|
Barlow Rail
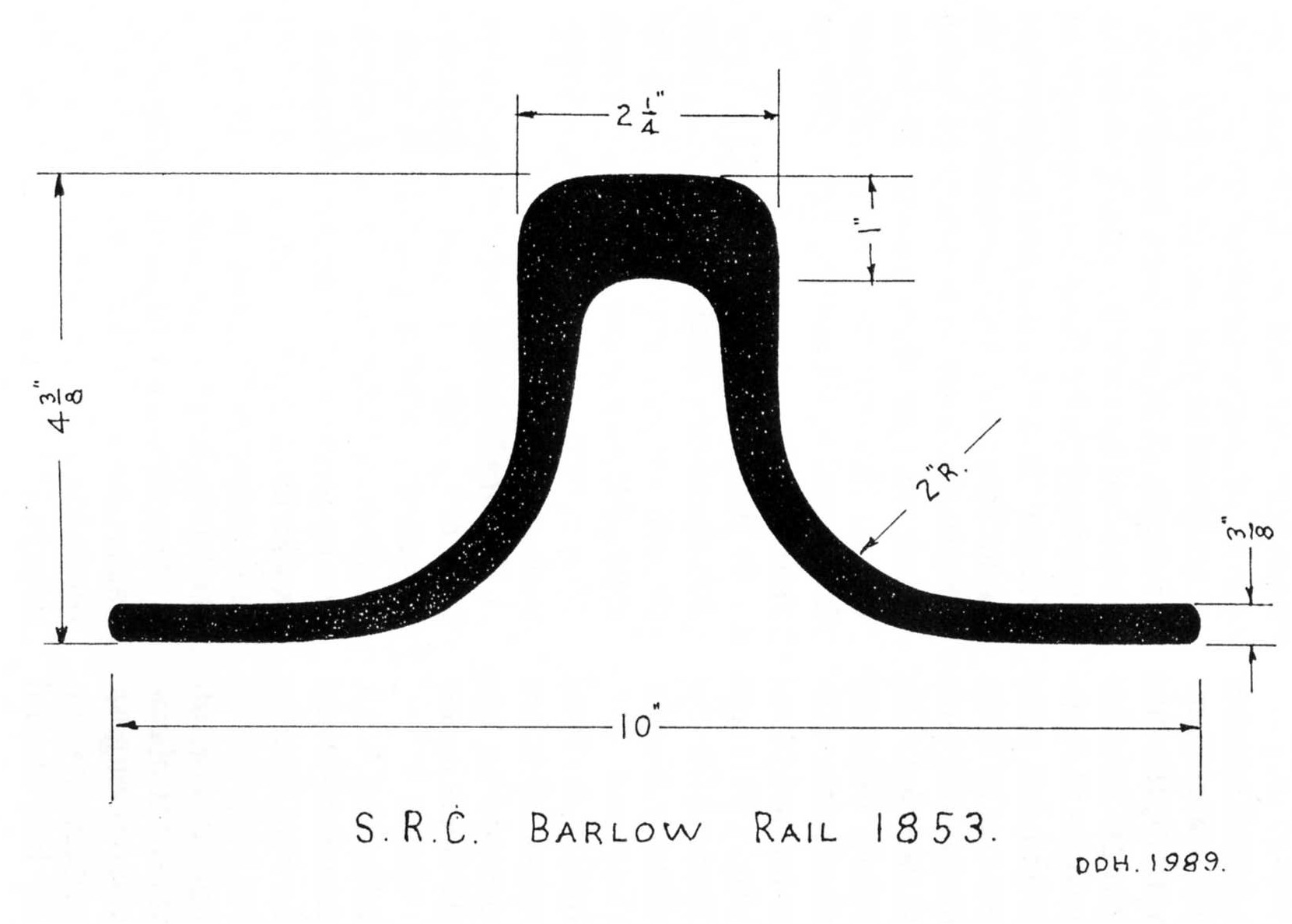
Barlow rail was a rolled rail section used on early railways. It has wide flaring feet and was designed to be laid direct on the ballast, without requiring sleepers. It was widely adopted on lightly trafficked railways, but was ultimately unsuccessful because of maintenance difficulties. It resembles the bridge rail used for Brunel's baulk road, but was of tapering form, rather than with the flat base of the heavier bridge rail intended for laying onto timber. Usage In the mid-nineteenth century, railway networks were expanding into areas where lighter traffic was expected. The first cost of conventional railway track was considerable, and cheaper alternatives were sought. The Barlow rail offered this benefit, by avoiding the cost of sleepers and chairs altogether. Laid directly in the ballast, it required no other ancillary equipment; however the rail itself was significantly heavier and more expensive than conventional rails. In practice it had several disadvantages; in partic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New South Wales Government Railways
The New South Wales Government Railways (NSWGR) was the agency of the Government of New South Wales that administered rail transport in New South Wales, Australia, between 1855 and 1932. Management The agency was managed by a range of different commission structures between 1857 and 1932, which reported to either the Minister for Public Works or the Minister for Transport. The inaugural Chief Commissioner was Ben Martindale and, following the enactment of the he became Commissioner of Railways. John Rae succeeded Martindale in 1861, and in 1877 Charles Goodchap was appointed Commissioner. The set up a corporate body of three railway commissioners to manage the railways and remove them from political influence, resulting in the resignation of Goodchap. This Board of Railway Commissioners of New South Wales was in place from 22 October 1888 to 4 April 1907, and was replaced by a sole Chief Commissioner of Railways and Tramways until 22 March 1932, when a panel arrangement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shipton On Cherwell
Shipton-on-Cherwell is a village on the River Cherwell about north of Kidlington in Oxfordshire, England. The village is part of the civil parish of Shipton-on-Cherwell and Thrupp. Manor The earliest known record of Shipton-on-Cherwell is from 1005, when an estate at Shipton was granted to the Benedictine Eynsham Abbey. Shortly before or after the Norman conquest of England an estate of five hides at Shipton seems to have been transferred from Eynsham to another Benedictine religious house, Evesham Abbey. However, after the death of Evesham's Abbot Æthelwig in 1077 or 1078 William of Normandy's half-brother Odo, Bishop of Bayeux took Shipton from Æthelwig's successor Walter. By the time of the Domesday Book in 1086, Odo had only 2½ hides at Shipton and these were let to Ilbert de Lacy. Hugh de Grandmesnil held the other 2½ hides and it is not clear whether the estate had been divided before or after the Conquest. Shipton Manor House was built in the 16th or 17th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Devon Railway Company
The South Devon Railway Company built and operated the railway from Exeter to Plymouth and Torquay in Devon, England. It was a broad gauge railway built by Isambard Kingdom Brunel. The line had to traverse difficult hilly terrain, and the company adopted the atmospheric system in which trains were drawn by a piston in a tube laid between the rails, a vacuum being created by stationary engines. The revolutionary system proved to have insuperable technical difficulties and was abandoned. The line continued as a conventional locomotive railway. The company promoted a number of branches, through the medium of nominally independent companies. Its original main line between Exeter and Plymouth remains in use today as an important part of the main line between London and Plymouth. Chronology * 1844 South Devon Railway Act passed by Parliament * 1846 opened to Newton Abbot * 1847 opened to Totnes, atmospheric trains start running * 1848 atmospheric trains withdrawn, Torquay branch o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxfordshire
Oxfordshire is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in the north west of South East England. It is a mainly rural county, with its largest settlement being the city of Oxford. The county is a centre of research and development, primarily due to the work of the University of Oxford and several notable science parks. These include the Harwell Science and Innovation Campus and Milton Park, both situated around the towns of Didcot and Abingdon-on-Thames. It is a landlocked county, bordered by six counties: Berkshire to the south, Buckinghamshire to the east, Wiltshire to the south west, Gloucestershire to the west, Warwickshire to the north west, and Northamptonshire to the north east. Oxfordshire is locally governed by Oxfordshire County Council, together with local councils of its five non-metropolitan districts: City of Oxford, Cherwell, South Oxfordshire, Vale of White Horse, and West Oxfordshire. Present-day Oxfordshire spanning the area south of the Thames was h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Didcot Railway Centre
Didcot Railway Centre is a railway museum and preservation engineering site in Didcot, Oxfordshire, England. The site was formerly a Great Western Railway engine shed and locomotive stabling point. Background The founders and commercial backers of the Great Western Railway (GWR) supported Isambard Kingdom Brunel's scheme to develop an integrated railway and steamship service which allowed trans-Atlantic passengers and freight quicker passage between London and New York City. However, whilst backing the scheme the railway had to make a profit, and so it took a number of detours and added both mainline and branch line traffic to increase its domestic earnings. This earned the railway the nickname ''The Great Way Round'' from its detractors. Whilst the route from London Paddington to Reading was relatively straight, the then obvious most direct route to Bristol would have taken the railway further south, thus avoiding both Didcot and Swindon. However, passenger and freight traffic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria (Australia)
Victoria is a state in southeastern Australia. It is the second-smallest state with a land area of , the second most populated state (after New South Wales) with a population of over 6.5 million, and the most densely populated state in Australia (28 per km2). Victoria is bordered by New South Wales to the north and South Australia to the west, and is bounded by the Bass Strait to the south (with the exception of a small land border with Tasmania located along Boundary Islet), the Great Australian Bight portion of the Southern Ocean to the southwest, and the Tasman Sea (a marginal sea of the South Pacific Ocean) to the southeast. The state encompasses a range of climates and geographical features from its temperate coastal and central regions to the Victorian Alps in the northeast and the semi-arid north-west. The majority of the Victorian population is concentrated in the central-south area surrounding Port Phillip Bay, and in particular within the metropolit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geelong
Geelong ( ) (Wathawurrung: ''Djilang''/''Djalang'') is a port city in the southeastern Australian state of Victoria, located at the eastern end of Corio Bay (the smaller western portion of Port Phillip Bay) and the left bank of Barwon River, about southwest of Melbourne, the state capital of Victoria. Geelong is the second largest Victorian city (behind Melbourne) with an estimated urban population of 268,277 as of June 2018, Estimated resident population, 30 June 2018. and is also Australia's second fastest-growing city. Geelong is also known as the "Gateway City" due to its critical location to surrounding western Victorian regional centres like Ballarat in the northwest, Torquay, Great Ocean Road and Warrnambool in the southwest, Hamilton, Colac and Winchelsea to the west, providing a transport corridor past the Central Highlands for these regions to the state capital Melbourne in its northeast. The City of Greater Geelong is also a member of thGateway Cities Allian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geelong And Melbourne Railway Company
The Geelong and Melbourne Railway Company was a railway company in Victoria, Australia. Alexander Thomson, a member of the Victorian Legislative Council, introduced and mentored a bill to incorporate the Geelong and Melbourne Railway Company. On 8 February 1853, the operation of Melbourne and Geelong Railway Company and Mount Alexander and Murray River Railway Company was approved by the Victoria Government. Thomson was one of the directors and presided at the first shareholder meeting. Work began at the Geelong end in 1854 but progress was slow due to a labour shortage caused by the Victorian gold rush, so the Victorian government hired out 100 prisoners to the company at a daily rate of five shillings each. They were housed in prison hulks moored in Corio Bay. English engineer and surveyor, Edward Snell, undertook the survey and design of the line, including a station and extensive workshops at Geelong, and a number of bluestone and timber bridges. Geelong and Melbourne Ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locomotive No
A locomotive or engine is a rail transport vehicle that provides the Power (physics), motive power for a train. If a locomotive is capable of carrying a payload, it is usually rather referred to as a multiple unit, Motor coach (rail), motor coach, railcar or power car; the use of these self-propelled vehicles is increasingly common for passenger trains, but rare for freight (see CargoSprinter). Traditionally, locomotives pulled trains from the front. However, Push-pull train, push-pull operation has become common, where the train may have a locomotive (or locomotives) at the front, at the rear, or at each end. Most recently railroads have begun adopting DPU or distributed power. The front may have one or two locomotives followed by a mid-train locomotive that is controlled remotely from the lead unit. __TOC__ Etymology The word ''locomotive'' originates from the Latin language, Latin 'from a place', Ablative case, ablative of 'place', and the Medieval Latin 'causing mot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Powerhouse Museum
The Powerhouse Museum is the major branch of the Museum of Applied Arts & Sciences (MAAS) in Sydney, the others being the historic Sydney Observatory at Observatory Park, Sydney, Observatory Hill, and the newer Museums Discovery Centre at Castle Hill, New South Wales, Castle Hill. Although often described as a science museum, the Powerhouse has a diverse collection encompassing all sorts of technology including decorative arts, science, communication, transport, costume, furniture, mass media, media, computer technology, space technology and steam engines. The museum has existed in various guises for over 125 years, previously named the Technological, Industrial and Sanitary Museum of New South Wales (1879–1882) and the Technological Museum (August 1893 – March 1988). the collection contains over 500,000 objects collected over the last 135 years, many of which are displayed or housed at the site it has occupied since 1988, and for which it is named – a converted electric t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



Oct2001.jpg)




