of attached separate army corps, reserve formations, rear services and logistics, including the Army Group North Rear Area. Operational history The Army Group North was created on the 2 September 1939 by reorganization of the 2nd Army Headquarters. Commander in Chief as of 27 August 1939 was Field Marshal Fedor von Bock. Invasion of Poland The first employment of Army Group North was in the invasion of Poland of 1939, where in September it controlled: * 3rd Army * 4th Army * a reserve of four divisions ** 10th Panzer Division ** 73rd Infantry Division ** 206th Infantry Division ** 208th Infantry Division. The Army Group was commanded by Fedor von Bock for the operation. After the end of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Group Centre
Army Group Centre (german: Heeresgruppe Mitte) was the name of two distinct strategic German Army Groups that fought on the Eastern Front in World War II. The first Army Group Centre was created on 22 June 1941, as one of three German Army formations assigned to the invasion of the Soviet Union (Operation Barbarossa). On 25 January 1945, after it was encircled in the Königsberg pocket, Army Group Centre was renamed Army Group North (), and Army Group A () became Army Group Centre. The latter formation retained its name until the end of the war in Europe on 11 May after VE Day. Formation The commander in chief on the formation of the Army Group Centre (22 June 1941) was Fedor von Bock. Order of battle at formation Campaign and operational history Operation Barbarossa On 22 June 1941, Nazi Germany and its Axis allies launched their surprise offensive into the Soviet Union. Their armies, totaling over three million men, were to advance in three geographical directi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Smolensk (1941)
The first Battle of Smolensk (german: Kesselschlacht bei Smolensk, ' Cauldron-battle at Smolensk'; ) was a battle during the second phase of Operation Barbarossa, the Axis invasion of the Soviet Union, in World War II. It was fought around the city of Smolensk between 10 July and 10 September 1941, about west of Moscow. The Ostheer had advanced into the USSR in the 18 days after the invasion on 22 June 1941. The Soviet 16th, 19th and the 20th armies were encircled and destroyed just to the east of Smolensk, though many of the men from the 19th and 20th armies managed to escape the pocket. Some historians have asserted that the cost to the Germans during this drawn-out battle and the delay in the drive towards Moscow led to the victory of the Red Army in the Battle of Moscow of December 1941. Background and planning On 22 June 1941, the Axis nations invaded the Soviet Union in Operation Barbarossa. At first, the campaign met with spectacular success, as the surprised Soviet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Front (Soviet Union)
The Western Front was a front of the Red Army, one of the Red Army Fronts during World War II. The Western Front was created on 22 June 1941 from the Western Special Military District (which before July 1940 was known as Belorussian Special Military District). The first Front Commander was Dmitry Pavlov (continuing from his position as District Commander since June 1940). The western boundary of the Front in June 1941 was long, from the southern border of Lithuania to the Pripyat River and the town of Włodawa. It connected with the adjacent North-Western Front, which extended from the Lithuanian border to the Baltic Sea, and the Southwestern Front in Ukraine. Operational history Front dispositions 22 June 1941 The 1939 partition of Poland according to the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact established a new western border with no permanent defense installations, and the army deployment within the Front created weak flanks. At the outbreak of war with Germany, the Western Special ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
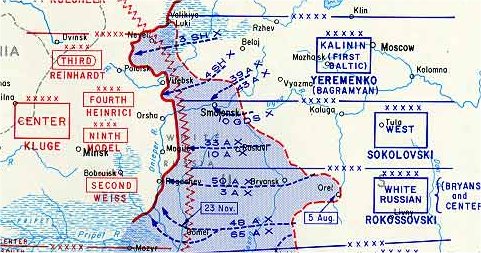
Battle Of Smolensk (1943)
The second Smolensk operation (7 August – 2 October 1943) was a Soviet strategic offensive operation conducted by the Red Army as part of the Summer-Autumn Campaign of 1943. Staged almost simultaneously with the Lower Dnieper Offensive (13 August – 22 September), the offensive lasted two months and was led by General Andrei Yeremenko, commanding the Kalinin Front, and Vasily Sokolovsky, commanding the Western Front. Its goal was to clear the German presence from the Smolensk and Bryansk regions. Smolensk had been under German occupation since the first Battle of Smolensk in 1941. Despite an impressive German defense, the Red Army was able to stage several breakthroughs, liberating several major cities, including Smolensk and Roslavl. As a result of this operation, the Red Army was able to start planning for the liberation of Belarus. However, the overall advance was quite modest and slow in the face of heavy German resistance, and the operation was therefore accomplished in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Moscow
The Battle of Moscow was a military campaign that consisted of two periods of strategically significant fighting on a sector of the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front during World War II. It took place between September 1941 and January 1942. The Soviet defensive effort frustrated Adolf Hitler, Hitler's attack on Moscow, the capital and largest city of the Soviet Union. Moscow was one of the primary Strategic goal (military), military and political objectives for Axis forces in their Operation Barbarossa, invasion of the Soviet Union. The German Strategic Offensive, named Operation Typhoon, called for two Pincer movement, pincer offensives, one to the north of Moscow against the Kalinin Front by the 3rd Panzer Army, 3rd and 4th Panzer Army, 4th Panzer Armies, simultaneously severing the Saint Petersburg–Moscow Railway, Moscow–Leningrad railway, and another to the south of Moscow Oblast against the Western Front (Soviet Union), Western Front south of Tula, Russia, Tul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the ''Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previously used term and was the manifestation of the Nazi regime's efforts to rearm Germany to a greater extent than the Treaty of Versailles permitted. After the Nazi rise to power in 1933, one of Adolf Hitler's most overt and audacious moves was to establish the ''Wehrmacht'', a modern offensively-capable armed force, fulfilling the Nazi régime's long-term goals of regaining lost territory as well as gaining new territory and dominating its neighbours. This required the reinstatement of conscription and massive investment and defense spending on the arms industry. The ''Wehrmacht'' formed the heart of Germany's politico-military power. In the early part of the Second World War, the ''Wehrmacht'' employed combined arms tactics (close-cover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

.jpg)