|
Bahram Gushnasp
Bahram Gushnasp, known in Byzantine Empire, Byzantine sources as Bargousnas, was an Iranian peoples, Iranian military officer from the House of Mihran. He is first mentioned during an unknown date, where he campaigned against the Himyarite Kingdom, Himyarites, and was quite successful; he managed to capture the Himyarite king Sanatources, sack his capital and take many captives. He is later mentioned in 573, as the head of the Sasanian garrison in the important city of Nisibis, when it was besieged by the Byzantine general Marcian (cousin of Justin II), Marcian. With the help of several other tribes, Bahram Gushnasp fought Marcian at Battle of Sargathon, Sargathon, a place near Nisibis. He was, however, defeated and is not mentioned in any source after that. It is known that he had several children named Mardansina, Gorduya, Gordiya. His most famous child was Bahram Chobin, who would later occupy high offices in the Sasanian state, and even manage to overthrow the Sasanian king hims ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Romanization (cultural), Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine the Great, Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I, Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iranian Peoples
Iranian peoples, or Iranic peoples, are the collective ethnolinguistic groups who are identified chiefly by their native usage of any of the Iranian languages, which are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages within the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. The Proto-Iranian language, Proto-Iranians are believed to have emerged as a separate branch of the Indo-Iranians in Central Asia around the mid-2nd millennium BC. At their peak of expansion in the mid-1st millennium BC, the territory of the Iranian peoples stretched across the entire Eurasian Steppe; from the Danube, Danubian Plains in the west to the Ordos Plateau in the east and the Iranian Plateau in the south.: "From the first millennium b.c., we have abundant historical, archaeological and linguistic sources for the location of the territory inhabited by the Iranian peoples. In this period the territory of the northern Iranians, they being equestrian nomads, extended over the whole zone of the ste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Mihran
The House of Mihrān or House of Mehrān (Middle Persian: 𐭬𐭨𐭥𐭠𐭭; New Persian: ), was a leading Iranian noble family (''šahrdārān''), one of the Seven Great Houses of the Sasanian İranian Empire which claimed descent from the earlier Arsacid dynasty. A branch of the family formed the Mihranid line of the kings of Caucasian Albania and the Chosroid Dynasty of Kartli. History First mentioned in a mid-3rd-century CE trilingual inscription at the '' Ka'ba-i Zartosht'', concerning the political, military, and religious activities of Shapur I, the second Sassanid king of Iran, the family remained the hereditary "margrave Margrave was originally the Middle Ages, medieval title for the military commander assigned to maintain the defence of one of the border provinces of the Holy Roman Empire or a monarchy, kingdom. That position became hereditary in certain Feudal ...s" of Ray throughout the Sassanid period. Several members of the family served as general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himyarite Kingdom
Himyar was a polity in the southern highlands of Yemen, as well as the name of the region which it claimed. Until 110 BCE, it was integrated into the Qataban, Qatabanian kingdom, afterwards being recognized as an independent kingdom. According to classical sources, their capital was the ancient city of Zafar, Yemen, Zafar, relatively near the modern-day city of Sana'a. Himyarite power eventually shifted to Sana'a as the population increased in the fifth century. After the establishment of their kingdom, it was ruled by kings from dhū-Raydān tribe. The kingdom was named Raydān.Jérémie Schiettecatte. Himyar. Roger S. Bagnall; Kai Brodersen; Craige B. Champion; Andrew Erskine; Sabine R. Huebner. ''The Encyclopedia of Ancient History'', John Wiley & Sons, 2017, 9781444338386.ff10.1002/9781444338386.wbeah30219ff. ffhalshs-01585072ff The kingdom conquered neighbouring Sabaeans, Saba' in c. 25 BCE (for the first time), Qataban in c. 200 CE, and Hadramaut, Haḍramaut c. 300 CE. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
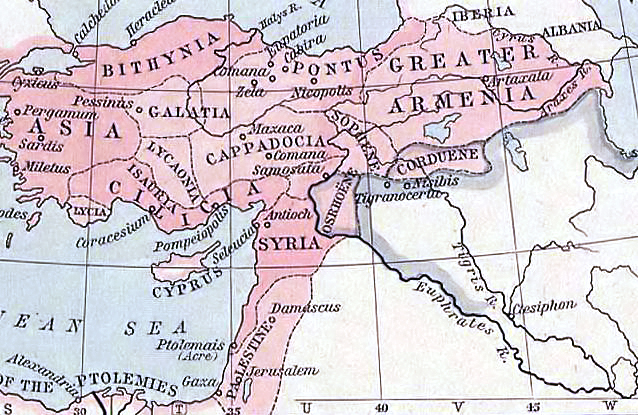
Nisibis
Nusaybin () is a municipality and Districts of Turkey, district of Mardin Province, Turkey. Its area is 1,079 km2, and its population is 115,586 (2022). The city is populated by Kurds of different tribal affiliation. Nusaybin is separated from the larger Kurds, Kurdish-majority city of Qamishli by the Syria–Turkey border. The city is at the foot of the Mount Izla escarpment at the southern edge of the Tur Abdin hills, standing on the banks of the Jaghjagh River (), the ancient Mygdonius (). The city existed in the Assyrian Empire and is recorded in Akkadian language, Akkadian inscriptions as ''Naṣibīna''. Having been part of the Achaemenid Empire, in the Hellenistic period the settlement was re-founded as a ''polis'' named "Antioch on the Mygdonius" by the Seleucid dynasty after the conquests of Alexander the Great. A part of first the Roman Republic and then the Roman Empire, the city (; ) was mainly Syriac language, Syriac-speaking, and control of it was contested be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcian (cousin Of Justin II)
Marcian (, ) was a Byzantine general and a kinsman of Emperor Justin II. According to John Malalas, he was Justin's cousin, and a nephew of Justinian I, while Michael the Syrian reports that his mother was Justin's maternal aunt. He was involved in the Byzantine–Sasanian War of 572–591: Marcian defeated Miranes at the Battle of Sargathon near Nisibis and put him to flight; 1200 Persians were killed and seventy taken prisoners, while the Roman loss was only seven. Marcian then laid siege to Nisibis Nusaybin () is a municipality and Districts of Turkey, district of Mardin Province, Turkey. Its area is 1,079 km2, and its population is 115,586 (2022). The city is populated by Kurds of different tribal affiliation. Nusaybin is separated ... and Theobothon. Chosroes, when he heard of this got together 40,000 cavalry and more than 100,000 infantry, and hastened to its assistance to attack the Romans. In the meantime Marcian was accused to the emperor of aiming at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Sargathon
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and the Battle of France, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mardansina
Mardansina (also spelled Mardan Sina) was a nobleman from the House of Mihran—he was the son of Bahram Gushnasp Bahram Gushnasp, known in Byzantine Empire, Byzantine sources as Bargousnas, was an Iranian peoples, Iranian military officer from the House of Mihran. He is first mentioned during an unknown date, where he campaigned against the Himyarite Kingdom, ... and thus the brother of the prominent Sasanian military leader Bahram Chobin, who managed to overthrow the Sasanian king himself briefly in 590–591, but was eventually defeated and killed. Mardansina thereafter became the new leader of the rebel movement of Bahram Chobin, and later took part in the rebellion of Vistahm (591–596 or 594/5–600). Sources * External links * https://www.academia.edu/12102614/AN_HISTORIOGRAPHICAL_STUDY_of_AB%C5%AA_%E1%B8%A4AN%C4%AAFA_A%E1%B8%A4MAD_IBN_D%C4%80W%C5%AAD_IBN_WANAND_AL-D%C4%AANAWAR%C4%AA_S_Kit%C4%81b_al-A%E1%B8%ABb%C4%81r_al-%E1%B9%ACiw%C4%81l {{Sasanian-bio-stub Yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahram Chobin
Bahrām Chōbīn () or Wahrām Chōbēn (Middle Persian: ; died 591), also known by his epithet Mehrbandak ("servant of Mithra"), was a nobleman, general, and political leader of the late Sasanian Empire and briefly its ruler as Bahram VI (). Son of general Bahram Gushnasp and hailing from the noble House of Mihran, Bahram began his career as the governor of Ray, and was promoted to the army chief ('' spahbed'') of the northwestern portions of the empire after capturing the Byzantine stronghold of Dara, fighting in the war of 572–591. After a massive Hephthalite-Turkic invasion of the eastern Sasanian domains in 588, he was appointed as the ''spahbed'' in Khorasan, beginning a campaign that ended in a decisive Iranian victory. Bahram earned an elevated position in Iran due to his noble descent, character, skills, and accomplishments. The Sasanian king (shah) Hormizd IV () was already distrustful of Bahram and stripped the increasingly popular general of his commands. Bahr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Death Unknown
A year is a unit of time based on how long it takes the Earth to orbit the Sun. In scientific use, the tropical year (approximately 365 solar days, 5 hours, 48 minutes, 45 seconds) and the sidereal year (about 20 minutes longer) are more exact. The modern calendar year, as reckoned according to the Gregorian calendar, approximates the tropical year by using a system of leap years. The term 'year' is also used to indicate other periods of roughly similar duration, such as the lunar year (a roughly 354-day cycle of twelve of the Moon's phasessee lunar calendar), as well as periods loosely associated with the calendar or astronomical year, such as the seasonal year, the fiscal year, the academic year, etc. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by changes in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People Of The Roman–Sasanian Wars
The term "the people" refers to the public or common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings identified the inherent problems in the right of "peoples" to self-determination, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Unknown
A year is a unit of time based on how long it takes the Earth to orbit the Sun. In scientific use, the tropical year (approximately 365 solar days, 5 hours, 48 minutes, 45 seconds) and the sidereal year (about 20 minutes longer) are more exact. The modern calendar year, as reckoned according to the Gregorian calendar, approximates the tropical year by using a system of leap years. The term 'year' is also used to indicate other periods of roughly similar duration, such as the lunar year (a roughly 354-day cycle of twelve of the Moon's phasessee lunar calendar), as well as periods loosely associated with the calendar or astronomical year, such as the seasonal year, the fiscal year, the academic year, etc. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by changes in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |