|
Baldwin Of Antioch
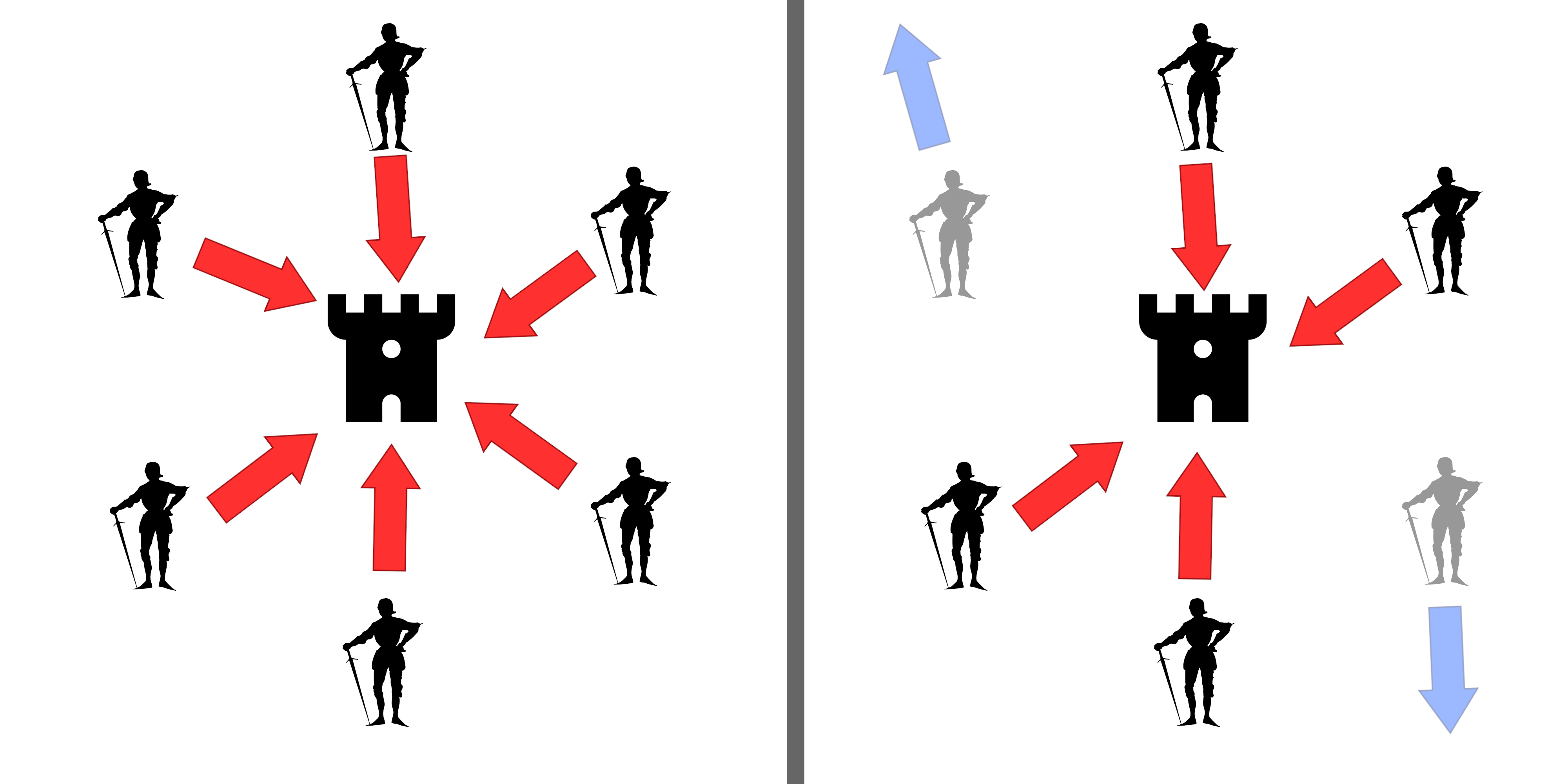
Baldwin of Antioch (died September 17, 1176) was a Frankish knight and general in service of the Byzantine Empire during the Byzantine–Seljuk Wars. He was the son of Princess Constance of Antioch and Raymond of Poitiers.Runciman, Steven. ''A History of the Crusades, Volume 2''. London: The Folio Society, 1994. (pgs. 365, 413)) His brother-in-law was Byzantine Emperor Manuel I Komnenos. An ally of the Emperor in his battles against the Seljuk Turks, Baldwin was one of his most trusted advisors and the only one of Manuel's senior commanders "of Western origin". Baldwin commanded the right wing of the Byzantine forces guarding the siege and baggage train, largely composed of Latin mercenaries, at the Battle of Myriokephalon on September 17, 1176. Upon approaching narrow Tzibritze Pass, the Seljuks launched an attack on Manuel's marching troops. Baldwin led a cavalry charge attempting to drive the Turks from the hills in a counterattack but was surrounded and killed together with all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, Weapons and Ornaments: Germanic Material Culture in Pre-Carolingian Central Europe, 400-750. BRILL, 2001, p.42. Later the term was associated with Romanization (cultural), Romanized Germanic dynasties within the collapsing Western Roman Empire, who eventually commanded the whole region between the rivers Loire and Rhine. They imposed power over many other post-Roman kingdoms and Germanic peoples. Beginning with Charlemagne in 800, Frankish rulers were given recognition by the Catholic Church as successors to the old rulers of the Western Roman Empire. Although the Frankish name does not appear until the 3rd century, at least some of the original Frankish tribes had long been known to the Romans under their own names, both as allies providi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Julius Norwich
John Julius Cooper, 2nd Viscount Norwich, (15 September 1929 – 1 June 2018), known as John Julius Norwich, was an English popular historian, travel writer, and television personality. Background Norwich was born at the Alfred House Nursing Home on Portland Place in Marylebone, London, on 15 September 1929. He was the son of Conservative politician and diplomat Duff Cooper, later Viscount Norwich, and of Lady Diana Manners, a celebrated beauty and society figure. He was given the name "Julius" in part because he was born by caesarean section. Such was his mother's fame as an actress and beauty that the birth attracted a crowd outside the nursing home and hundreds of letters of congratulations. Through his father, he was descended from King William IV and his mistress Dorothea Jordan. He was educated at Egerton House School in Dorset Square, London, later becoming a boarder at the school when it was evacuated to Northamptonshire before the outbreak of the Second Worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frankish Warriors
Frankish may refer to: * Franks, a Germanic tribe and their culture ** Frankish language or its modern descendants, Franconian languages * Francia, a post-Roman state in France and Germany * East Francia, the successor state to Francia in Germany * West Francia, the successor state to Francia in France * Crusaders * Levantines (Latin Christians) See also * Name of the Franks The name of the Franks (Latin ''Franci''), alongside the derived names of '' Francia'' and '' Franconia'' (and the adjectives ''Frankish'' and ''Franconian''), are derived from the name given to a Germanic tribal confederation which emerged in t ... * Franks (other) * Franconian (other) {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Generals
A Byzantine fault (also Byzantine generals problem, interactive consistency, source congruency, error avalanche, Byzantine agreement problem, and Byzantine failure) is a condition of a computer system, particularly distributed computing systems, where components may fail and there is imperfect information on whether a component has failed. The term takes its name from an allegory, the "Byzantine generals problem", developed to describe a situation in which, in order to avoid catastrophic failure of the system, the system's actors must agree on a concerted strategy, but some of these actors are unreliable. In a Byzantine fault, a component such as a server can inconsistently appear both failed and functioning to failure-detection systems, presenting different symptoms to different observers. It is difficult for the other components to declare it failed and shut it out of the network, because they need to first reach a consensus regarding which component has failed in the first p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12th-century Byzantine Military Personnel
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christians Of The Second Crusade
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χριστός), a translation of the Biblical Hebrew term '' mashiach'' (מָשִׁיחַ) (usually rendered as ''messiah'' in English). While there are diverse interpretations of Christianity which sometimes conflict, they are united in believing that Jesus has a unique significance. The term ''Christian'' used as an adjective is descriptive of anything associated with Christianity or Christian churches, or in a proverbial sense "all that is noble, and good, and Christ-like." It does not have a meaning of 'of Christ' or 'related or pertaining to Christ'. According to a 2011 Pew Research Center survey, there were 2.2 billion Christians around the world in 2010, up from about 600 million in 1910. Today, about 37% of all Christians live in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1176 Deaths
Year 1176 ( MCLXXVI) was a leap year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar, the 1176th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 176th year of the 2nd millennium, the 76th year of 12th century, and the 7th year of the 1170s decade. Events By place Byzantine Empire * Summer – Emperor Manuel I (Komnenos) assembles a Byzantine expeditionary force, and marches towards Iconium, the Seljuk capital. Meanwhile, hordes of Seljuk Turks destroy crops and poison water supplies, to make Manuel's march more difficult, and harass the Byzantine army, in order to force it into the Meander Valley. Kilij Arslan II, ruler of the Sultanate of Rum, hears of the expedition, and sends envoys to ask for peace. * September 17 – Battle of Myriokephalon: The Seljuk Turks defeat the Byzantine forces led by Manuel I, who are ambushed when moving through a narrow mountain pass near Lake Beyşehir. The Byzantines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Missing
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andronikos Kontostephanos
Andronikos Komnenos Kontostephanos ( el, ; ca. 1132/33 – after 1183), Latinized Andronicus Contostephanus, was a major figure in the Eastern Roman Empire during the reign of his uncle Manuel I Komnenos as a general, admiral, politician and a leading aristocrat. Background and family Born ca. 1132/33, Andronikos Kontostephanos was the third and youngest son of Stephen Kontostephanos, who held the title ''panhypersebastos'' and the rank of '' megas doux'', and the 'purple-born' princess Anna Komnene, daughter of Emperor John II Komnenos (reigned 1118–43) and his empress Irene of Hungary; he was thus the nephew of Emperor Manuel I Komnenos (r. 1143–80). Andronikos had two older brothers, John and Alexios, and a sister, Irene. The Kontostephanoi were an aristocratic Byzantine family that rose to occupy a prominent place at the heart of Byzantine politics and power through their intermarrying with the imperial house of the Komnenoi. Andronikos himself is believed to have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counterattack
A counterattack is a tactic employed in response to an attack, with the term originating in " war games". The general objective is to negate or thwart the advantage gained by the enemy during attack, while the specific objectives typically seek to regain lost ground or destroy the attacking enemy (this may take the form of an opposing sports team or military units). A saying, attributed to Napoleon Bonaparte illustrate the tactical importance of the counterattack : "the greatest danger occurs at the moment of victory". In the same spirit, in his Battle Studies, Ardant du Pic noticed that "he, general or mere captain, who employs every one in the storming of a position can be sure of seeing it retaken by an organised counter-attack of four men and a corporal". A counterattack is a military tactic that occurs when one side successfully defends off the enemy’s attack and begins to push the enemy back with an attack of its own. In order to perform a successful counterattack, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knight
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of knighthood by a head of state (including the Pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church or the country, especially in a military capacity. Knighthood finds origins in the Greek '' hippeis'' and '' hoplite'' (ἱππεῖς) and Roman ''eques'' and '' centurion'' of classical antiquity. In the Early Middle Ages in Europe, knighthood was conferred upon mounted warriors. During the High Middle Ages, knighthood was considered a class of lower nobility. By the Late Middle Ages, the rank had become associated with the ideals of chivalry, a code of conduct for the perfect courtly Christian warrior. Often, a knight was a vassal who served as an elite fighter or a bodyguard for a lord, with payment in the form of land holdings. The lords trusted the knights, who were skilled in battle on horseback. Knighthood in the Middle Ages was closely linked with horsemanship (and especially the joust) from its origins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavalry Charge
A charge is an offensive maneuver in battle in which combatants advance towards their enemy at their best speed in an attempt to engage in a decisive close combat. The charge is the dominant shock attack and has been the key tactic and decisive moment of many battles throughout history. Modern charges usually involve small groups of fireteams equipped with weapons with a high rate of fire and striking against individual defensive positions (such as a concertainer or bunker), instead of large groups of combatants charging another group or a fortified line. Infantry charges Ancient charges It may be assumed that the charge was practiced in prehistoric warfare, but clear evidence only comes with later literate societies. The tactics of the classical Greek phalanx included an ordered approach march, with a final charge to contact. Highland charge In response to the introduction of firearms, Irish and Scottish troops at the end of the 16th century developed a tactic t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |