|
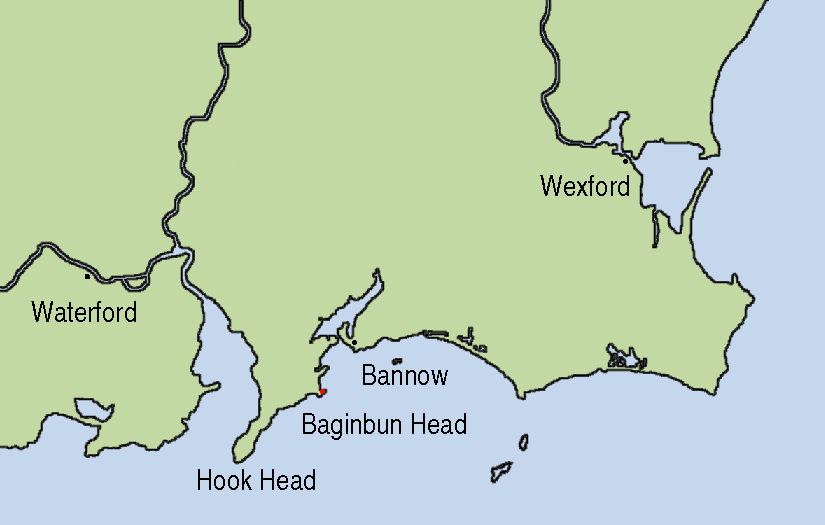
Bannow
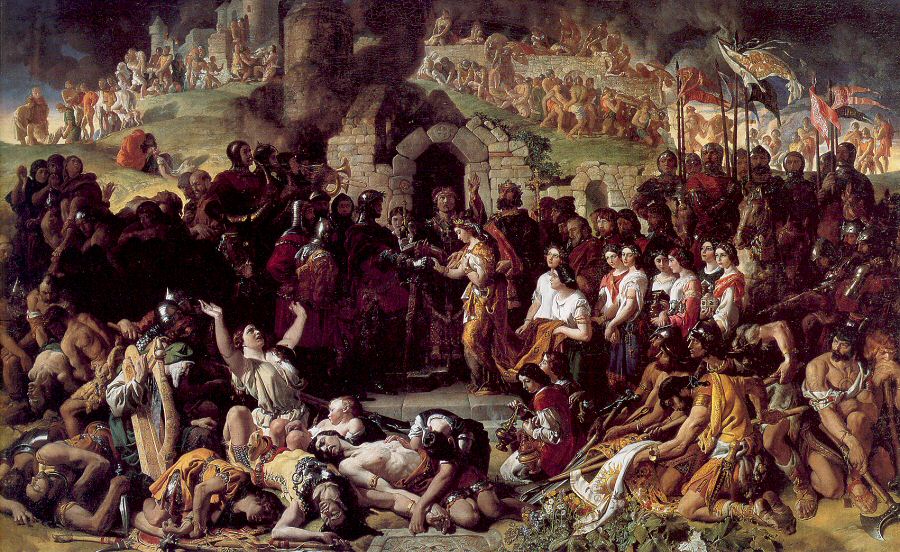
Bannow () is a village and civil parish lying east of Bannow Bay on the south-west coast of County Wexford, Ireland. In modern times the main settlement is the village of Carrig-on-Bannow (or ''Carrig''). In Norman times there was a borough called Bannow on Bannow Island at the mouth of the Bay. This town has since disappeared, probably due to the silting up of the natural harbour channels in the 14th century, and the former island is now attached to the rest of the parish. History It is believed that the Vikings had a strong early presence in the area, due to the survival of numerous Norse place-names in the locality. The Norman conquest of Ireland began in Bannow Bay in 1169, when three ships commanded by Robert Fitz-Stephen arrived at the behest of Diarmait MacMurrough to support his claim to the Kingdom of Leinster. Another group of Normans under Raymond le Gros landed the following year on the far side of Bannow Bay, on the Hook Peninsula at Baginbun, which was then cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Wexford
County Wexford ( ga, Contae Loch Garman) is a county in Ireland. It is in the province of Leinster and is part of the Southern Region. Named after the town of Wexford, it was based on the historic Gaelic territory of Hy Kinsella (''Uí Ceinnsealaigh''), whose capital was Ferns. Wexford County Council is the local authority for the county. The population of the county was 149,722 at the 2016 census. History The county is rich in evidence of early human habitation.Stout, Geraldine. "Essay 1: Wexford in Prehistory 5000 B.C. to 300 AD" in ''Wexford: History and Society'', pp 1 - 39. ''Portal tombs'' (sometimes called dolmens) exist at Ballybrittas (on Bree Hill) and at Newbawn — and date from the Neolithic period or earlier. Remains from the Bronze Age period are far more widespread. Early Irish tribes formed the Kingdom of Uí Cheinnsealaig, an area that was slightly larger than the current County Wexford. County Wexford was one of the earliest areas of Ireland to be C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bannow (Parliament Of Ireland Constituency)
Bannow was a constituency represented in the Irish House of Commons to 1800. Borough This constituency was the parliamentary borough of Bannow in County Wexford. History In the Patriot Parliament of 1689 summoned by James II, Bannow was represented with two members. Following the Act of Union 1800 the borough was disenfranchised. Members of Parliament *1634–1635: Pierce Neville and Walter Furlong (or Walter Stapleton) *1639–1649: Christopher Hollywood (expelled 1642) and Gerald Cheevers (expelled 1642) *1661–1666: Dr Dudley Loftus and Henry Warren 1689–1801 Notes References Bibliography * * * Johnston-Liik, E. M. (2002). History of the Irish Parliament, 1692–1800., Publisher: Ulster Historical Foundation (28 Feb 2002), *T. W. Moody Theodore William Moody (26 November 1907 – 11 February 1984) was a historian from Belfast, Northern Ireland. Background Early life Moody was born in Belfast, to a poor family who made their living from dressmaking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman Conquest Of Ireland
The Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland took place during the late 12th century, when Anglo-Normans gradually conquered and acquired large swathes of land from the Irish, over which the kings of England then claimed sovereignty, all allegedly sanctioned by the Papal bull ''Laudabiliter''. At the time, Gaelic Ireland was made up of several kingdoms, with a High King claiming lordship over most of the other kings. The Norman invasion was a watershed in Ireland's history, marking the beginning of more than 800 years of direct English and, later, British, involvement in Ireland. In May 1169, Anglo-Norman mercenaries landed in Ireland at the request of Diarmait mac Murchada (Dermot MacMurragh), the deposed King of Leinster, who sought their help in regaining his kingship. They achieved this within weeks and raided neighbouring kingdoms. This military intervention was sanctioned by King Henry II of England. In return, Diarmait had sworn loyalty to Henry and promised land to the Normans. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Fitz-Stephen
Robert FitzStephen (died 1183) was a Cambro-Norman soldier, one of the leaders of the Norman invasion of Ireland, for which he was granted extensive lands in Ireland. He was a son of the famous Nest, daughter of Rhys ap Tewdwr, the last king of Deheubarth (South Wales). His father was Nest's second husband, Stephen, Constable of Cardigan ( cy, Aberteifi). Following the death of her first husband, Gerald de Windsor, her sons had married her to Stephen, her husband's constable for Cardigan. By Stephen, she had another son, possibly two; the eldest was Robert, and the younger may have been Hywel. Career In Wales Robert succeeded his father in his office (''Custos Campe Abertivi''). He first appears in history in 1157, when King Henry II of England invaded Gwynedd. While the main royal army faced the forces of Owain Gwynedd east of the River Conwy, a force including Robert and his half-brother Henry Fitzroy (the illegitimate son of Nest and King Henry I) attacked Anglesey by sea. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diarmait MacMurrough
Diarmait Mac Murchada (Modern Irish: Diarmaid Mac Murchadha), anglicised as Dermot MacMurrough, Dermod MacMurrough, or Dermot MacMorrogh (c. 1110 – c. 1 May 1171), was a King of Leinster in Ireland. In 1167, he was deposed by the High King of Ireland, Ruaidrí Ua Conchobair (Rory O'Connor). The grounds for the deposition were that Mac Murchada had, in 1152, abducted Derbforgaill, the wife of the king of Breifne, Tiernan O'Rourke ( ga, Tighearnán Ua Ruairc). To recover his kingdom, Mac Murchada solicited help from King Henry II of England. His issue unresolved, he gained the military support of the 2nd Earl of Pembroke (Richard de Clare, nicknamed "Strongbow"). At that time, Strongbow was in opposition to Henry II due to his support for Stephen, King of England against Henry's mother in the Anarchy. In exchange for his aid, Strongbow was promised in marriage to Mac Murchada's daughter Aoife with the right to succeed to the Kingship of Leinster. Henry II then mounted a larger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hook Peninsula
The Hook Peninsula is a peninsula in County Wexford, Ireland. It has been a gateway to south-east Ireland for successive waves of newcomers, including the Vikings, Anglo-Normans and the English. The coastline has a number of beaches. The peninsula's fishing villages, bird watching on the mudflats of Bannow Estuary, deep sea angling, snorkeling and swimming are part of the area's maritime life. The area's rivers, valleys, estuaries and hills have long provided south-west Wexford with rich grazing land. See also * Hook Head, headland on the peninsula * Hook Lighthouse, at the tip of the peninsula * Fethard-on-Sea, a village * Duncannon, a village * Loftus Hall, a country house * Slade Slade are an English rock band formed in Wolverhampton in 1966. They rose to prominence during the glam rock era in the early 1970s, achieving 17 consecutive top 20 hits and six number ones on the UK Singles Chart. The ''British Hit Singles ..., a village overlooked by Slade Castle Furt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borough Constituency
In the United Kingdom (UK), each of the electoral areas or divisions called constituencies elects one member to the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons. Within the United Kingdom there are five bodies with members elected by electoral districts called "constituency, constituencies" as opposed to "Ward (electoral subdivision), wards": * The House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons (see Constituencies of the Parliament of the United Kingdom) * The Scottish Parliament (see Scottish Parliament constituencies and regions) * The Senedd Cymru – Welsh Parliament, Senedd (see National Assembly for Wales constituencies and electoral regions, Senedd constituencies and electoral regions) * The Northern Ireland Assembly (see Northern Ireland Assembly constituencies) * The London Assembly (see List of London Assembly constituencies) Between 1921 and 1973 the following body also included members elected by constituencies: * The Parliament of Northern Irela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parliament Of Ireland
The Parliament of Ireland ( ga, Parlaimint na hÉireann) was the legislature of the Lordship of Ireland, and later the Kingdom of Ireland, from 1297 until 1800. It was modelled on the Parliament of England and from 1537 comprised two chambers: the House of Commons and the House of Lords. The Lords were members of the Irish peerage (’lords temporal’) and bishops (’ lords spiritual’; after the Reformation, Church of Ireland bishops). The Commons was directly elected, albeit on a very restricted franchise. Parliaments met at various places in Leinster and Munster, but latterly always in Dublin: in Christ Church Cathedral (15th century),Richardson 1943 p.451 Dublin Castle (to 1649), Chichester House (1661–1727), the Blue Coat School (1729–31), and finally a purpose-built Parliament House on College Green. The main purpose of parliament was to approve taxes that were then levied by and for the Dublin Castle administration. Those who would pay the bulk of taxation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raymond FitzGerald
Raymond (or Redmond) Fitz William Fitz Gerald (died 1185–1198), nicknamed ''Le Gros'' ("the Large"), was a Cambro-Norman commander during the Norman invasion of Ireland. Raymond was among the first of a small band of Norman knights who landed on the South coast of Ireland before being reinforced by a larger force led by Richard de Clare, 2nd Earl of Pembroke. He was active consolidating Norman rule over Ireland before he retired to his estates in Waterford where he died in the late 12th century. Family and youth Raymond grew up in Wales, and was a grandson of Princess Nest ferch Rhys, daughter of Rhys ap Tewdwr, the last independent Prince of South Wales. His father was William FitzGerald, Lord of Carew. Career He was sent by Strongbow to Ireland in 1170, and landed at Baginbun Head at the Hook Peninsula, near Waterford, where he was besieged in his entrenchments by the combined Irish and Ostmen, whom he repulsed. Although vastly outnumbered in this battle, (his cousi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiler Fitzhenry
Meiler FitzHenry (sometimes spelled Meilyr; died 1220) was a Cambro-Norman nobleman and Lord Chief Justice of Ireland during the Lordship of Ireland. Background and early life Meilyr FitzHenry was the son of Henry FitzHenry, an illegitimate son of King Henry I, by Nest, daughter of Rhys ap Tewdwr, the last king of Deheubarth (South Wales). He was thus related to the noblest Norman and native families of South Wales. Robert Fitz-Stephen, Maurice FitzGerald, David FitzGerald, bishop of St. David's, and William FitzGerald of Carew were his uncles. Meilyr's cousins included Raymond le Gros, Gerald of Wales, prince Rhys ap Gruffydd, the famous Lord Rhys, as well as Henry II. In 1158 his father, Henry FitzHenry, was killed in battle during Henry II's campaign in Wales. Meilyr, Henry's oldest son, succeeded to his father's possessions of Narberth and Pebidiog, the central and north-eastern parts of the modern Pembrokeshire. In Ireland In 1169 he accompanied his uncle Robert Fitz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chancel
In church architecture, the chancel is the space around the altar, including the choir and the sanctuary (sometimes called the presbytery), at the liturgical east end of a traditional Christian church building. It may terminate in an apse. Overview The chancel is generally the area used by the clergy and choir during worship, while the congregation is in the nave. Direct access may be provided by a priest's door, usually on the south side of the church. This is one definition, sometimes called the "strict" one; in practice in churches where the eastern end contains other elements such as an ambulatory and side chapels, these are also often counted as part of the chancel, especially when discussing architecture. In smaller churches, where the altar is backed by the outside east wall and there is no distinct choir, the chancel and sanctuary may be the same area. In churches with a retroquire area behind the altar, this may only be included in the broader definition of chancel. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nave
The nave () is the central part of a church, stretching from the (normally western) main entrance or rear wall, to the transepts, or in a church without transepts, to the chancel. When a church contains side aisles, as in a basilica-type building, the strict definition of the term "nave" is restricted to the central aisle. In a broader, more colloquial sense, the nave includes all areas available for the lay worshippers, including the side-aisles and transepts.Cram, Ralph Adams Nave The Catholic Encyclopedia. Vol. 10. New York: Robert Appleton Company, 1911. Accessed 13 July 2018 Either way, the nave is distinct from the area reserved for the choir and clergy. Description The nave extends from the entry—which may have a separate vestibule (the narthex)—to the chancel and may be flanked by lower side-aisles separated from the nave by an arcade. If the aisles are high and of a width comparable to the central nave, the structure is sometimes said to have three naves. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |