|
Bassignana Porta Diingresso Con Stemma
Bassignana (in Piedmontese dialect ''Bassgnan-na'') is a municipality in the Province of Alessandria, Piedmont, northern Italy. The village is situated near the confluence of the Po River and the Tanaro river. Main sights include remains of the castle, dating to Lombard times, and a Romanesque pieve (10th century) with 12th century Byzantine frescoes. History The first inhabitants of whom there is written news belonged to the Ligurian tribe of the Marici: they had crossed the Pennine in the postglacial era and had settled south of the Po river, in the area between Stradella and Casale Monferrato. Such people were closely linked to that of the Levi, who had settled further north: the founding of Ticinum, the modern Pavia, is attributed to the Levi and to the Marici. Some toponomastic traces of that period exist in the area: Bosco Marengo stems from ''Lucus Maricum'' and Pietra Marazzi from ''Petra Maricorum or Mariciorum''. In the 6th century BC the Po valley was occupied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piedmont
it, Piemontese , population_note = , population_blank1_title = , population_blank1 = , demographics_type1 = , demographics1_footnotes = , demographics1_title1 = , demographics1_info1 = , demographics1_title2 = , demographics1_info2 = , demographics1_title3 = , demographics1_info3 = , timezone1 = CET , utc_offset1 = +1 , timezone1_DST = CEST , utc_offset1_DST = +2 , postal_code_type = , postal_code = , area_code_type = ISO 3166 code , area_code = IT-21 , blank_name_sec1 = GDP (nominal) , blank_info_sec1 = €137 billion (2018) , blank1_name_sec1 = GDP per capita , blank1_info_sec1 = €31,500 (2018) , blank2_name_sec1 = HDI (2019) , blank2_info_sec1 = 0.898 · 10th of 21 , blank_name_sec2 = NUTS Region , blank_info_sec2 = ITC1 , website www.regione ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laevi
The Laevi, or Levi (who are not to be confused with descendants of Levi), were a LigurianLivius, '' Ab Urbe condita'' 5.34-35.3. people in Gallia Transpadana, on the river Ticinus, who, in conjunction with the Marici, built the town of Ticinum (the modern Pavia Pavia (, , , ; la, Ticinum; Medieval Latin: ) is a town and comune of south-western Lombardy in northern Italy, south of Milan on the lower Ticino river near its confluence with the Po. It has a population of c. 73,086. The city was the cap ...). They joined Bellovesus' migrations towards Italy, together with the Aeduii, Bituriges, Ambarri, Arverni, Aulerci, Carnutes and Senones. References * Harry Thurston Peck, ''Harpers Dictionary of Classical Antiquities'' (1898). Article available onlinhere Gauls Ligures Historical Celtic peoples {{ethno-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
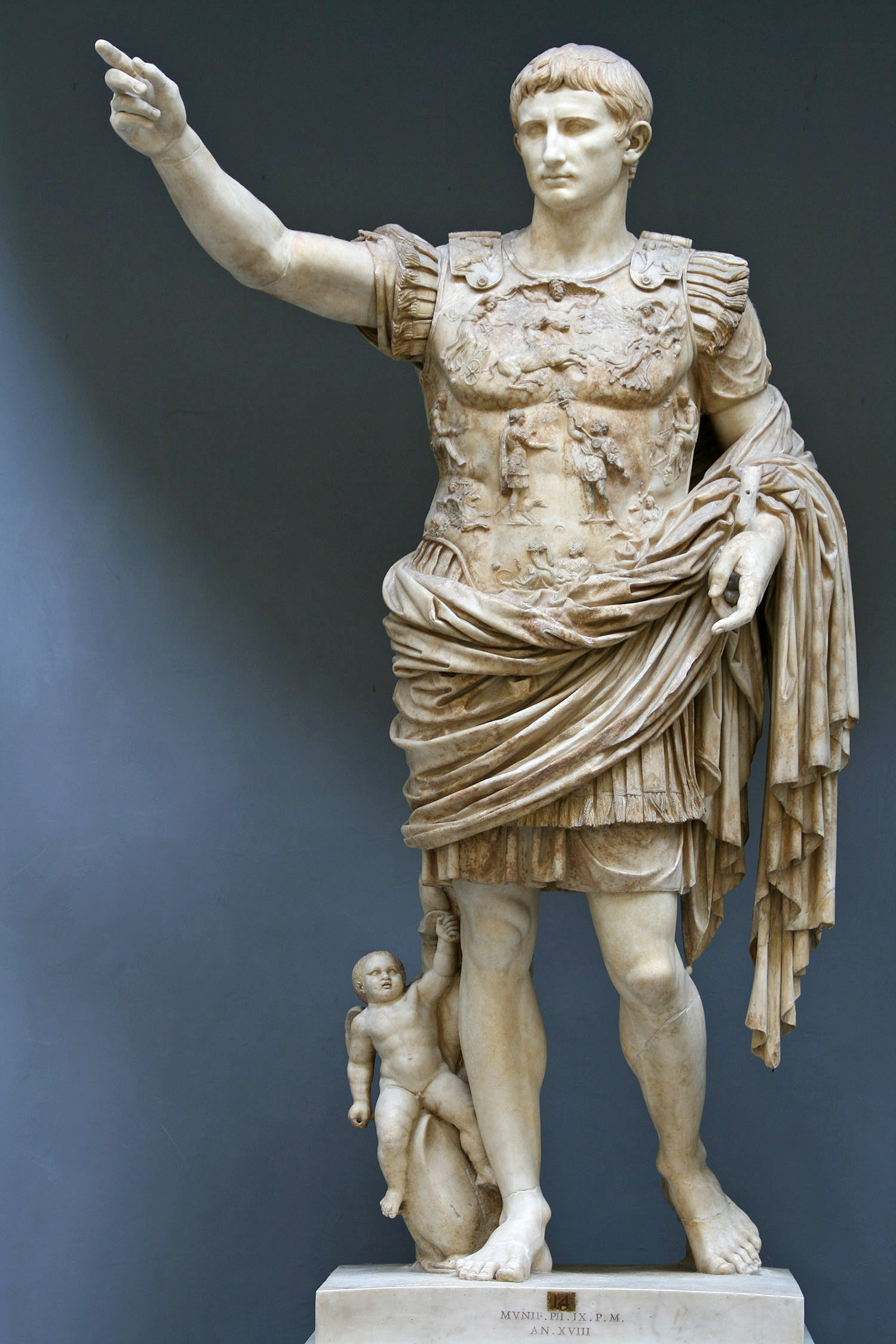
Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereignty, sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), mother (empress dowager), or a woman who rules in her own right and name (empress regnant). Emperors are generally recognized to be of the highest monarchic honour, honor and royal and noble ranks, rank, surpassing kings. In Europe, the title of Emperor has been used since the Middle Ages, considered in those times equal or almost equal in dignity to that of Pope due to the latter's position as visible head of the Church and spiritual leader of the Catholic part of Western Europe. The Emperor of Japan is the only currently List of current sovereign monarchs, reigning monarch whose title is translated into English as "Emperor". Both emperors and kings are monarchs or sovereigns, but both emperor and empress are considered the higher monarch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, Weapons and Ornaments: Germanic Material Culture in Pre-Carolingian Central Europe, 400-750. BRILL, 2001, p.42. Later the term was associated with Romanized Germanic dynasties within the collapsing Western Roman Empire, who eventually commanded the whole region between the rivers Loire and Rhine. They imposed power over many other post-Roman kingdoms and Germanic peoples. Beginning with Charlemagne in 800, Frankish rulers were given recognition by the Catholic Church as successors to the old rulers of the Western Roman Empire. Although the Frankish name does not appear until the 3rd century, at least some of the original Frankish tribes had long been known to the Romans under their own names, both as allies providing soldiers, and as e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period from 395 to 476, where there were separate coequal courts dividing the governance of the empire in the Western and the Eastern provinces, with a distinct imperial succession in the separate courts. The terms Western Roman Empire and Eastern Roman Empire were coined in modern times to describe political entities that were ''de facto'' independent; contemporary Romans did not consider the Empire to have been split into two empires but viewed it as a single polity governed by two imperial courts as an administrative expediency. The Western Roman Empire collapsed in 476, and the Western imperial court in Ravenna was formally dissolved by Justinian in 554. The Eastern imperial court survived until 1453. Though the Empire had seen periods with m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of '' toponyms'' (proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of any geographical feature, and full scope of the term also includes proper names of all cosmographical features. In a more specific sense, the term ''toponymy'' refers to an inventory of toponyms, while the discipline researching such names is referred to as ''toponymics'' or ''toponomastics''. Toponymy is a branch of onomastics, the study of proper names of all kinds. A person who studies toponymy is called ''toponymist''. Etymology The term toponymy come from grc, τόπος / , 'place', and / , 'name'. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' records ''toponymy'' (meaning "place name") first appearing in English in 1876. Since then, ''toponym'' has come to replace the term ''place-name'' in professional discourse among geographers. Topon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Sulpicius Gallus
Gaius Sulpicius Gallus or Galus () was a general, statesman and orator of the Roman Republic. In 169 BC, he served as ''praetor urbanus''.Livy xliii.14 Under Lucius Aemilius Paulus, his intimate friend, he commanded the 2nd legion in the campaign against Perseus, king of Macedonia, and gained great reputation for having predicted a lunar eclipse on the night before the Battle of Pydna (168 BC). On his return from Macedonia he was elected consul (166 BC), and in the same year reduced the Ligurians to submission. In 164 BC he was sent as ambassador to Greece and Asia, where he held a meeting at Sardis to investigate the charges brought against Eumenes II of Pergamon by the representatives of various cities of Asia Minor. Gallus was a man of great learning, an excellent Greek scholar, and in his later years devoted himself to the study of astronomy, on which subject he is quoted as an authority by Pliny. He was able to predict a lunar eclipse in the year 168 BC, and was regarded by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Claudius Marcellus
Marcus Claudius Marcellus (; 270 – 208 BC), five times elected as consul of the Roman Republic, was an important Roman military leader during the Gallic War of 225 BC and the Second Punic War. Marcellus gained the most prestigious award a Roman general could earn, the ''spolia opima'', for killing the Gallic military leader and king Viridomarus in hand-to-hand combat in 222 BC at the Battle of Clastidium. Furthermore, he is noted for having conquered the fortified city of Syracuse in a protracted siege during which Archimedes, the famous mathematician, scientist, and inventor, was killed, despite Marcellus ordering the soldiers not to harm him. Marcus Claudius Marcellus died in battle in 208 BC, leaving behind a legacy of military conquests and a reinvigorated Roman legend of the ''spolia opima''. Early life: distinguished soldier and politician Little is known of Marcus Claudius Marcellus' early years, since ancient historians and biographers were more concerned with the mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), Roman Republic (509–27 BC) and Roman Empire (27 BC–476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. Ancient Rome began as an Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian Peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually dominated the Italian Peninsula, assimilated the Greek culture of southern Italy ( Magna Grecia) and the Etruscan culture and acquired an Empire that took in much of Europe and the lands and peoples surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. It was among the largest empires in the ancient world, with an estimated 50 to 90 million inhabitants, roughly 20% of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apogee of their influence and territorial expansion during the 4th century bc, extending across the length of Europe from Britain to Asia Minor."; . " e Celts, were Indo-Europeans, a fact that explains a certain compatibility between Celtic, Roman, and Germanic mythology."; . "The Celts and Germans were two Indo-European groups whose civilizations had some common characteristics."; . "Celts and Germans were of course derived from the same Indo-European stock."; . "Celt, also spelled Kelt, Latin Celta, plural Celtae, a member of an early Indo-European people who from the 2nd millennium bce to the 1st century bce spread over much of Europe."; in Europe and Anatolia, identified by their use of Celtic langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
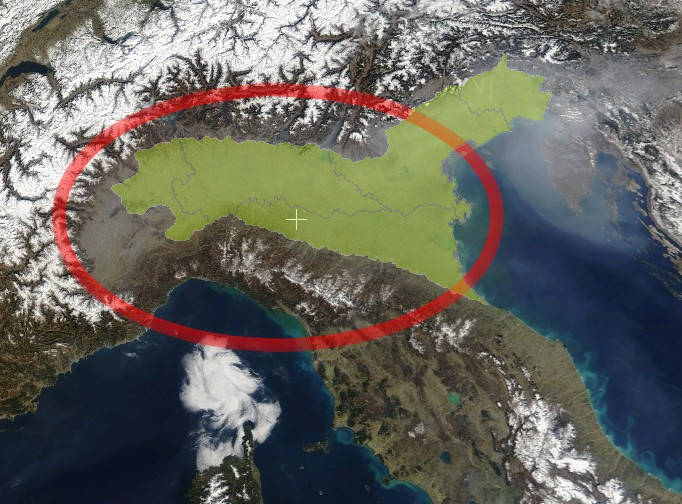
Po Valley
The Po Valley, Po Plain, Plain of the Po, or Padan Plain ( it, Pianura Padana , or ''Val Padana'') is a major geographical feature of Northern Italy. It extends approximately in an east-west direction, with an area of including its Venetic extension not actually related to the Po river basin; it runs from the Western Alps to the Adriatic Sea. The flatlands of Veneto and Friuli are often considered apart since they do not drain into the Po, but they effectively combine into an unbroken plain, making it the largest in Southern Europe. It has a population of 17 million, or a third of Italy's total population. The plain is the surface of an in-filled system of ancient canyons (the "Apennine Foredeep") extending from the Apennines in the south to the Alps in the north, including the northern Adriatic. In addition to the Po and its affluents, the contemporary surface may be considered to include the Savio, Lamone and Reno to the south, and the Adige, Brenta, Piave and Tagliamen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pietra Marazzi
Pietra Marazzi is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Alessandria in the Italian region Piedmont, located about east of Turin and about northeast of Alessandria. Pietra Marazzi borders the following municipalities: Alessandria, Montecastello, and Pecetto di Valenza Pecetto di Valenza ( pms, Apsèj) is a commune of the Province of Alessandria in the Piedmont region of northwest Italy with a population of 1282 (December 2008 estimate). It is south of the river Po, and about northeast of the provincial capita .... References Cities and towns in Piedmont {{Alessandria-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |