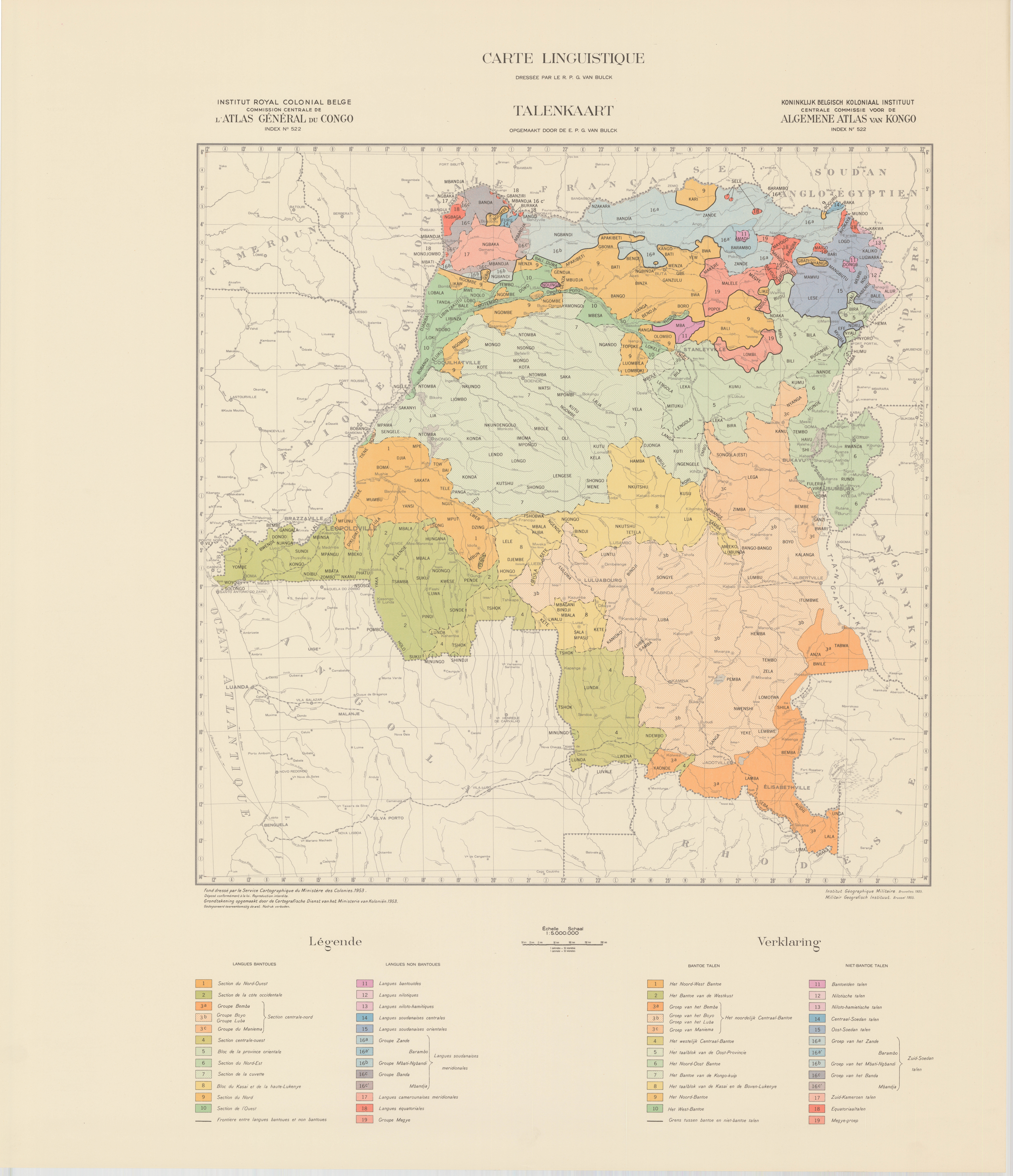
|
Banana District
Banana District (french: District de Banana, nl, District Banana) was a district of the Congo Free State and Belgian Congo. It disappeared in a reorganization of 1910. Location Banana used to be a fishing village in a sheltered cove. A map of the Congo Free State in 1897 shows the town of Banana on the north side of the bay where the Congo River enters the Atlantic Ocean. The Banana District extended a short distance along the north bank of the river to the Boma District. To the north it bordered the Portuguese territory of Cabinda, and the Portuguese territory to the south of the Congo faced it across the river. History The people of Banana were in contact with Europeans for four centuries before the Belgians established their colony. From November 1874 to 12 August 1877 Henry Morton Stanley made his first trans-Africa exploration, crossing the African continent from Zanzibar to Banana. During the expedition he explored Lake Victoria and Lake Tanganyika, and recorded the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Districts Of The Belgian Congo
The Districts of the Belgian Congo were the primary administrative divisions when Belgium annexed the Congo Free State in 1908, each administered by a district commissioner. In 1914 they were distributed among four large provinces, with some boundary changes. In 1933 the provinces were restructured into six, again with boundary changes. The number of districts fluctuated between 12 and 26 through splits and consolidations, first rising, then falling, then rising again. History The Congo Free State was annexed by Belgium in 1908 to become the Belgian Congo. At first the structure of districts was retained. In 1910 the western districts of Banana, Boma, Matadi and Cataractes were consolidated into one administrative unit, Bas-Congo, reducing the number to twelve. Parts of the Stanley Falls and Lualaba districts were combined to form Katanga in 1910, which was called a vice-government general. Otherwise, the Free State districts were maintained until 28 March 1912. An ''arrêté ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Tanganyika
Lake Tanganyika () is an African Great Lake. It is the second-oldest freshwater lake in the world, the second-largest by volume, and the second-deepest, in all cases after Lake Baikal in Siberia. It is the world's longest freshwater lake. The lake is shared among four countries—Tanzania, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), Burundi, and Zambia, with Tanzania (46%) and DRC (40%) possessing the majority of the lake. It drains into the Congo River system and ultimately into the Atlantic Ocean. Etymology "Tanganika" was the name of the lake that Henry Morton Stanley encountered when he was at Ujiji in 1876. The name first originated from the Bembe language when they arrived in South Kivu around the 7th century, they discovered the lake and started calling it “êtanga ‘ya’ni’â” which means “a big river” in their Bantu language. Stanley found also other names for the lake among different ethnic groups, like the Kimana, the Yemba and the Msaga. An alt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emin Pasha Relief Expedition
The Emin Pasha Relief Expedition of 1886 to 1889 was one of the last major European expeditions into the interior of Africa in the nineteenth century, ostensibly to the relief of Emin Pasha, General Charles Gordon's besieged governor of Equatoria, threatened by Mahdist forces. The expedition was led by Henry Morton Stanley and came to be both celebrated for its ambition in crossing "darkest Africa", and notorious for the deaths of so many of its members and the disease unwittingly left in its wake. Anxiety about Equatoria The Mahdists captured Khartoum in 1885 and Egyptian administration of the Sudan collapsed. The extreme southern province Equatoria was nearly cut off from the outside world, located as it was on the upper reaches of the Nile near Lake Albert. Emin Pasha was an Ottoman doctor and naturalist who had been appointed Governor of Equatoria. He was able to send and receive letters via Buganda and Zanzibar and had been informed in February 1886 that the Egyptian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bas-Congo District
Bas-Congo (french: District du Bas-Congo, nl, District Beneden-Congo) was a district of the Belgian Congo and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It went through various significant changes in extent. It roughly corresponds to the present province of Kongo Central. Location A map of the Congo Free State in 1897 shows four small districts along the lower reaches of the Congo River. From the sea they were Banana District, Boma District, Matadi District and Cataractes District. Above them Stanley Pool District extended north along the east shore of the Congo River. The Free State was annexed by Belgium in 1908 as the Belgian Congo. In 1910 the districts of Banana, Boma, Matadi and Cataracts were consolidated into the Bas-Congo District. Bas-Congo contained the port of Boma, the main port of entry to the Belgian Congo. The district was bounded to the south by Portuguese possessions, now Angola, and to the north by a Portuguese enclave of Cabinda and then by the French Congo, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vivi, Democratic Republic Of The Congo
Vivi is a village in the Bas-Congo province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is located on the north side of the Congo River, opposite the provincial capital of Matadi. It was found in 1879 by Henry Morton Stanley. It served as the first capital of the Congo Free State ''(Work and Progress) , national_anthem = Vers l'avenir , capital = Vivi Boma , currency = Congo Free State franc , religion = Catholicism (''de facto'') , leader1 = Leopo ... from July, 1885 to May 1, 1886, when the capital was relocated to Boma. References Populated places in Kongo Central {{DRCongo-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boma, Democratic Republic Of The Congo
Boma is a port town on the Congo River, some upstream from the Atlantic Ocean, in the Kongo Central province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, adjacent to the border with Angola. It had an estimated population of 162,521 in 2012. Boma was the capital city of the Congo Free State and Belgian Congo (the modern Democratic Republic of the Congo) from 1 May 1886 to 1923, when the capital was moved to Léopoldville (since renamed Kinshasa). The port handles exports of tropical timber, bananas, cacao, and palm products. History Boma was founded by European merchants in the 16th century as an entrepôt, including for the slave trade. Trade was chiefly in the hands of Dutch merchants, but British, French and Portuguese firms also had factories there. No European power exercised sovereignty, though claims were from time to time put forward by Portugal. British explorer Henry Morton Stanley arrived here on 9 August 1877, after crossing Africa from east to west.Stanley, H. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal Postal Union
The Universal Postal Union (UPU, french: link=no, Union postale universelle), established by the Treaty of Bern of 1874, is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) that coordinates postal policies among member nations, in addition to the worldwide postal system. The UPU contains four bodies consisting of the Congress, the Council of Administration (CA), the Postal Operations Council (POC) and the International Bureau (IB). It also oversees the Telematics and Express Mail Service (EMS) cooperatives. Each member agrees to the same terms for conducting international postal duties. The UPU's headquarters are located in Bern, Switzerland. History Bilateral treaties Before the establishment of the UPU, every pair of countries that exchanged mail had to negotiate a postal treaty with each other. In the absence of a treaty providing for direct delivery of letters, mail had to be forwarded through an intermediate country. Postal arrangements were complex and overlapping. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leopold II Of Belgium
* german: link=no, Leopold Ludwig Philipp Maria Viktor , house = Saxe-Coburg and Gotha , father = Leopold I of Belgium , mother = Louise of Orléans , birth_date = , birth_place = Brussels, Belgium , death_date = , death_place = Laeken, Brussels, Belgium , burial_place = Church of Our Lady of Laeken , religion = Roman Catholicism Leopold II (french: link=no, Léopold Louis Philippe Marie Victor, nl, Leopold Lodewijk Filips Maria Victor; 9 April 1835 – 17 December 1909) was the second King of the Belgians from 1865 to 1909 and the self-made autocratic ruler of the Congo Free State from 1885 to 1908. Born in Brussels as the second but eldest-surviving son of Leopold I and Louise of Orléans, Leopold succeeded his father to the Belgian throne in 1865 and reigned for exactly 44 years until his death, the longest reign of a Belgian monarch to date. He died without surviving legitimate sons. The current Belgian king descends from his ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Association Of The Congo
The International Association of the Congo (french: Association internationale du Congo), also known as the International Congo Society, was an association founded on 17 November 1879 by Leopold II of Belgium to further his interests in the Congo. It replaced the Belgian ("Committee for the Study of the Upper Congo"), which was part of the International African Association front organisation created for the exploitation of the Congo. The goals of the International Congo Society was to establish control of the Congo Basin and to exploit its economic resources. The Berlin Conference recognised the society as sovereign over the territories it controlled and on August 1, 1885, i.e. four and half months after the closure of the Berlin Conference, King Leopold's Vice-Administrator General in the Congo, announced that the society and the territories it occupied were henceforth called "the Congo Free State". Ownership and control The official stockholders of the Committee for the St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanley Pool
The Pool Malebo, formerly Stanley Pool, also known as Mpumbu, Lake Nkunda or Lake Nkuna by local indigenous people in pre-colonial times, is a lake-like widening in the lower reaches of the Congo River."Malebo Pool" ''''. Accessed June 2011. The river serves as the border between the Republic of the Congo on the north and the to the south. The pool's for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luama River
The Luama River is a tributary of the Lualaba River in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Location The Luama rises in the mountains to the west of Lake Tanganyika, in the Kalemie Territory of Tanganyika District. It flows north and northwest into Kabambare Territory of Maniema, then turns to the southwest, entering the Lualaba above Kasongo. The river has five sources in the mountains, two of which are above in altitude. The headwater regions upstream of Pene Mende include a system of wetlands about in length and covering about . Below these wetlands the river drops down three waterfalls and includes several minor rapids. The Luama enters the Lualaba from the east after the rapids below Kangolo and just before the Lualaba turns northwest in the stretch above Kibombo. The Luama River defines the southern boundary of the range of eastern gorillas, which is bounded by the Lualaba river to the west, the Albertine rift to the east and the Lindi River to the north. Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Victoria
Lake Victoria is one of the African Great Lakes. With a surface area of approximately , Lake Victoria is Africa's largest lake by area, the world's largest tropical lake, and the world's second-largest fresh water lake by surface area after Lake Superior in North America. In terms of volume, Lake Victoria is the world's ninth-largest continental lake, containing about of water. Lake Victoria occupies a shallow depression in Africa. The lake has an average depth of and a maximum depth of .United Nations, ''Development and Harmonisation of Environmental Laws Volume 1: Report on the Legal and Institutional Issues in the Lake Victoria Basin'', United Nations, 1999, page 17 Its catchment area covers . The lake has a shoreline of when digitized at the 1:25,000 level, with islands constituting 3.7% of this length. The lake's area is divided among three countries: Kenya occupies 6% (), Uganda 45% (), and Tanzania 49% (). Though having multiple local language names ( luo, Nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |