|
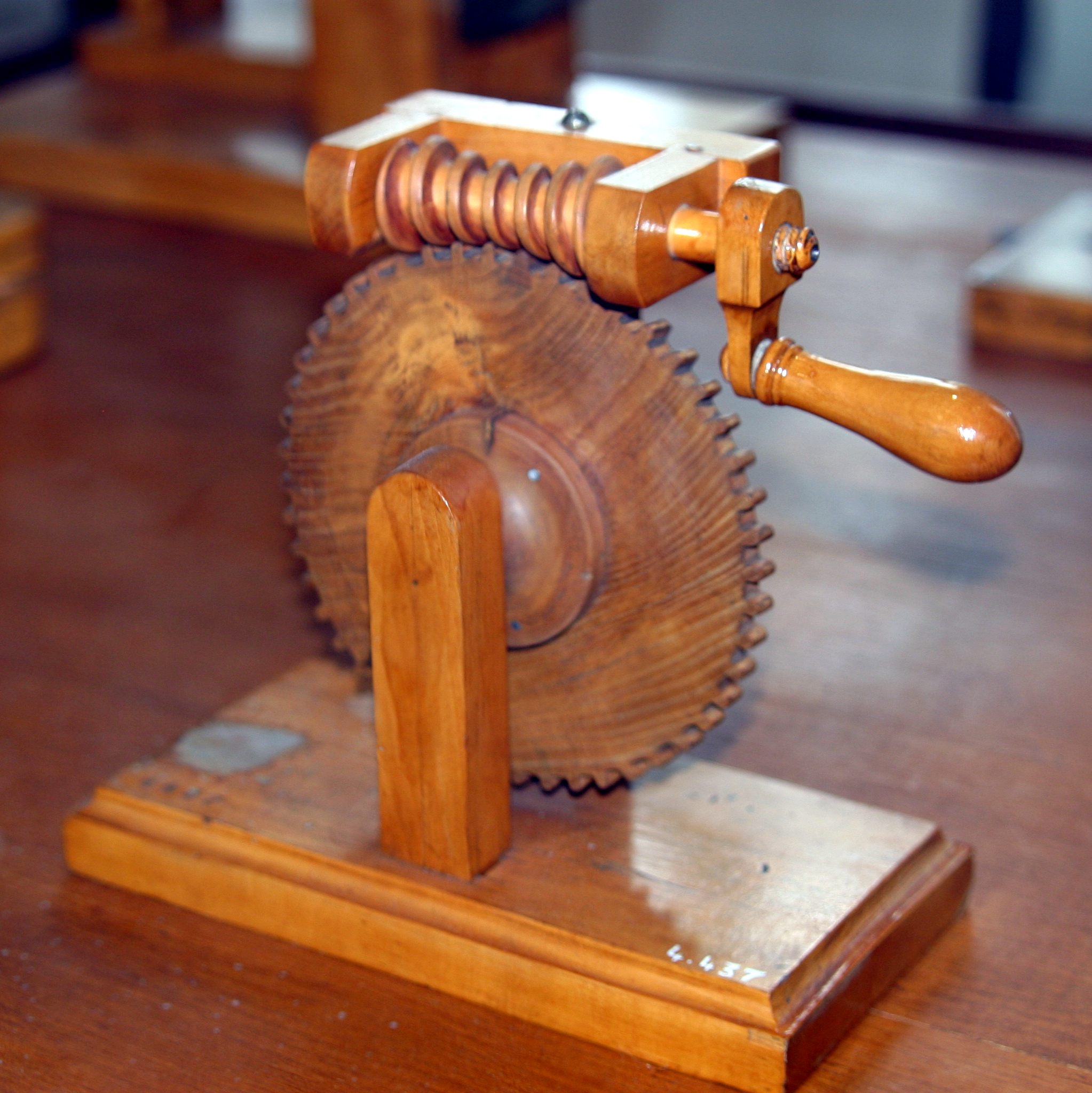
Barring Engine
A barring engine (also called barring motor) is a small engine that forms part of the installation of a large engine, and is used to turn the main engine to a favourable position from which it can be started. If the main engine has stopped close to its Dead centre (engineering), dead centre it is unable to restart itself. Barring may also be done to turn the engine over slowly (unloaded) for maintenance, or to prevent belt drives being left too long in one position and taking a "set". Originally they were used to turn Stationary steam engine, stationary steam engines to a position from which they could be started. These early barring engines were themselves small steam engines. Today they are found on most large marine vessels, such as supertankers and container ships, and are driven by pneumatic, compressed air. For modern large scale power plant, after a generation unit has been shut down, the shaft line and casing is gradually cooled, where cooling might not be even for the up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uniflow Steam Engine, Bradford Industrial Museum - Geograph
Uniflow may refer to: * UniFlow (Fire Show and Circus Performance Show Group) * Uniflow diesel engine * Uniflow steam engine The uniflow type of steam engine uses steam that flows in one direction only in each half of the cylinder. Thermal efficiency is increased by having a temperature gradient along the cylinder. Steam always enters at the hot ends of the cylinder and ... * UniFLOW Output Manager (Printing software) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
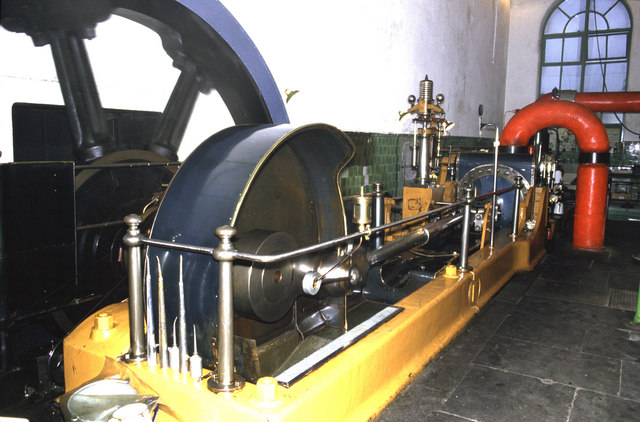
Corliss Barring Engine, Science Museum
Corliss is both a surname and a given name. People Given name * Corliss Lamont (1902–1995), American philosopher, political activist, and philanthropist * C. C. Moseley (1894–1974), American aviator and aviation businessman * Corliss Palmer (1899–1952), American silent film actress * Corliss P. Stone (1806–1873), mayor of Seattle and businessman * Corliss Waitman (born 1995), Belgian-born American football punter for the Pittsburgh Steelers * Corliss Williamson (born 1973), basketball player Surname * Augustus W. Corliss (1837–1907), American writer, historian and Civil War veteran * George Henry Corliss (1817–1888), inventor of the Corliss steam engine * George W. Corliss (1834–1903), American Civil War recipient of the Medal of Honor * Guy C. H. Corliss (1858–1937), American judge and justice of the Supreme Court of North Dakota * Jack Corliss, scientist and discoverer of undersea hydrothermal vents * Jeb Corliss (born 1976), American skydiver and base jumper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
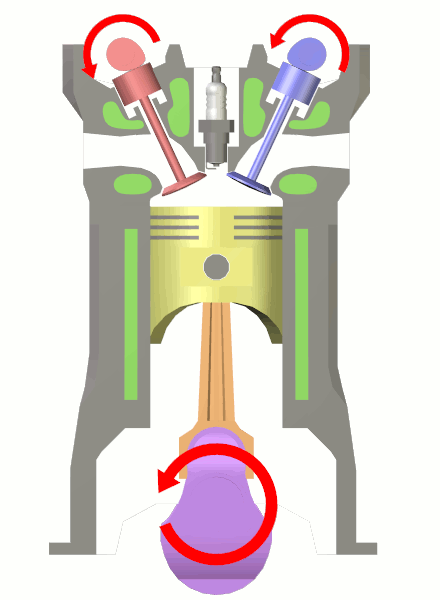
Dead Centre (engineering)
In a reciprocating engine, the dead centre is the position of a piston in which it is either farthest from, or nearest to, the crankshaft. The former is known as Top Dead Centre (TDC) while the latter is known as Bottom Dead Centre (BDC). More generally, the dead centre is any position of a crank where the applied force is straight along its axis, meaning no turning force can be applied. Many sorts of machines are crank driven, including unicycles, bicycles, tricycles, various types of machine presses, gasoline engines, diesel engines, steam locomotives, and other steam engines. Crank-driven machines rely on the energy stored in a flywheel to overcome the dead centre, or are designed, in the case of multi-cylinder engines, so that dead centres can never exist on all cranks at the same time. A steam locomotive is an example of the latter, the connecting rods being arranged such that the dead centre for each cylinder occurs out of phase with the other one (or more) cylinde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stationary Steam Engine
Stationary steam engines are fixed steam engines used for pumping or driving mills and factories, and for power generation. They are distinct from locomotive engines used on railways, traction engines for heavy steam haulage on roads, steam cars (and other motor vehicles), agricultural engines used for ploughing or threshing, marine engines, and the steam turbines used as the mechanism of power generation for most nuclear power plants. They were introduced during the 18th century and widely made for the whole of the 19th century and most of the first half of the 20th century, only declining as electricity supply and the internal combustion engine became more widespread. Types of stationary steam engine There are different patterns of stationary steam engines, distinguished by the layout of the cylinders and crankshaft: * Beam engines have a rocking beam providing the connection between the vertical cylinder and crankshaft. *Table engines have the crosshead above the vert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
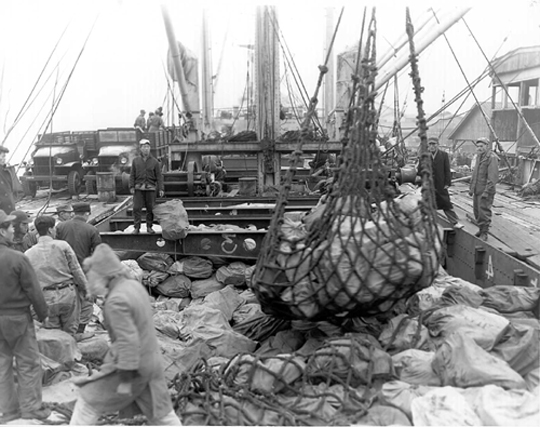
Supertanker
An oil tanker, also known as a petroleum tanker, is a ship designed for the bulk cargo, bulk transport of petroleum, oil or its products. There are two basic types of oil tankers: crude tankers and product tankers. Crude tankers move large quantities of unrefined petroleum, crude oil from its point of extraction to oil refinery, refineries. Product tankers, generally much smaller, are designed to move refined products from refineries to points near consuming markets. Oil tankers are often classified by their size as well as their occupation. The size classes range from inland or coastal tankers of a few thousand metric tons of deadweight tonnage, deadweight (DWT) to the mammoth ultra large crude carriers (ULCCs) of . Tankers move approximately of oil every year.UNCTAD 2006, p. 4. Second only to pipeline transport, pipelines in terms of efficiency,Huber, 2001: 211. the average cost of transport of crude oil by tanker amounts to only US. Some specialized types of oil tankers have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Container Ships
A container ship (also called boxship or spelled containership) is a cargo ship that carries all of its load in truck-size intermodal containers, in a technique called containerization. Container ships are a common means of commercial intermodal freight transport and now carry most seagoing non-bulk cargo. Container ship capacity is measured in twenty-foot equivalent units (TEU). Typical loads are a mix of 20-foot (1-TEU) and 40-foot (2-TEU) ISO-standard containers, with the latter predominant. Today, about 90% of non-bulk cargo worldwide is transported by container ships, and the largest modern container ships can carry up to 24,000 TEU (e.g., '' Ever Ace''). Container ships now rival crude oil tankers and bulk carriers as the largest commercial seaborne vessels. History There are two main types of dry cargo: bulk cargo and break bulk cargo. Bulk cargoes, like grain or coal, are transported unpackaged in the hull of the ship, generally in large volume. Break-bulk car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pneumatic
Pneumatics (from Greek ‘wind, breath’) is a branch of engineering that makes use of gas or pressurized air. Pneumatic systems used in Industrial sector, industry are commonly powered by compressed air or compressed inert gases. A centrally located and electrically-powered Gas compressor, compressor powers Pneumatic cylinder, cylinders, air motors, pneumatic actuators, and other pneumatic devices. A pneumatic system controlled through manual or automatic solenoid valves is selected when it provides a lower cost, more flexible, or safer alternative to electric motors, and hydraulic actuators. Pneumatics also has applications in dentistry, construction, mining, and other areas. Gases used in pneumatic systems Pneumatic systems in fixed installations, such as factories, use compressed air because a sustainable supply can be made by compressing Atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric air. The air usually has moisture removed, and a small quantity of oil is added at the compressor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
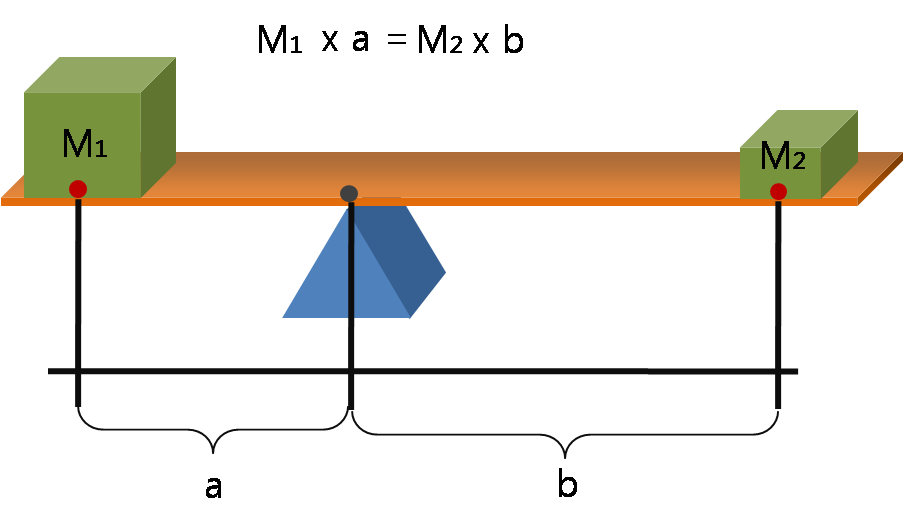
Lever
A lever is a simple machine consisting of a beam or rigid rod pivoted at a fixed hinge, or ''fulcrum''. A lever is a rigid body capable of rotating on a point on itself. On the basis of the locations of fulcrum, load and effort, the lever is divided into three types. Also, leverage is mechanical advantage gained in a system. It is one of the six simple machines identified by Renaissance scientists. A lever amplifies an input force to provide a greater output force, which is said to provide leverage. The ratio of the output force to the input force is the mechanical advantage of the lever. As such, the lever is a mechanical advantage device, trading off force against movement. Etymology The word "lever" entered English around 1300 from Old French, in which the word was ''levier''. This sprang from the stem of the verb ''lever'', meaning "to raise". The verb, in turn, goes back to the Latin ''levare'', itself from the adjective ''levis'', meaning "light" (as in "not heavy"). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Worm Gear
A worm drive is a gear arrangement in which a worm (which is a gear in the form of a screw) meshes with a worm wheel (which is similar in appearance to a spur gear). The two elements are also called the worm screw and worm gear. The terminology is often confused by imprecise use of the term ''worm gear'' to refer to the worm, the worm wheel, or the worm drive as a unit. The worm drive or "endless screw" was invented by either Archytas of Terentum, Apollonius of Perga, or Archimedes, the last one being the most probable author.Witold Rybczynski, '' One good turn : a natural history of the screwdriver and the screw''. London, 2000. Page 139. The worm drive later appeared in the Indian subcontinent, for use in roller cotton gins, during the Delhi Sultanate in the thirteenth or fourteenth centuries.Irfan Habib''Economic History of Medieval India, 1200–1500'', page 53 Pearson Education Explanation A gearbox designed using a worm and worm wheel is considerably smaller than on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engine Starter
A starter (also self-starter, cranking motor, or starter motor) is a device used to rotate (crank) an internal-combustion engine so as to initiate the engine's operation under its own power. Starters can be electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic. The starter can also be another internal-combustion engine in the case, for instance, of very large engines, or diesel engines in agricultural or excavation applications. Internal combustion engines are feedback systems, which, once started, rely on the inertia from each cycle to initiate the next cycle. In a four-stroke engine, the third stroke releases energy from the fuel, powering the fourth (exhaust) stroke and also the first two (intake, compression) strokes of the next cycle, as well as powering the engine's external load. To start the first cycle at the beginning of any particular session, the first two strokes must be powered in some other way than from the engine itself. The starter motor is used for this purpose and it is not req ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Engineer (UK Magazine)
''The Engineer'' is a London-based monthly magazine and website covering the latest developments and business news in engineering and technology in the UK and internationally. History and description ''The Engineer'' was founded in January 1856. It was established by Edward Charles Healey, an entrepreneur and engineering enthusiast with financial interests in the railways whose friends included Robert Stephenson and Isambard Kingdom Brunel. The journal was created as a technical magazine for engineers. ''The Engineer'' began covering engineering including inventions and patents during a high point of British economic manufacturing power. In the 19th century it also published stock prices of raw materials. Together with the contemporary ''Engineering'' journal the work is considered a valuable historical resource for the study of British economic history. On 10 July 2012 the magazine announced its final print edition, the editor Jon Excell citing "increasing distribution and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musgrave Non-dead-centre Engine
Musgrave's ''non-dead-centre'' engine was a stationary steam engine of unusual design, intended to solve the problem of stopping on dead centre. It was designed in 1887 to serve as a marine engine. It used a pair of linked cylinders to prevent the engine from stopping in a position where no turning force can be applied. At least one engine is known to survive. Dead centres The ' dead centre' of a piston engine with cranks is when the piston is at the ''exact'' top or bottom of the stroke and so the piston cannot exert any torque on the crankshaft. If a steam engine stops on dead centre, it will be unable to restart from that position. Several solutions to this have been applied. One of the simplest is to try not to stop in this position, the crudest to apply a strong arm with a crowbar to turn the engine over a little. Small steam barring engines were also used to move the engine away from dead centre before starting. If the engine has multiple cylinders, most geometries for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |