|
Battle Of Arklow (1649)
The Battle of Arklow was a minor skirmish that took place at Glascarrig on the coast road near Arklow in County Wicklow on 1 November 1649. It was fought between the army of the Parliamentarians and the combined forces of the Irish Royalists and Confederates during the Irish Confederate Wars. Background By late October 1649, the Irish had suffered a number of major defeats at the hands of the army of the English Parliament – a defeat at the Battle of Rathmines and the loss of the important towns of Drogheda and Wexford. Ormonde was keen to regain the initiative. In October, he received word from Castlehaven that a column of English soldiers was preparing to march from Dublin to Wexford to reinforce Cromwell's troops in the south. This presented the Irish leadership with a chance to engage the Parliamentarians without risking too many soldiers. The Baron of Inchiquin and Theobald Taaffe (who had fought on opposite sides at the Battle of Knocknanuss only two years bef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cromwellian Conquest Of Ireland
The Cromwellian conquest of Ireland or Cromwellian war in Ireland (1649–1653) was the re-conquest of Ireland by the forces of the English Parliament, led by Oliver Cromwell, during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms. Cromwell invaded Ireland with the New Model Army on behalf of England's Rump Parliament in August 1649. Following the Irish Rebellion of 1641, most of Ireland came under the control of the Irish Catholic Confederation. In early 1649, the Confederates allied with the English Royalists, who had been defeated by the Parliamentarians in the English Civil War. By May 1652, Cromwell's Parliamentarian army had defeated the Confederate and Royalist coalition in Ireland and occupied the country, ending the Irish Confederate Wars (or Eleven Years' War). However, guerrilla warfare continued for a further year. Cromwell passed a series of Penal Laws against Roman Catholics (the vast majority of the population) and confiscated large amounts of their land. As punishment for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
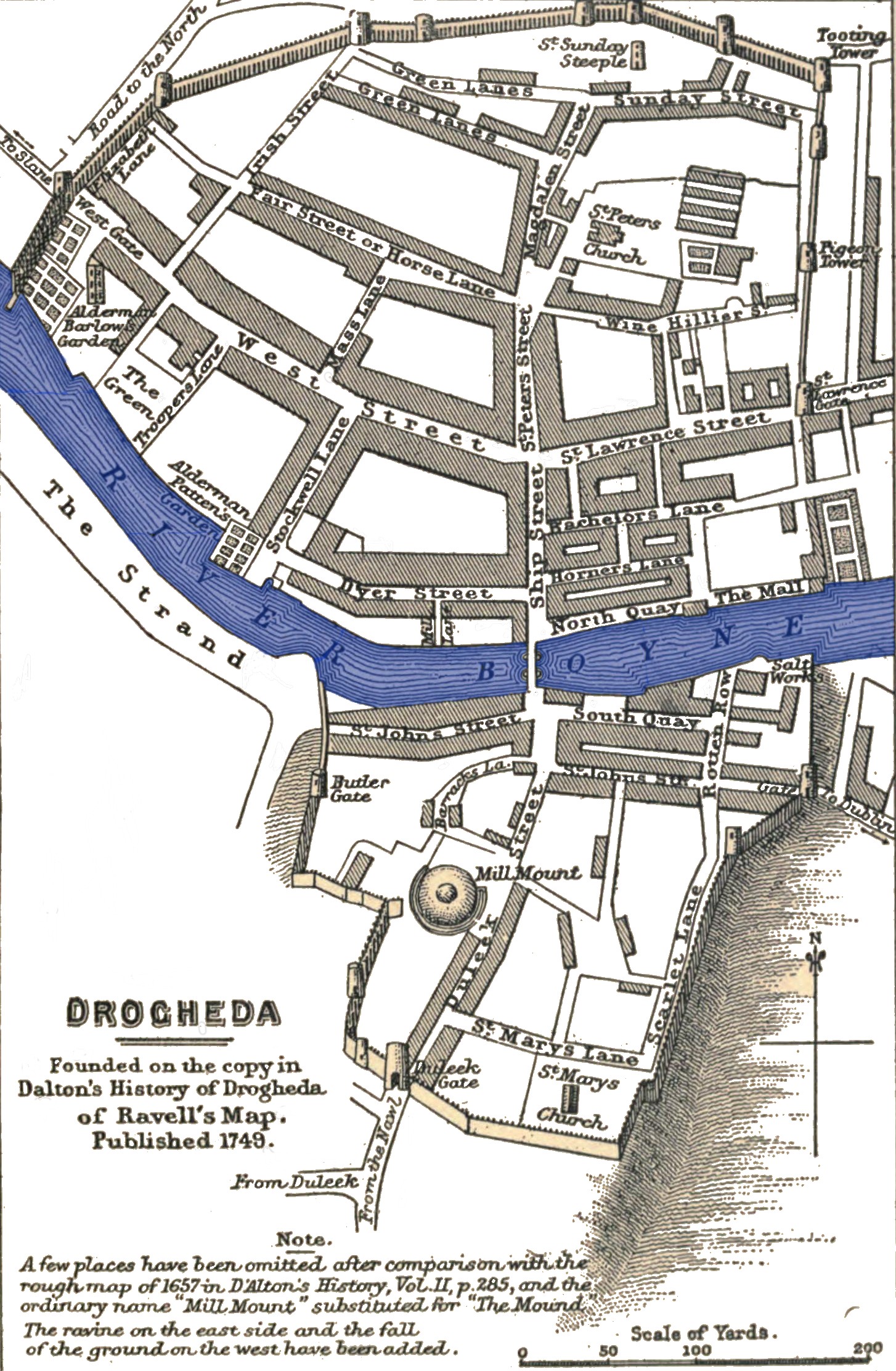
Siege Of Drogheda
The siege of Drogheda or the Drogheda massacre took place 3–11 September 1649, at the outset of the Cromwellian conquest of Ireland. The coastal town of Drogheda was held by the Irish Catholic Confederation and English Royalists under the command of Sir Arthur Aston when it was besieged by Parliamentarian forces under Oliver Cromwell. After Aston rejected an invitation to surrender, the town was stormed and much of the garrison was executed including an unknown but "significant number" of civilians. The outcome of the siege and the extent to which civilians were targeted is a significant topic of debate among historians. Background Since 1642, most of Ireland had been under the control of the Irish Catholic Confederation, who had taken much of the country in the aftermath of the 1641 Irish rebellion. In 1648, the Irish Confederates allied themselves with the English Royalists to oppose the English Parliamentarians. With his New Model Army, Oliver Cromwell landed in I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Involving England
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Of The Irish Confederate Wars
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Battles
This is a list of conflicts in Ireland, including wars, armed rebellions, battles and skirmishes. Irish Warriors participated in many wars in Europe and “England” as well and are not completely recognized on this page. List of wars and rebellions in Ireland List of battles in Ireland Prehistoric era 5th century *459 – Ath Dara *464 – First Battle of Dumha Aichir *468 – Bri Ele *470 – Second Battle of Dumha Aichir *476 – First Battle of Granard *478 – Ocha *480 – Second Battle of Granard *483 – Battle of Ochae *489 – Tailtin *491 – Cell Losnaid *492 – Sleamhain, in Meath *493 – Battle for the Body of St. Patrick *494 – Ceann Ailbhe *496 – Druim Lochmaighe *497 – Inde Mor, in Crioch Ua nGabhla *499 – Seaghais 6th century *500 – Lochmagh *501 – Freamhain, in Meath *506 – Luachair *507 – Druim Deargaighe *528 – Luachair *531 – Claenloch *537 – Sligeach *544 – Cuil Conaire *546 – Cuilne *556 – Cuil U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wexford
Wexford () is the county town of County Wexford, Ireland. Wexford lies on the south side of Wexford Harbour, the estuary of the River Slaney near the southeastern corner of the island of Ireland. The town is linked to Dublin by the M11/N11 National Primary Route; and to Rosslare Europort, Cork and Waterford by the N25. The national rail network connects it to Dublin and Rosslare Europort. It had a population of 20,188 according to the 2016 census. History The town was founded by the Vikings in about 800 AD. They named it ''Veisafjǫrðr'', meaning "inlet of the mudflats", and the name has changed only slightly into its present form. According to a story recorded in the ''Dindsenchas'', the name "Loch Garman" comes from a man named '' Garman mac Bomma Licce'' who was chased to the river mouth and drowned as a consequence of stealing the queen's crown from Temair during the feast of Samhain. For about three hundred years it was a Viking town, a city-state, largely independ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapparees
Rapparees or raparees (from the Irish ''ropairí'', plural of ''ropaire'', whose primary meaning is "thruster, stabber," and by extension a wielder of the half-pike or pike), were Irish guerrilla fighters who operated on the Jacobite side during the 1690s Williamite war in Ireland. Subsequently, the name was also given to bandits and highwaymen in Ireland – many former guerrillas having turned to crime after the war ended. They were in many cases outlawed members of the Gaelic nobility of Ireland and still held to the code of conduct of the traditional chiefs of the Irish clans. They share many similarities with the hajduks of Eastern Europe. Wood kerne and Tories There was a long tradition of guerrilla warfare in Ireland before the 1690s. Irish irregulars in the 16th century were known as ''ceithearnaigh choille'', "wood-kerne", a reference to native Irish foot-soldiers called ''ceithearnaigh'', or "kerne". In the Irish Confederate Wars of the 1640s and 50s, irregu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Knocknanuss
The Battle of Knocknanauss was fought in 1647, during the Irish Confederate Wars, part of the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, between Confederate Ireland’s Munster army and an English Parliamentarian army under Murrough O’Brien. The battle resulted in a crushing defeat for the Irish Confederates. Background In the summer of 1647, Murrough O’Brien (later created the Earl of Inchiquin), commander of the English Parliamentarian forces in Cork, ravaged and burned the Confederate territory in Munster. This caused severe food shortages and earned O’Brien the Irish nickname, Murchadh an Dóiteáin, "Murrough the Burner" In addition, Inchiquinn took the Rock of Cashel, which was garrisoned by Confederate troops and rich in emotive religious symbolism. In the sack of the castle, O’Brien's troops massacred the garrison and all the clergy they found there. The Confederates' Munster army was incapable of stopping O’Brien because of political infighting between officers who su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Tuchet, 3rd Earl Of Castlehaven
James Tuchet, 3rd Earl of Castlehaven ( - 11 October 1684) was the son of Mervyn Tuchet, 2nd Earl of Castlehaven and his first wife, Elizabeth Barnham (1592 - ). Castlehaven played a prominent role in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms that took place in the middle of the 17th century, and was particularly active in the conflicts in Ireland at this time. Titles He succeeded to the Irish earldom of Castlehaven and Baron Audley of Orier on 14 May 1631, when his father was attainted and beheaded. Most of his estates in England were taken over by others. He was created Baron Audley of Hely with remainder "to his heirs forever" on 3 June 1633, with the place and precedency of George, his grandfather, formerly Baron Audley, in an effort to nullify his father's attainder. However, this was considered insufficient, legally, until a bill was passed by Parliament in 1678 allowing him to inherit the original Barony of Audley. War in Ireland Castlehaven was involved in the defence of Irel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Butler, 1st Duke Of Ormonde
Lieutenant-General James FitzThomas Butler, 1st Duke of Ormond, KG, PC (19 October 1610 – 21 July 1688), was a statesman and soldier, known as Earl of Ormond from 1634 to 1642 and Marquess of Ormond from 1642 to 1661. Following the failure of the senior line of the Butler family, he was the second representative of the Kilcash branch to inherit the earldom. His friend, the Earl of Strafford, secured his appointment as commander of the government army in Ireland. Following the outbreak of the Irish Rebellion of 1641, he led government forces against the Irish Catholic Confederation; when the First English Civil War began in August 1642, he supported the Royalists and in 1643 negotiated a ceasefire with the Confederation which allowed his troops to be transferred to England. Shortly before the Execution of Charles I in January 1649, he agreed the Second Ormonde Peace, an alliance between the Confederation and Royalist forces which fought against the Cromwellian conquest o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sack Of Wexford
The Sack of Wexford took place from 2 to 11 October 1649, during the campaign known as the Cromwellian conquest of Ireland. It was part of the wider 1641 to 1653 Irish Confederate Wars, and an associated conflict of the Wars of the Three Kingdoms. A Roundhead, Parliamentarian force under Oliver Cromwell stormed the town after negotiations broke down, killing most of the garrison. Many civilians also died, either during the sack, or drowned attempting to escape across the River Slaney. Along with Siege_of_Drogheda, Drogheda, Wexford is still remembered as an infamous atrocity. Background On 17 January 1649, the Confederate_Ireland, Catholic Confederation signed a treaty with the James_Butler,_1st_Duke_of_Ormond, Duke of Ormond, Royalist leader in Ireland. Two weeks later, they were joined by Ulster_Protestants, Ulster Presbyterians, who objected to the execution of Charles_I_of_England, Charles I by the newly established Commonwealth_of_England, Commonwealth. This was off ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Rathmines
The Battle of Rathmines was fought on 2 August 1649, near the modern Dublin suburb of Rathmines, during the Irish Confederate Wars, an associated conflict of 1638 to 1651 Wars of the Three Kingdoms. It has been described as the 'decisive battle of the Engagement in Ireland.' In late July 1649, a combined Irish Confederate/Royalist army under the Earl of Ormond, tried to capture Dublin, held by forces loyal to the Commonwealth, commanded by Michael Jones. Despite their superior numbers, Ormond's troops were routed by Jones' veterans, many of whom were members of the New Model Army. Their victory secured Dublin, enabling another 12,000 troops under Oliver Cromwell to land unimpeded, and begin the Cromwellian conquest of Ireland. Background The Irish Rebellion of 1641 led to the establishment of the Catholic Confederation, based in Kilkenny, and the Irish Confederate Wars. From 1641 to 1643, the main struggle was between the Confederation and Irish and English Royalists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
