|
Ballistic Training
Ballistic training, also incorrectly referred to as power training, is a form of training which involves throwing weights, and jumping with weights, in order to increase explosive power. The term ballistic refers to a method of training, where the athletes' body or an external object is explosively projected into a flight phase 1and can, therefore, include exercises such as jumps, throws, or strikes. The intention in ballistic exercises is to maximise the acceleration phase of an object's movement and minimise the deceleration phase. For instance, throwing a medicine ball maximises the acceleration of the ball; this can be contrasted with a standard weight training exercise where there would be a pronounced deceleration phase at the end of the repetition i.e. at the end of a bench press exercise the barbell is decelerated and brought to a halt. Similarly, an athlete jumping whilst holding a trap bar maximises the acceleration of the weight through the process of holding it whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballistic Training Medicine Ball Throw
Ballistics may refer to: Science * Ballistics, the science that deals with the motion, behavior, and effects of projectiles ** Forensic ballistics, the science of analyzing firearm usage in crimes ** Internal ballistics, the study of the processes accelerating a projectile ** Transition ballistics, the study of the projectile's behavior when it leaves the barrel ** External ballistics, the study of the passage of the projectile through space or the air ** Terminal ballistics, the study of the interaction of a projectile with its target * Ballistic conduction, conduction of electricity with negligible charge scattering * Ballistic movement of muscles in an animal Combat * Ballistic missile, a missile that follows a sub-orbital flightpath * Ballistic knife, a specialized combat knife with a detachable, self-propelled blade * Ballistic shield, a shield meant to protect the user from bullets Arts and media Comics * Ballistic (Image Comics), a comic character of Top Cow Product ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
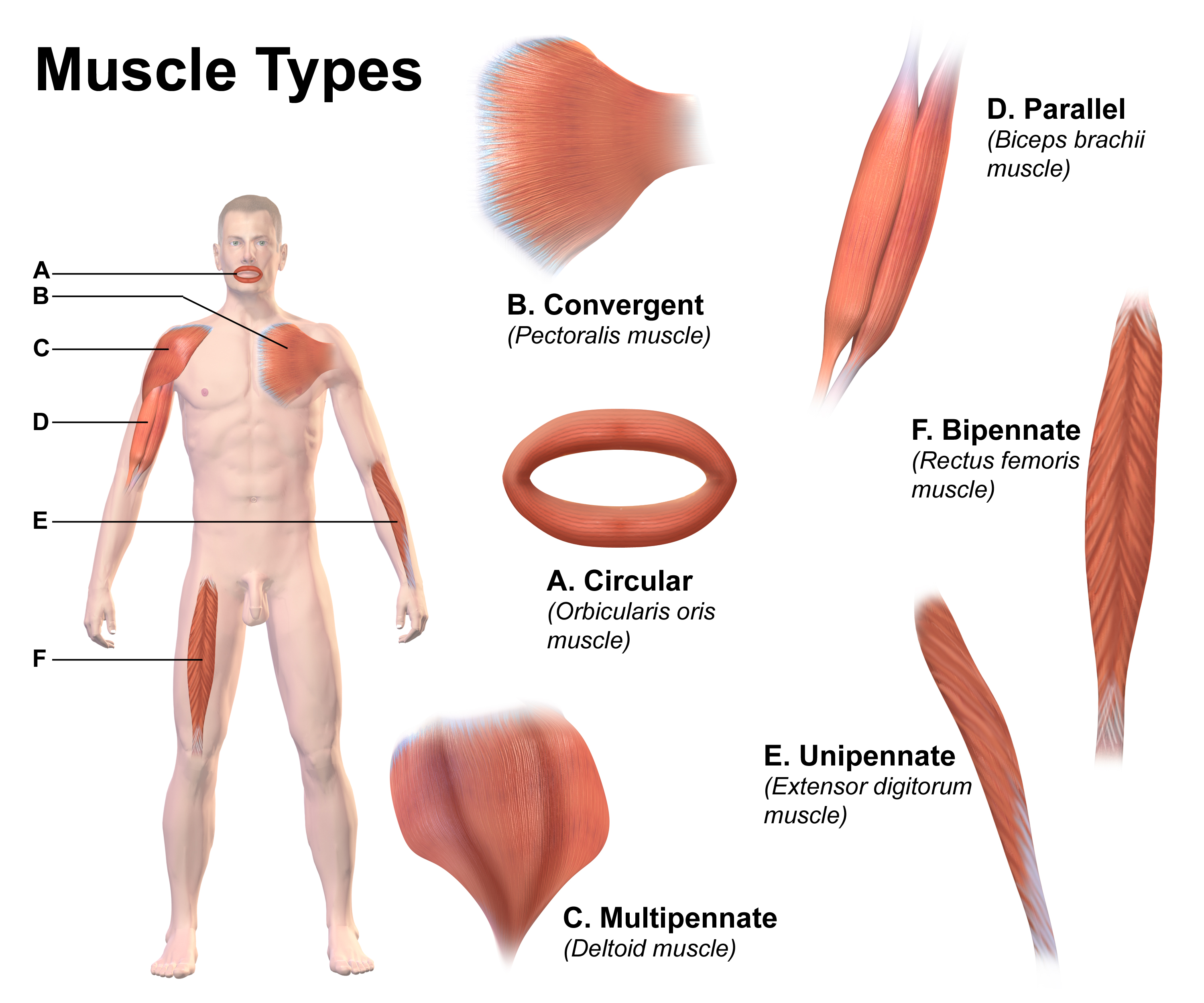
Muscle Fiber
A muscle cell is also known as a myocyte when referring to either a cardiac muscle cell (cardiomyocyte), or a smooth muscle cell as these are both small cells. A skeletal muscle cell is long and threadlike with many nuclei and is called a muscle fiber. Muscle cells (including myocytes and muscle fibers) develop from embryonic precursor cells called myoblasts. Myoblasts fuse to form multinucleated skeletal muscle cells known as syncytia in a process known as myogenesis. Skeletal muscle cells and cardiac muscle cells both contain myofibrils and sarcomeres and form a striated muscle tissue. Cardiac muscle cells form the cardiac muscle in the walls of the heart chambers, and have a single central nucleus. Cardiac muscle cells are joined to neighboring cells by intercalated discs, and when joined in a visible unit they are described as a ''cardiac muscle fiber''. Smooth muscle cells control involuntary movements such as the peristalsis contractions in the esophagus and stom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strength Training
Strength training or resistance training involves the performance of physical exercises that are designed to improve strength and endurance. It is often associated with the lifting of weights. It can also incorporate a variety of training techniques such as bodyweight exercises, isometrics, and plyometrics. Training works by progressively increasing the force output of the muscles and uses a variety of exercises and types of equipment. Strength training is primarily an anaerobic activity, although circuit training also is a form of aerobic exercise. Strength training can increase muscle, tendon, and ligament strength as well as bone density, metabolism, and the lactate threshold; improve joint and cardiac function; and reduce the risk of injury in athletes and the elderly. For many sports and physical activities, strength training is central or is used as part of their training regimen. Principles and training methods The basic principles of strength training ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Training
Power training typically involves exercises which apply the maximum amount of force as fast as possible; on the basis that strength + speed = power. Jumping with weights or throwing weights are two examples of power training exercises. Regular weight training exercises such as the clean and jerk and power clean may also be considered as being power training exercises due to the explosive speed required to complete the lifts. Power training may also involve contrasting exercises such as heavy lifts and plyometrics, known as complex training, in an attempt to combine the maximal lifting exertions with dynamic movements. This combination of a high strength exercise with a high speed exercise may lead to an increased ability to apply power. Power training frequently specifically utilises two physiological processes which increase in conjunction with one another during exercise. These are deep breathing, which results in increased intra-abdominal pressure; and post-activation potentati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Training
Complex training, also known as contrast training or post-activation potentiation training, involves the integration of strength training and plyometrics in a training system designed to improve explosive power. According to Jace Derwin: Complex training relies upon the performance of a strength exercise, often resistance based, followed by a plyometric exercise. The strength and the plyometric exercise are usually biomechanically similar i.e. they move through similar ranges of movement. For example, a back squat followed by a box jump; or a bench press exercise followed by a jumping clap push up. Such a combination is referred to as a pair or a contrast pair. The resistance based exercise will often be a near maximal effort—about 75–90% of the athlete's maximal lift. The plyometric portion of the training should be completed in an explosive manner. Sets are often used. Between the performance of the strength exercise and the plyometric exercise there is between a 3–12 mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calisthenics
Calisthenics (American English) or callisthenics (British English) ( /ˌkælɪsˈθɛnɪks/) is a form of strength training consisting of a variety of movements that exercise large muscle groups (gross motor movements), such as standing, grasping, pushing, etc. These exercises are often performed rhythmically and with minimal equipment, as bodyweight exercises. They are intended to increase strength, fitness, and flexibility, through movements such as pulling, pushing, bending, jumping, or swinging, using one's body weight for resistance. Calisthenics can provide the benefits of muscular and aerobic conditioning, in addition to improving psychomotor skills such as balance, agility, and coordination. Urban calisthenics is a form of street workout; calisthenics groups perform exercise routines in urban areas. Individuals and groups train to perform advanced calisthenics skills such as muscle-ups, levers, and various freestyle moves such as spins and flips. Sports teams and mili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plyometrics
Plyometrics, also known as jump training or plyos, are exercises in which muscles exert maximum force in short intervals of time, with the goal of increasing power (speed-strength). This training focuses on learning to move from a muscle extension to a contraction in a rapid or "explosive" manner, such as in specialized repeated jumping. Plyometrics are primarily used by athletes, especially martial artists, sprinters and high jumpers, to improve performance, and are used in the fitness field to a much lesser degree. Overview Plyometrics include explosive exercises to activate the quick response and elastic properties of the major muscles. It was initially adopted by Soviet Olympians in the 1950s, and then by sportspeople worldwide. Sports using plyometrics include basketball, tennis, badminton, squash and volleyball as well as the various codes of football. The term "plyometrics" was coined by Fred Wilt after watching Soviet athletes prepare for their events in track and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kettlebell Lifting
Kettlebell Sport lifting (russian: гиревой спорт, ''girevoy sport'', GS) a.k.a. Girya is a repetitive weight lifting sport performed with kettlebells in a given period of time. Competitive kettlebell lifting has a long history in Russia and Eastern Europe, but developed as an organised, standard sport under the name kettlebell lifting during the 1960s. Lifts The sport consists of three main lifts: the snatch, jerk and the long cycle. Jerk and Long Cycle can be performed with one bell or two kettlebells of equal weight. *Snatch: A single kettlebell is swung using one hand from between the knees to above the head in a single motion. *Jerk: Two kettlebells are grasped in each hand and swung to the 'rack position' at chest level, then jerked above the head. It can be performed with one kettlebell. *Long Cycle: Two kettlebells are cleaned from knee level to chest level, then jerked to above the head. It can be performed with one kettlebell. Rules Classic competiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henneman's Size Principle
Henneman’s size principle describes relationships between properties of motor neurons and the muscle fibers they innervate and thus control, which together are called motor units. Motor neurons with large cell bodies tend to innervate fast-twitch, high-force, less fatigue-resistant muscle fibers, whereas motor neurons with small cell bodies tend to innervate slow-twitch, low-force, fatigue-resistant muscle fibers. In order to contract a particular muscle, motor neurons with small cell bodies are recruited (i.e. begin to fire action potentials) before motor neurons with large cell bodies. It was proposed by Elwood Henneman. History At the time of Henneman’s initial study of motor neuron recruitment, it was known that neurons varied greatly in size, that is in the diameter and extent of the dendritic arbor, size of the soma, and diameter of axon. However, the functional significance of neuron size was not yet known. In 1965, Henneman and colleagues published five papers descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1-RM
One-repetition maximum (one rep maximum or 1RM) in weight training is the maximum amount of weight that a person can possibly lift for one repetition. It may also be considered as the maximum amount of force that can be generated in one maximal contraction. One repetition maximum can be used for determining an individual's maximum strength and is the method for determining the winner in events such as powerlifting and weightlifting competitions. One repetition maximum can also be used as an upper limit, in order to determine the desired "load" for an exercise (as a percentage of the 1RM). Calculating 1RM The 1RM can either be calculated directly using maximal testing or indirectly using submaximal estimation. The submaximal estimation method is preferred as it is safer, quicker, and less unnerving for inexperienced exercisers; however, it may underestimate the actual 1RM. One rep maximum calculators are used to ''predict'' a one rep maximum lift. The degree of accuracy can vary l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain (precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets). The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal cord are both enclosed in the meninges. The meninges provide a barrier to chemicals d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fast Twitch Muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are often known as muscle fibers. The muscle tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles under the control of the somatic nervous system. The other types of muscle are cardiac muscle which is also striated and smooth muscle which is non-striated; both of these types of muscle tissue are classified as involuntary, or, under the control of the autonomic nervous system. A skeletal muscle contains multiple fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber, and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the fusion of developmental myoblasts in a pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |