|
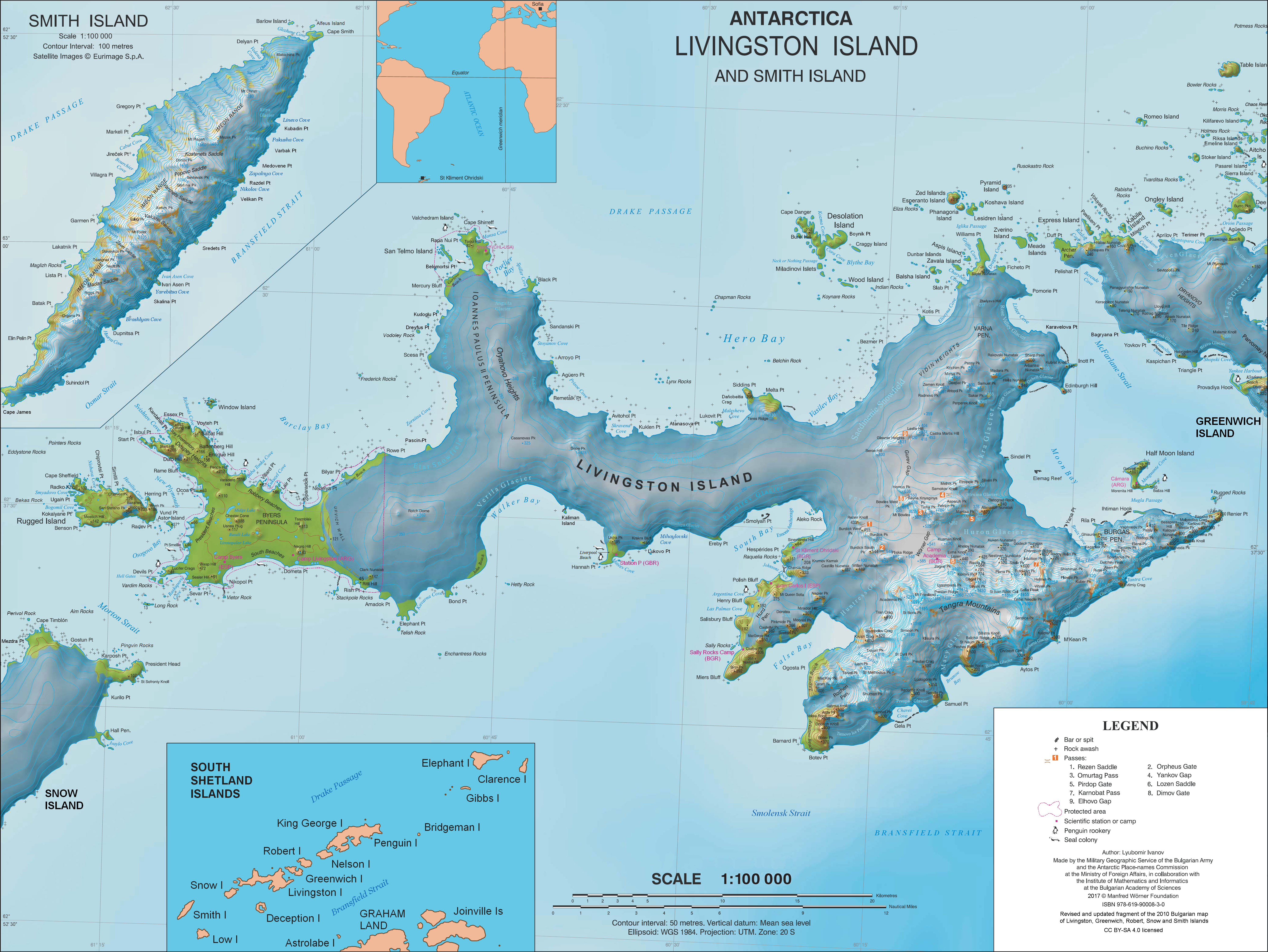
Basilisk Crag
Basilisk Crag is a linear serrated cliff in the South Shetland Islands. It trends north-east, rising to about above sea level on the southeast shore of Griffin Cove, Livingston Island. The cliff is one of several features given the name of “fabulous beasts” in the Williams Point area. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1998 after the Basilisk In European bestiaries and legends, a basilisk ( or ) is a legendary reptile reputed to be a serpent king, who causes death to those who look into its eyes. According to the ''Naturalis Historia'' of Pliny the Elder, the basilisk of Cyrene is ..., reputed "king of the serpents", and also because the feature was thought to crudely resemble the modern-day basilisk lizard. References * Cliffs of Antarctica South Shetland Islands {{LivingstonIsland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cliff
In geography and geology, a cliff is an area of rock which has a general angle defined by the vertical, or nearly vertical. Cliffs are formed by the processes of weathering and erosion, with the effect of gravity. Cliffs are common on coasts, in mountainous areas, escarpments and along rivers. Cliffs are usually composed of rock that is resistant to weathering and erosion. The sedimentary rocks that are most likely to form cliffs include sandstone, limestone, chalk, and dolomite. Igneous rocks such as granite and basalt also often form cliffs. An escarpment (or scarp) is a type of cliff formed by the movement of a geologic fault, a landslide, or sometimes by rock slides or falling rocks which change the differential erosion of the rock layers. Most cliffs have some form of scree slope at their base. In arid areas or under high cliffs, they are generally exposed jumbles of fallen rock. In areas of higher moisture, a soil slope may obscure the talus. Many cliffs also fea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Shetland Islands
The South Shetland Islands are a group of Antarctic islands with a total area of . They lie about north of the Antarctic Peninsula, and between southwest of the nearest point of the South Orkney Islands. By the Antarctic Treaty of 1959, the islands' sovereignty is neither recognized nor disputed by the signatories and they are free for use by any signatory for non-military purposes. The islands have been claimed by the United Kingdom since 1908 and as part of the British Antarctic Territory since 1962. They are also claimed by the governments of Chile (since 1940, as part of the Antártica Chilena province) and Argentina (since 1943, as part of Argentine Antarctica, Tierra del Fuego Province). Several countries maintain research stations on the islands. Most of them are situated on King George Island, benefitting from the airfield of the Chilean base Eduardo Frei. There are sixteen research stations in different parts of the islands, with Chilean stations being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Griffin Cove
Griffin Cove is the 800 m wide cove indenting for 260 m the northwest coast of Varna Peninsula, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica and entered between Gargoyle Bastion to the northeast and Organpipe Point to the southwest. The feature is named after the griffin, a legendary bird often portrayed as a monster. Location The cove is centred at which is 17.15 km northeast of Siddins Point and 1.95 km south by west of Williams Point Williams Point is the point forming both the north extremity of Varna Peninsula and the northeast tip of Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Separated from Zed Islands to the north by Iglika Passage. The discovery of ... (British mapping in 1968, and Bulgarian mapping in 2005 and 2009). Maps * L.L. Ivanov et al. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich Island, South Shetland Islands. Scale 1:100000 topographic map. Sofia: Antarctic Place-names Commission of Bulgaria, 2005. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livingston Island
Livingston Island (Russian name ''Smolensk'', ) is an Antarctic island in the Southern Ocean, part of the South Shetlands Archipelago, a group of Antarctic islands north of the Antarctic Peninsula. It was the first land discovered south of 60° south latitude in 1819, a historic event that marked the end of a centuries-long pursuit of the mythical ''Terra Australis Incognita'' and the beginning of the exploration and utilization of real Antarctica. The name Livingston, although of unknown derivation, has been well established in international usage since the early 1820s. Geography Livingston Island is situated in West Antarctica northwest of Cape Roquemaurel on the Antarctic mainland, south-southeast of Cape Horn in South America, southeast of the Diego Ramírez Islands (the southernmost land of South America), due south of the Falkland Islands, southwest of South Georgia Islands, and from the South Pole.L. IvanovGeneral Geography and History of Livingston Island.In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Williams Point
Williams Point is the point forming both the north extremity of Varna Peninsula and the northeast tip of Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Separated from Zed Islands to the north by Iglika Passage. The discovery of the South Shetland Islands was first reported in 1819 by William Smith, Master of the brig ''Williams'' who had sighted the point on 19 February that year. An 1820 publication suggests that Smith gave the name ‘Williams’ to a point of land in this vicinity. In recent years the place name Williams Point has been established in international usage for the point described. Location The point is located at which is 9.47 km north of Miziya Peak in Vidin Heights, 8.8 km east of Desolation Island, 1.5 km south of Zed Islands and 5.5 km west of Duff Point on Greenwich Island. British mapping in 1822, Chilean in 1971, Argentine in 1980, Spanish in 1991, and Bulgarian in 2005 and 2009. Maps Chart of South Shetland inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee
The UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee (or UK-APC) is a United Kingdom government committee, part of the Foreign and Commonwealth Office, responsible for recommending names of geographical locations within the British Antarctic Territory (BAT) and the South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands (SGSSI). Such names are formally approved by the Commissioners of the BAT and SGSSI respectively, and published in the BAT Gazetteer and the SGSSI Gazetteer maintained by the Committee. The BAT names are also published in the international Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica maintained by Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research, SCAR. The Committee may also consider proposals for new place names for geographical features in areas of Antarctica outside BAT and SGSSI, which are referred to other Antarctic place-naming authorities, or decided by the Committee itself if situated in the unclaimed sector of Antarctica. Names attributed by the committee * Anvil Crag, named for descriptive featu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basilisk
In European bestiaries and legends, a basilisk ( or ) is a legendary reptile reputed to be a serpent king, who causes death to those who look into its eyes. According to the ''Naturalis Historia'' of Pliny the Elder, the basilisk of Cyrene is a small snake, "being not more than twelve inches in length", that is so venomous, it leaves a wide trail of deadly venom in its wake, and its gaze is likewise lethal. The basilisk's weakness is the odor of the weasel, which, according to Pliny, was thrown into the basilisk's hole, recognizable because some of the surrounding shrubs and grass had been scorched by its presence. It is possible that the legend of the basilisk and its association with the weasel in Europe was inspired by accounts of certain species of Asiatic snakes (such as the king cobra) and their natural predator, the mongoose. Etymology The word originates from the Greek form ''basilískos'' ( el, βασιλίσκος; la, basiliscus), which means "little king", "littl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basiliscus (genus)
''Basiliscus'' is a genus of large Corytophanidae, corytophanid lizards, commonly known as basilisks, which are Endemism, endemic to southern Mexico, Central America, and northern South America. The genus contains four species, which are commonly known as the Jesus Christ lizard, or simply the Jesus lizard, due to their ability to run across water for significant distances before sinking due to the large surface area of their feet. Taxonomy and etymology Both the Genus, generic name, ''Basiliscus'', and the common name, "basilisk", derive from the Greek language, Greek ''basilískos'' (βασιλίσκος) meaning "little king". The Specific name (zoology), specific epithet, ''vittatus'', which is Latin for "striped", was given in Carl Linnaeus' 10th edition of Systema Naturae, 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae''. Physiology Basilisks on average measure in total length (including tail). Their growth is perpetual, fast when they are young and nonlinear for mature basilisks. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cliffs Of Antarctica
In geography and geology, a cliff is an area of rock which has a general angle defined by the vertical, or nearly vertical. Cliffs are formed by the processes of weathering and erosion, with the effect of gravity. Cliffs are common on coasts, in mountainous areas, escarpments and along rivers. Cliffs are usually composed of rock that is resistant to weathering and erosion. The sedimentary rocks that are most likely to form cliffs include sandstone, limestone, chalk, and dolomite. Igneous rocks such as granite and basalt also often form cliffs. An escarpment (or scarp) is a type of cliff formed by the movement of a geologic fault, a landslide, or sometimes by rock slides or falling rocks which change the differential erosion of the rock layers. Most cliffs have some form of scree slope at their base. In arid areas or under high cliffs, they are generally exposed jumbles of fallen rock. In areas of higher moisture, a soil slope may obscure the talus. Many cliffs also featur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |