|
Ballyconneely
Ballyconneely () is a village and small ribbon development in west Connemara, County Galway Ireland. Name 19th century antiquarian John O'Donovan documents a number of variants of the village, including Ballyconneely, Baile 'ic Conghaile, Ballykineely, Ballycunneely, and Balyconneely. An Post Placenames Branch archival notes Baile Uí Chonghaile, Baile 'ic Confhaola and other various spellings. The surname, Conneely is ''Mac Conghaile'' originally (Ó Conghaile contemporaneously), whereas ''Ó Conghaola'' (modern spelling ''Ó Conaola'' - Conneally) is an entirely unrelated sept located in southern County Galway belonging to the Uí bhFhiachrach Aidne. An Post archival notes local lore from the early 20th century that attests the origin of the village's name to that of ''Muintear Chlann Chonghaile'' or ''Clann Mhic Conghaile'', that is to say, the Conneelys. Location Settlements are spread out north on the road to Clifden and south on the road to Roundstone. This peninsula, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
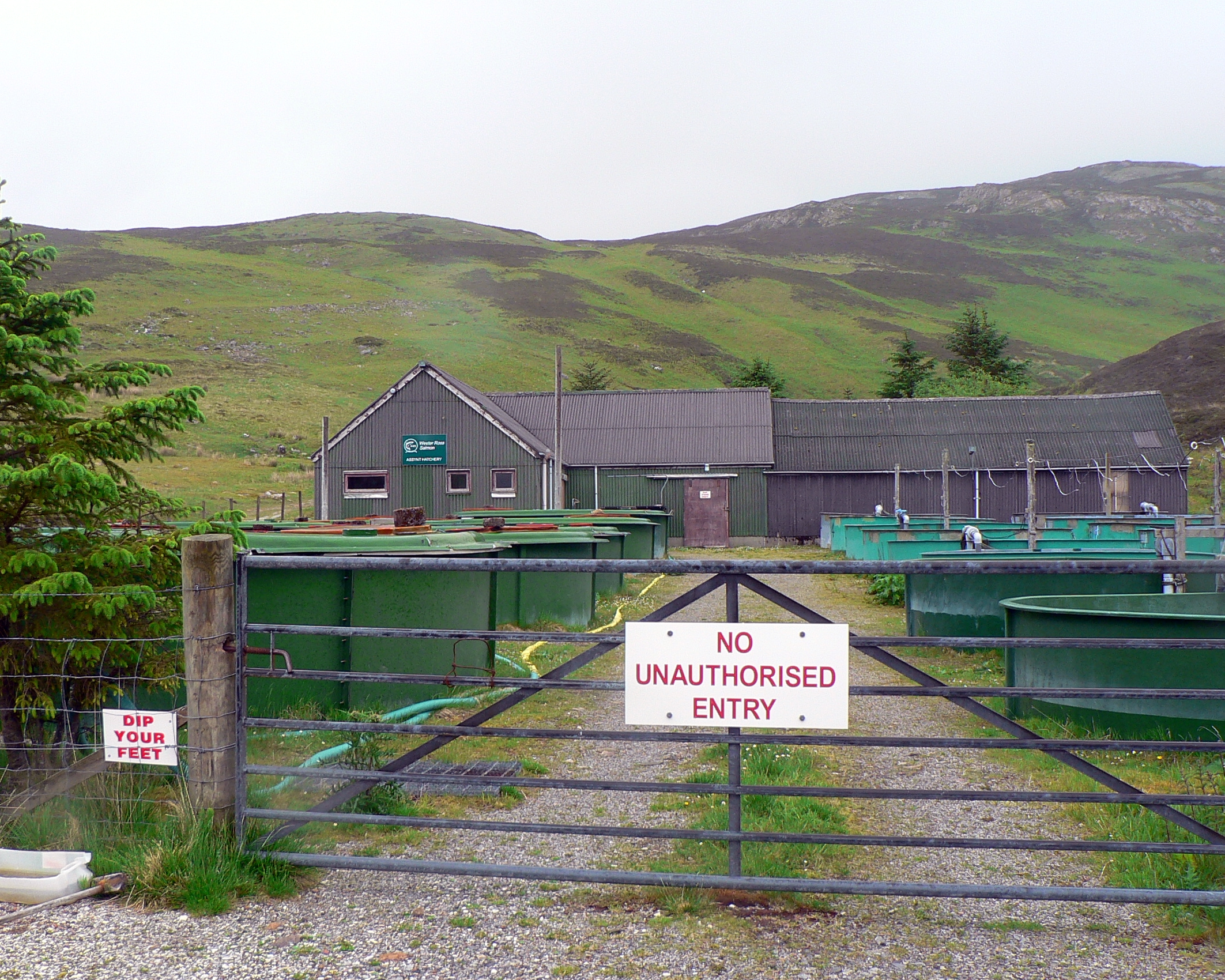
Aquaculture Of Salmon
The aquaculture of salmonids is the farming and harvesting of salmonids under controlled conditions for both commercial and recreational purposes. Salmonids (particularly salmon and rainbow trout), along with carp, and tilapia are the three most important fish species in aquaculture. The most commonly commercially farmed salmonid is the Atlantic salmon. In the U.S. Chinook salmon and rainbow trout are the most commonly farmed salmonids for recreational and subsistence fishing through the National Fish Hatchery System. In Europe, brown trout are the most commonly reared fish for recreational restocking. Commonly farmed nonsalmonid fish groups include tilapia, catfish, sea bass, and bream. In 2007, the aquaculture of salmonids was worth US$10.7 billion globally. Salmonid aquaculture production grew over ten-fold during the 25 years from 1982 to 2007. In 2012, the leading producers of salmonids were Norway, Chile, Scotland and Canada. Much controversy exists about the ecological a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connemara
Connemara (; )( ga, Conamara ) is a region on the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast of western County Galway, in the west of Ireland. The area has a strong association with traditional Irish culture and contains much of the Connacht Irish-speaking Gaeltacht, which is a key part of the identity of the region and is the largest Gaeltacht in the country. Historically, Connemara was part of the territory of Iar Connacht (West Connacht). Geographically, it has many mountains (notably the Twelve Bens), peninsulas, coves, islands and small lakes. Connemara National Park is in the northwest. It is mostly rural and its largest settlement is Clifden. Etymology "Connemara" derives from the tribal name , which designated a branch of the , an early tribal grouping that had a number of branches located in different parts of . Since this particular branch of the lived by the sea, they became known as the (sea in Irish is , genitive case, genitive , hence "of the sea"). Definition One common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conneely
Conneely from ('' Mac Conghaile'') or (''Ó Conghaile''), is an Irish family name. Frequent examples of the name can be found in the West of Ireland, particularly in the Connemara area of County Galway. A coastal village in County Galway is named Ballyconneely. Overview The original Irish language Gaelic version of the surname is Mac Conghaile, though sometimes rendered Ó Conghaile (due to an 18–19th century shift from Mac to O'). According to an entry in ''Irish Septs'' (David Austin Larkin): Mac Conghaile -a Conmaicne Mara sept of Ballyconneely Townland, Parish and Bay, Roundstone, Connemara, Galway; Marshall of Uí Maine. The name Connemara comes from the tribe of Conmac, or Conmaicne, a warrior tribe which was sent to the area by the ancient Gaelic Kings of Connacht to ensure their hegemony. The branch of the tribe which went to the coastal area became known as Conmaicnemara, or 'the tribe of Cormac by the sea'. In medieval times Connemara was ruled by the O'Cadhlas and la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clifden
Clifden (, meaning "stepping stones") is a coastal town in County Galway, Ireland, in the region of Connemara, located on the Owenglin River where it flows into Clifden Bay. As the largest town in the region, it is often referred to as "the Capital of Connemara". Frequented by tourists, Clifden is linked to Galway city by the N59. History 19th century The town was founded at the start of the 19th century by John D'Arcy (1785–1839) who lived in Clifden Castle (built around 1818, now a ruin) west of Clifden. He had inherited the estate in 1804 when it was mostly inhabited by fishermen and farmers. The idea of establishing a town on the coast was first voiced by him in 1812. Bad communications and a lack of private capital prevented fast progress until the 1820s when the potato crop failed in 1821–22 and D'Arcy petitioned the government in Dublin for assistance. The engineer Alexander Nimmo was sent to the area in 1822. He constructed a quay at Clifden (finished in 1831) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marconi Wireless
Wireless telegraphy or radiotelegraphy is transmission of text messages by radio waves, analogous to electrical telegraphy using cables. Before about 1910, the term ''wireless telegraphy'' was also used for other experimental technologies for transmitting telegraph signals without wires. In radiotelegraphy, information is transmitted by pulses of radio waves of two different lengths called "dots" and "dashes", which spell out text messages, usually in Morse code. In a manual system, the sending operator taps on a switch called a telegraph key which turns the transmitter on and off, producing the pulses of radio waves. At the receiver the pulses are audible in the receiver's speaker as beeps, which are translated back to text by an operator who knows Morse code. Radiotelegraphy was the first means of radio communication. The first practical radio transmitters and receivers invented in 1894–1895 by Guglielmo Marconi used radiotelegraphy. It continued to be the only type of r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many famous scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it. In print since 1845, it is the oldest continuously published magazine in the United States. ''Scientific American'' is owned by Springer Nature, which in turn is a subsidiary of Holtzbrinck Publishing Group. History ''Scientific American'' was founded by inventor and publisher Rufus Porter (painter), Rufus Porter in 1845 as a four-page weekly newspaper. The first issue of the large format newspaper was released August 28, 1845. Throughout its early years, much emphasis was placed on reports of what was going on at the United States Patent and Trademark Office, U.S. Patent Office. It also reported on a broad range of inventions including perpetual motion machines, an 1860 device for buoying vessels by Abraham Lincoln, and the universal joint which now can be found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Breton Island
Cape Breton Island (french: link=no, île du Cap-Breton, formerly '; gd, Ceap Breatainn or '; mic, Unamaꞌki) is an island on the Atlantic coast of North America and part of the province of Nova Scotia, Canada. The island accounts for 18.7% of Nova Scotia's total area. Although the island is physically separated from the Nova Scotia peninsula by the Strait of Canso, the long Canso Causeway connects it to mainland Nova Scotia. The island is east-northeast of the mainland with its northern and western coasts fronting on the Gulf of Saint Lawrence with its western coast forming the eastern limits of the Northumberland Strait. The eastern and southern coasts front the Atlantic Ocean with its eastern coast also forming the western limits of the Cabot Strait. Its landmass slopes upward from south to north, culminating in the highlands of its northern cape. One of the world's larger saltwater lakes, ("Arm of Gold" in French), dominates the island's centre. The total population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland". Most of the population are native English-speakers, and the province's population is 969,383 according to the 2021 Census. It is the most populous of Canada's Atlantic provinces. It is the country's second-most densely populated province and second-smallest province by area, both after Prince Edward Island. Its area of includes Cape Breton Island and 3,800 other coastal islands. The Nova Scotia peninsula is connected to the rest of North America by the Isthmus of Chignecto, on which the province's land border with New Brunswick is located. The province borders the Bay of Fundy and Gulf of Maine to the west and the Atlantic Ocean to the south and east, and is separated from Prince Edward Island and the island of Newfoundland by the Northumberland and Cabot straits, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connemara Pony
The Connemara Pony (Irish: ''Capaillín Chonamara'') is a pony breed originating in Ireland. They are known for their athleticism, versatility and good disposition. The breed makes excellent show ponies. History The Connemara region in County Galway in western Ireland, where the breed first became recognised as a distinct type, is a very harsh landscape, thus giving rise to a pony breed of hardy, strong individuals. Some believe that the Connemara developed from Scandinavian ponies that the Vikings first brought to Ireland. Another source was likely the Irish Hobby, a now-extinct breed established prior to the 13th century. Legend, however, says that galleons from the Spanish Armada ran aground in 1588, and the Andalusians on board were set loose. The Spanish horses bred with the native stock, refining the local ponies. For additional strength and stamina, Arabian blood was added in the 18th century. They were also crossed with Hackneys and Thoroughbreds. Too much cross ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Alcock (RAF Officer)
Captain Sir John William Alcock (5 November 189218 December 1919) was a British Royal Navy and later Royal Air Force officer who, with navigator Lieutenant Arthur Whitten Brown, piloted the first non-stop transatlantic flight from St. John's, Newfoundland to Clifden, Ireland in June 1919. He died in a flying accident in France in December later that same year. Early life John Alcock was born on 5 November 1892, perhaps in the coach-house adjoining Basford House on Seymour Grove, Firswood, Manchester, England. He attended Heyhouses School in Lytham St. Annes. He first became interested in flying at the age of 17. His first job was at the Empress Motor Works in Manchester. In 1910 he became an assistant to Works Manager Charles Fletcher, an early Manchester aviator and Norman Crossland, a motor engineer and founder of Manchester Aero Club. It was during this period that Alcock met the Frenchman Maurice Ducrocq who was both a demonstration pilot and UK sales representative f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabian Horse
The Arabian or Arab horse ( ar, الحصان العربي , DIN 31635, DMG ''ḥiṣān ʿarabī'') is a horse breed, breed of horse that originated on the Arabian Peninsula. With a distinctive head shape and high tail carriage, the Arabian is one of the most easily recognizable horse breeds in the world. It is also one of the oldest breeds, with archaeological evidence of horses in the Middle East that resemble modern Arabians dating back 4,500 years. Throughout history, Arabian horses have spread around the world by both war and trade, used to improve other breeds by adding speed, refinement, endurance, and strong bone. Today, Arabian bloodlines are found in almost every modern breed of riding horse. The Arabian developed in a desert climate and was prized by the nomadic Bedouin people, often being brought inside the family tent for shelter and protection from theft. Selective breeding for traits, including an ability to form a cooperative relationship with humans, create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg , image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg , national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond") , national_anthem = (English: "Royal March") , image_map = , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Madrid , coordinates = , largest_city = Madrid , languages_type = Official language , languages = Spanish language, Spanish , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = , ethnic_groups_ref = , religion = , religion_ref = , religion_year = 2020 , demonym = , government_type = Unitary state, Unitary Parliamentary system, parliamentary constitutional monarchy , leader_title1 = Monarchy of Spain, Monarch , leader_name1 = Felipe VI , leader_title2 = Prime Minister of Spain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |