|
Banksia Spinulosa
''Banksia spinulosa'', the hairpin banksia, is a species of woody shrub, of the genus ''Banksia'' in the family Proteaceae, native to eastern Australia. Widely distributed, it is found as an understorey plant in open dry forest or heathland from Victoria to northern Queensland, generally on sandstone though sometimes also clay soils. It generally grows as a small shrub to in height, though can be a straggly tree to . It has long narrow leaves with inflorescences which can vary considerably in coloration; while the spikes are gold or less commonly yellowish, the emergent styles may be a wide range of colours – from black, purple, red, orange or yellow. ''Banksia spinulosa'' was named by James Edward Smith in England in 1793, after being collected by John White, most likely in 1792. He gave it the common name prickly-leaved banksia, though this has fallen out of use. With four currently recognised varieties, the species has had a complicated taxonomic history, with two var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georges River National Park
Georges River National Park is a protected Australian National Park, under the management of the NSW National Parks and Wildlife Service. The park falls in the regions of the Sutherland Shire Council and Canterbury-Bankstown Council. Located in the city of Sydney, 25 km south-west of the CBD, surrounded by neighbouring suburbs of Lugano, Illawong, Alfords Point, Padstow Heights, Revesby Heights, Picnic Point and Sandy Point. The primary use of the park is to service for recreational activities such as; bush walking, picnics, barbeques, boating, fishing, and water/jet skiing. The park is Segmented into 15 sectors along the riverbanks of the Georges River, encompassing 514 hectares (1,270-acres), housing many native aquatic and terrestrial Australian flora and fauna. The traditional custodians are the Dharug people located on the north side of the river, and Dharawal people located on the south of the river. The park is legally protected under the National Parks and Wildlif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with currently about 69,963 species described. Vertebrates comprise such groups as the following: * jawless fish, which include hagfish and lampreys * jawed vertebrates, which include: ** cartilaginous fish (sharks, rays, and ratfish) ** bony vertebrates, which include: *** ray-fins (the majority of living bony fish) *** lobe-fins, which include: **** coelacanths and lungfish **** tetrapods (limbed vertebrates) Extant vertebrates range in size from the frog species ''Paedophryne amauensis'', at as little as , to the blue whale, at up to . Vertebrates make up less than five percent of all described animal species; the rest are invertebrates, which lack vertebral columns. The vertebrates traditionally include the hagfish, which do no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of Australia (series)
''Flora of Australia'' is a 59 volume series describing the vascular plants, bryophytes and lichens present in Australia and its external territories. The series is published by the Australian Biological Resources Study who estimate that the series when complete will describe over 20 000 plant species.Orchard, A. E. 1999. Introduction. In A. E. Orchard, ed. ''Flora of Australia - Volume 1'', 2nd edition pp 1-9. Australian Biological Resources Study It was orchestrated by Alison McCusker. Series Volume 1 of the series was published in 1981, a second extended edition was released in 1999. The series uses the Cronquist system of taxonomy. The ABRS also published the ''Fungi of Australia'', the ''Algae of Australia'' and the ''Flora of Australia Supplementary Series''. A new online ''Flora of Australia'' was launched by ABRS in 2017, and no more printed volumes will be published. Volumes published :1. Introduction (1st edition) 1981 :1. Introduction (2nd edition) 1999 Othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthesis
Anthesis is the period during which a flower is fully open and functional. It may also refer to the onset of that period. The onset of anthesis is spectacular in some species. In ''Banksia'' species, for example, anthesis involves the extension of the style far beyond the upper perianth parts. Anthesis of flowers is sequential within an inflorescence An inflorescence is a group or cluster of flowers arranged on a stem that is composed of a main branch or a complicated arrangement of branches. Morphologically, it is the modified part of the shoot of seed plants where flowers are formed o ..., so when the style and perianth are different colours, the result is a striking colour change that gradually sweeps along the inflorescence. Flowers with diurnal anthesis generally are brightly colored in order to attract diurnal insects, such as butterflies. Flowers with nocturnal anthesis generally are white or less colorful, and as such, they contrast more strongly with the night ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpel
Gynoecium (; ) is most commonly used as a collective term for the parts of a flower that produce ovules and ultimately develop into the fruit and seeds. The gynoecium is the innermost whorl of a flower; it consists of (one or more) ''pistils'' and is typically surrounded by the pollen-producing reproductive organs, the stamens, collectively called the androecium. The gynoecium is often referred to as the "female" portion of the flower, although rather than directly producing female gametes (i.e. egg cells), the gynoecium produces megaspores, each of which develops into a female gametophyte which then produces egg cells. The term gynoecium is also used by botanists to refer to a cluster of archegonia and any associated modified leaves or stems present on a gametophyte shoot in mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. The corresponding terms for the male parts of those plants are clusters of antheridia within the androecium. Flowers that bear a gynoecium but no stamens are called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tepal
A tepal is one of the outer parts of a flower (collectively the perianth). The term is used when these parts cannot easily be classified as either sepals or petals. This may be because the parts of the perianth are undifferentiated (i.e. of very similar appearance), as in ''Magnolia'', or because, although it is possible to distinguish an outer whorl of sepals from an inner whorl of petals, the sepals and petals have similar appearance to one another (as in ''Lilium''). The term was first proposed by Augustin Pyramus de Candolle in 1827 and was constructed by analogy with the terms "petal" and "sepal". (De Candolle used the term ''perigonium'' or ''perigone'' for the tepals collectively; today, this term is used as a synonym for ''perianth''.) p. 39. Origin Undifferentiated tepals are believed to be the ancestral condition in flowering plants. For example, '' Amborella'', which is thought to have separated earliest in the evolution of flowering plants, has flowers with undiffer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perianth
The perianth (perigonium, perigon or perigone in monocots) is the non-reproductive part of the flower, and structure that forms an envelope surrounding the sexual organs, consisting of the calyx (sepals) and the corolla (petals) or tepals when called a perigone. The term ''perianth'' is derived from Greek περί (, "around") and άνθος (, "flower"), while ''perigonium'' is derived from περί () and γόνος (, "seed, sex organs"). In the mosses and liverworts (Marchantiophyta), the perianth is the sterile tubelike tissue that surrounds the female reproductive structure (or developing sporophyte). Flowering plants In flowering plants, the perianth may be described as being either dichlamydeous/heterochlamydeous in which the calyx and corolla are clearly separate, or homochlamydeous, in which they are indistinguishable (and the sepals and petals are collectively referred to as tepals). When the perianth is in two whorls, it is described as biseriate. While the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnarvon Gorge
Carnarvon Gorge is located in the Southern Brigalow Belt bioregion in Central Queensland (Australia), 593 km northwest of Brisbane. Primarily created by water erosion, Carnarvon Gorge is around 30 kilometres long, located in Carnarvon National Park, and six hundred metres deep at the mouth. It is the most visited feature within Carnarvon National Park due to the diversity of experiences it contains and the ease with which it can be accessed. The closest towns are Injune and Rolleston. In 2009 as part of the Q150 celebrations, the Carnarvon Gorge was announced as one of the Q150 Icons of Queensland for its role as a "Natural attraction". History Some western researchers have suggested that Aboriginal people did not live in the gorge permanently, due to defensive concerns and lack of food resources, whilst others suggest that permanent occupation was not allowed due to the gorge being considered sacred. The dreamtime stories tell a tale of the Rainbow Serpent which made the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
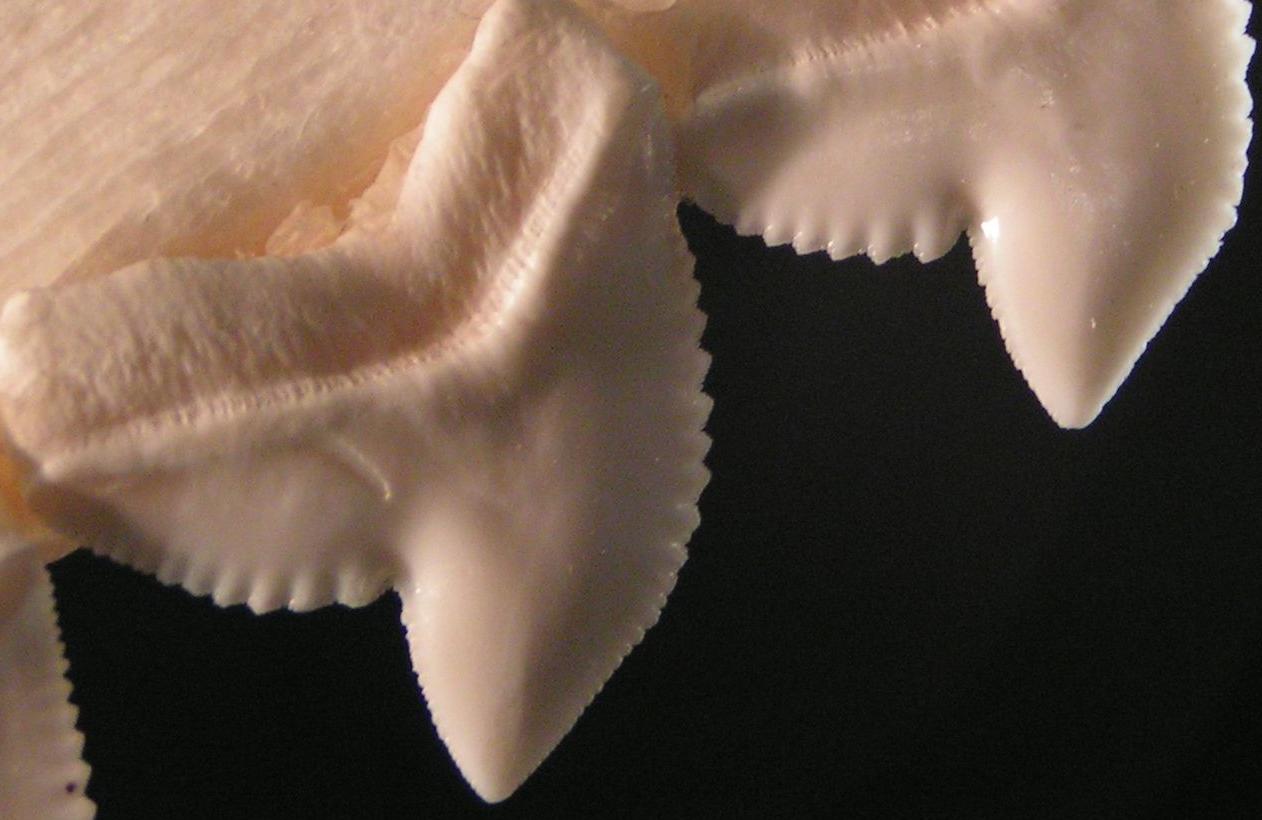
Serrate
Serration is a saw-like appearance or a row of sharp or tooth-like projections. A serrated cutting edge has many small points of contact with the material being cut. By having less contact area than a smooth blade or other edge, the applied pressure at each point of contact is greater and the points of contact are at a sharper angle to the material being cut. This causes a cutting action that involves many small splits in the surface of the material being cut, which cumulatively serve to cut the material along the line of the blade. In nature, serration is commonly seen in the cutting edge on the teeth of some species, usually sharks. However, it also appears on non-cutting surfaces, for example in botany where a toothed leaf margin or other plant part, such as the edge of a carnation petal, is described as being serrated. A serrated leaf edge may reduce the force of wind and other natural elements. Probably the largest serrations on Earth occur on the skylines of mountains (th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leaf Shape
The following is a list of terms which are used to describe leaf morphology in the description and taxonomy of plants. Leaves may be simple (a single leaf blade or lamina) or compound (with several leaflets). The edge of the leaf may be regular or irregular, may be smooth or bearing hair, bristles or spines. For more terms describing other aspects of leaves besides their overall morphology see the leaf article. The terms listed here all are supported by technical and professional usage, but they cannot be represented as mandatory or undebatable; readers must use their judgement. Authors often use terms arbitrarily, or coin them to taste, possibly in ignorance of established terms, and it is not always clear whether because of ignorance, or personal preference, or because usages change with time or context, or because of variation between specimens, even specimens from the same plant. For example, whether to call leaves on the same tree "acuminate", "lanceolate", or "linear" could ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lenticel
A lenticel is a porous tissue consisting of cells with large intercellular spaces in the periderm of the secondarily thickened organs and the bark of woody stems and roots of dicotyledonous flowering plants. It functions as a pore, providing a pathway for the direct exchange of gases between the internal tissues and atmosphere through the bark, which is otherwise impermeable to gases. The name lenticel, pronounced with an , derives from its lenticular (lens-like) shape. The shape of lenticels is one of the characteristics used for tree identification. Evolution Before there was much evidence for the existence and functionality of lenticels, the fossil record has shown the first primary mechanism of aeration in early vascular plants to be the stomata. However, in woody plants, with vascular and cork cambial activity and secondary growth, the entire epidermis may be replaced by a suberized periderm or bark in which the functions of the stomata are replaced by lenticels. The e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lignotuber
A lignotuber is a woody swelling of the root crown possessed by some plants as a protection against destruction of the plant stem, such as by fire. Other woody plants may develop basal burls as a similar survival strategy, often as a response to coppicing or other environmental stressors. However, lignotubers are specifically part of the normal course of development of the plants that possess them, and often develop early on in growth. The crown contains buds from which new stems may sprout, as well as stores of starch that can support a period of growth in the absence of photosynthesis. The term "lignotuber" was coined in 1924 by Australian botanist Leslie R. Kerr. Plants possessing lignotubers include many species in Australia: ''Eucalyptus marginata'' (Jarrah), ''Eucalyptus brevifolia'' (snappy gum) and ''Eucalyptus ficifolia'' (scarlet gum) all of which can have lignotubers wide and deep, as well as most mallees (where it is also known as a mallee root) and many ''Banksia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)