|
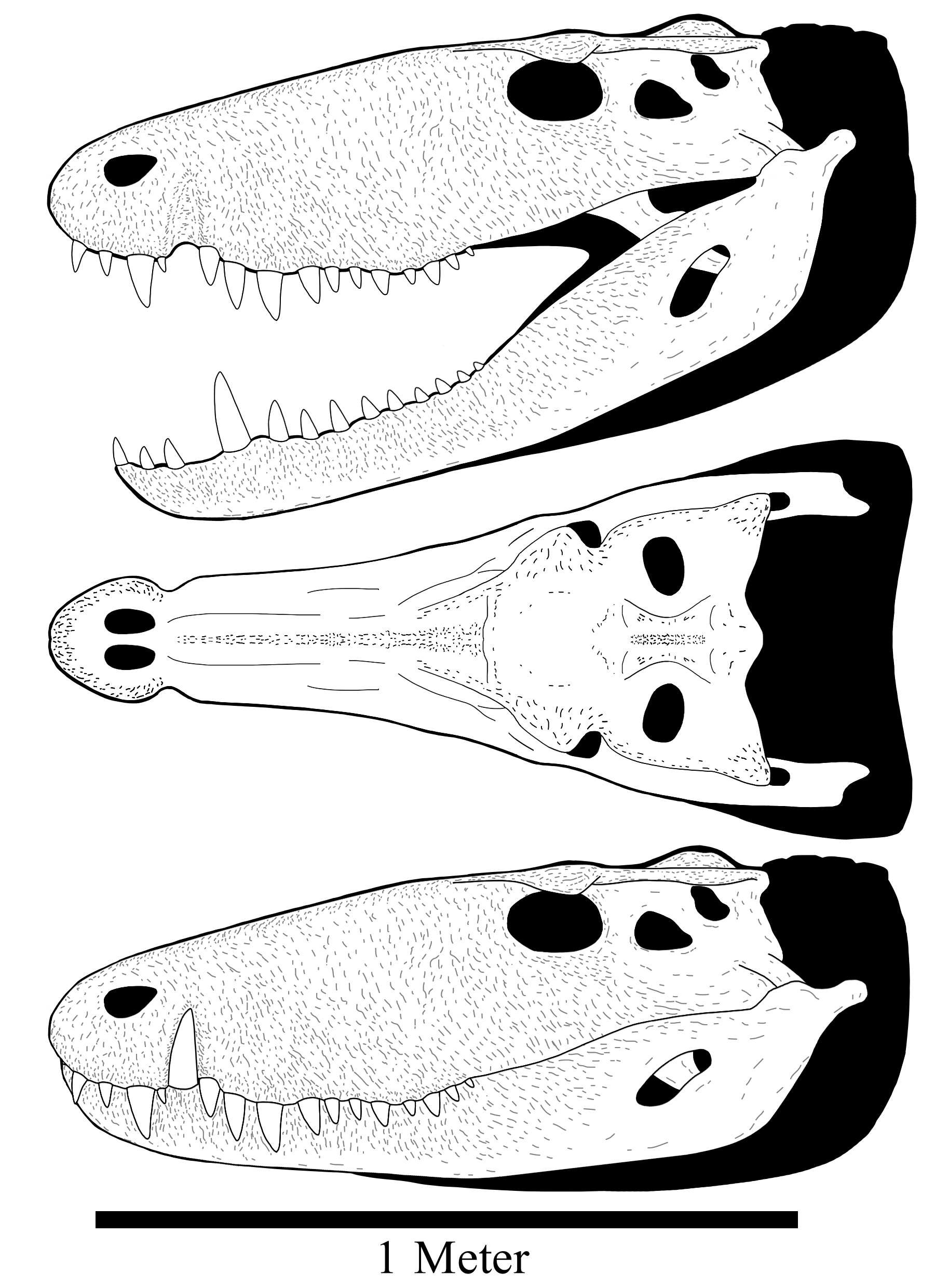
Barinasuchus
''Barinasuchus'' (meaning " Barinas crocodile," in reference to where the type material was found) is an extinct genus of sebecid mesoeucrocodylian. Its fossils have been found in middle Eocene-age rocks of the Divisadero Largo Formation of Argentina, middle Miocene-age rocks of the Ipururo Formation of Peru, and middle Miocene-age rocks of the Parángula Formation of Venezuela.''Barinasuchus'' at .org Description ''Barinasuchus'' was described in 2007 by Alfredo Paolillo and Omar Linares. The comes ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Largest Prehistoric Animals
The largest prehistoric animals include both vertebrate and invertebrate species. Many of them are described below, along with their typical range of size (for the general dates of extinction, see the link to each). Many species mentioned might not actually be the largest representative of their clade due to the incompleteness of the fossil record and many of the sizes given are merely estimates since no complete specimen have been found. Their body mass, especially, is largely conjecture because soft tissue was rarely fossilized. Generally the size of extinct species was subject to energetic and biomechanical constraints. Non-mammalian synapsids (Synapsida) Caseasaurs (Caseasauria) The herbivorous ''Alierasaurus'' was the largest caseid and the largest amniote to have lived at the time, with an estimated length around . '' Cotylorhynchus hancocki'' is also large, with an estimated length and weight of at least and more than . Edaphosaurids (Edaphosauridae) The larges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2007 In Paleontology
Plants *A fossilized rainforest is discovered in a coal mine. Angiosperms Fungi newly named Arthropoda New taxa Fish Bony fish * * * Cartilaginous fish * Archosauromorphs Pseudosuchians Pterosaurs Newly named non-dinosaurian dinosauromorphs Newly named non-avian dinosauromorphs Data courtesy of George Olshevky's dinosaur genera list. Newly named birds Lepidosauromorpha Plesiosaurs * * Synapsids Non-mammalian Mammals Footnotes Complete author list As science becomes more collaborative, papers with large numbers of authors are becoming more common. To prevent the deformation of the tables, these footnotes list the contributors to papers that erect new genera and have many authors. References {{Portal, Paleontology 2007 in paleontology, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divisaderan
The Divisaderan age is a South American land mammal age, covering a period of geologic time (42.0–36.0 Ma) within the Middle and Late Eocene epochs of the Paleogene. It follows the Mustersan age and is followed by the Tinguirirican age.Divisaderan at .org Etymology The age is named after the Divisadero Largo Formation of Divisadero Largo, Mendoza, |
Laventan
The Laventan ( es, Laventense) age is a period of geologic time (13.8 to 11.8 Ma) within the Middle Miocene epoch of the Neogene, used more specifically within the SALMA classification in South America. It follows the Colloncuran and precedes the Mayoan age.Madden et al., 1997 Etymology The age is named after the Miocene Lagerstätte La Venta, where a rich biodiversity from the Middle Miocene has been recovered from the Honda Group. Formations Fossil content Correlations The Laventan (13.8 to 11.8 Ma) correlates with: * NALMA ** latest Barstovian (15.97-13.65 Ma)Barstovian at Fossilworks.org ** early |
Notosuchia
Notosuchia is a suborder of primarily Gondwanan mesoeucrocodylian crocodylomorphs that lived during the Jurassic and Cretaceous. Some phylogenies recover Sebecosuchia as a clade within Notosuchia, others as a sister group (see below); if Sebecosuchia is included within Notosuchia its existence is pushed into the Middle Miocene, about 11 million years ago. Fossils have been found from South America, Africa, Asia, and Europe. Notosuchia was a clade of terrestrial crocodilians that evolved a range of feeding behaviours, including herbivory ('' Chimaerasuchus''), omnivory (''Simosuchus''), and terrestrial hypercarnivory (''Baurusuchus''). It included many members with highly derived traits unusual for crocodylomorphs, including mammal-like teeth, flexible bands of shield-like body armor similar to those of armadillos (''Armadillosuchus''), and possibly fleshy cheeks and pig-like snouts (''Notosuchus''). The suborder was first named in 1971 by Zulma Gasparini and has since undergone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sebecid
Sebecidae is an extinct family of prehistoric terrestrial sebecosuchian crocodylomorphs. The oldest known member of the group is ''Ogresuchus furatus'' known from the Upper Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) Tremp Formation (Spain). Sebecids were diverse, abundant and broadly distributed in South America (mostly in Argentina, Brazil and Bolivia) during the Cenozoic, until the Middle Miocene; although it has been suggested that at least some forms could have survived until the Miocene-Pliocene boundary in Brazil. This group included many medium- and large-sized genera, from ''Sebecus'' to a giant indeterminate unnamed species from the Miocene. Phylogeny The following cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to d ... simplified after Diego Pol and Jaime E. Powell (2011). Refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sebecus
''Sebecus'' (meaning " Sebek" in Latin) is an extinct genus of sebecid crocodylomorph from Eocene of South America. Like other sebecosuchians, it was entirely terrestrial and carnivorous. The genus is currently represented by two species, the type ''S. icaeorhinus'' and ''S. ayrampu''. Several other species have been referred to ''Sebecus'', but were later reclassified as their own genera. History and species Named by American paleontologist George Gaylord Simpson in 1937, ''Sebecus'' was one of the first known sebecosuchians. Simpson described the type species, ''S. icaeorhinus'', from a fragmented skull and lower jaw found in the Sarmiento Formation. The specimen was discovered by the American Museum of Natural History's First Scarritt Expedition to Patagonia, during 1930 and 1931. Teeth had been known since 1906 when Argentine paleontologist Florentino Ameghino associated them with carnivorous dinosaurs. The more complete material found by Simpson firmly established that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratiotosuchus
''Stratiotosuchus'' (from Greek, (stratiōtēs, "soldier") and (suchos, "crocodile")) is an extinct genus of baurusuchid mesoeucrocodylian from the Adamantina Formation in Brazil. It lived during the Late Cretaceous. The first fossils were found in the 1980s, and the type species ''Stratiotosuchus maxhechti'' was named in 2001. A hyperpredator, it and other baurusuchids may have filled niches occupied elsewhere by theropod dinosaurs. Description ''Stratiotosuchus'' has a deep, laterally compressed skull long. ''Stratiotosuchus'' reached up to in total length (including tail), making it about the same size as ''Baurusuchus''. The teeth are ziphodont, meaning that they are laterally compressed, curved, and serrated. Like other baurusuchids, ''Stratiotosuchus'' has a reduced number of teeth: three in its premaxilla and five in its maxilla. When the jaw is closed, the teeth of the upper jaw overlie those of the lower jaw and shear closely together. ''Stratiotosuchus'' has on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crocodylus Porosus
The saltwater crocodile (''Crocodylus porosus'') is a crocodilian native to saltwater habitats and brackish wetlands from India's east coast across Southeast Asia and the Sundaic region to northern Australia and Micronesia. It has been listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List since 1996. It was hunted for its skin throughout its range up to the 1970s, and is threatened by illegal killing and habitat loss. It is regarded as dangerous to humans. The saltwater crocodile is considered to be the largest living reptile. Males can grow up to a length of , rarely exceeding , and a weight of . Females are much smaller and rarely surpass . It is also called the estuarine crocodile, Indo-Pacific crocodile, marine crocodile, sea crocodile, and informally as the saltie. A large and opportunistic hypercarnivorous apex predator, they ambush most of their prey and then drown or swallow it whole. They are capable of prevailing over almost any animal that enters their territory, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', "dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope Carbon-13, 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope Carbon-12, 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Popigai impact structure, Siberia and in what is now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saltwater Crocodile
The saltwater crocodile (''Crocodylus porosus'') is a crocodilian native to saltwater habitats and brackish wetlands from India's east coast across Southeast Asia and the Sundaic region to northern Australia and Micronesia. It has been listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List since 1996. It was hunted for its skin throughout its range up to the 1970s, and is threatened by illegal killing and habitat loss. It is regarded as dangerous to humans. The saltwater crocodile is considered to be the largest living reptile. Males can grow up to a length of , rarely exceeding , and a weight of . Females are much smaller and rarely surpass . It is also called the estuarine crocodile, Indo-Pacific crocodile, marine crocodile, sea crocodile, and informally as the saltie. A large and opportunistic hypercarnivorous apex predator, they ambush most of their prey and then drown or swallow it whole. They are capable of prevailing over almost any animal that enters their territory, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |