|
Bahr Negus Yeshaq
Yeshaq (died 1578) was the Bahr Negus, or ruler of the Medri Bahri, during the mid to late 16th century A subordinate of Ethiopian Emperor Dawit II, he was noted for supporting Gelawdewos during the Ethiopian-Adal war, and rebelling against his successors.E.A Wallis Budge, ''Ethiopia and the Ethiopians'', vol. 2 p. 359 Reign Bahr Negus Yeshaq first appears in history about the time the Portuguese fleet arrived at Massawa in 1541. When Christovão da Gama marched inland with his 400 matchlockmen, Yeshaq not only provided him provisions and places to camp in his realm, but also about 500 soldiers and information about the land.As described by Miguel de Castanhoso in his account of the Portuguese expedition (translated in R.S. Whiteway, ''The Portuguese Expedition to Abyssinia'' ondon: The Hakluyt Society, 1902. The father of the ''Bahr negus'', who had despaired of the rightful Emperor being restored to power and had come to be a valuable supporter of Ahmed Gragn, sought pardon fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethiopian Aristocratic And Court Titles
Until the end of the Ethiopian monarchy in 1974, there were two categories of nobility in Ethiopia and Eritrea. The Mesafint ( gez, መሳፍንት , modern , singular መስፍን , modern , "prince"), the hereditary nobility, formed the upper echelon of the ruling class. The Mekwanint ( gez, መኳንንት , modern , singular መኰንን , modern or am, መኮንን , "officer") were the appointed nobles, often of humble birth, who formed the bulk of the aristocracy. Until the 20th century, the most powerful people at court were generally members of the ''Mekwanint'' appointed by the monarch, while regionally, the ''Mesafint'' enjoyed greater influence and power. Emperor Haile Selassie greatly curtailed the power of the ''Mesafint'' to the benefit of the ''Mekwanint'', who by then were essentially coterminous with the Ethiopian government. The ''Mekwanint'' were officials who had been granted specific offices in the Abyssinian government or court. Higher ranks from the titl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Özdemir Pasha
Özdemir Pasha (died 1561, Sana, Yemen Eyalet) was a Mamluk general for the Ottoman Empire, of Kumyk descent.''Mustafa Müftüoğlu.'' Yalan söyleyen tarih utansın!--. — Çile Yayınevi, 1981. — 384 с. He joined Hadım Süleyman Pasha's campaign to India in 1538 (see Ottoman naval expeditions in the Indian Ocean). Later he became the Ottoman governor of Yemen and invaded Abyssinia in 1557 for the Ottoman Empire. Özdemir Pasha was well-regarded for bringing some measure of stability in the otherwise difficult-to-govern Yemeni eyalet. Under his supervision, cities were garrisoned, fortresses were built and the trade routes were secured. His rule was cut short by his death in 1561 in Sana, Yemen. His son, Özdemiroğlu Osman Pasha, became the grand vizier of the Ottoman Empire The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
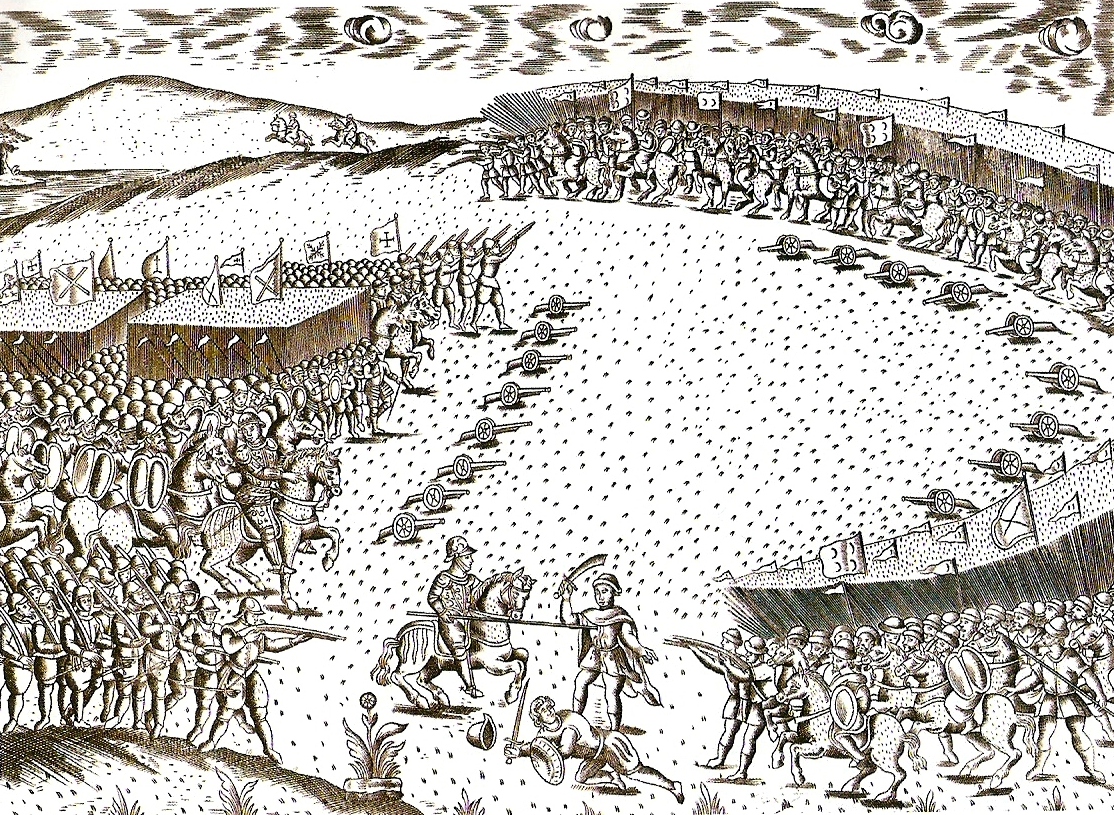
Military Personnel Killed In Action
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1578 Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 1578 ( MDLXXVIII) was a common year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events January–June * January 31 – Battle of Gembloux: Spanish forces under Don John of Austria and Alexander Farnese defeat the Dutch; Farnese begins to recover control of the French-speaking Southern Netherlands. * April 27 – The Duel of the Mignons claims the lives of two favorites of Henry III of France, and two favourites of Henry I, Duke of Guise. * May 26 – The ''Alteratie'' in Amsterdam ends Catholic rule, and opens Catholic worship there. * May 31 – Martin Frobisher sails from Harwich, England to Frobisher Bay, Canada, on his third expedition. * June 11 – Humphrey Gilbert is granted letters patent from the English crown to establish a colony in North America. July–December * July – Martin Frobisher holds the first Thanksgiving celebration by Europeans in North America, on N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Bruce
James Bruce of Kinnaird (14 December 1730 – 27 April 1794) was a Scottish traveller and travel writer who confirmed the source of the Blue Nile. He spent more than a dozen years in North Africa and Ethiopia and in 1770 became the first European to trace the origins of the Blue Nile from Egypt and Sudan. Early life James Bruce was born at the family seat of Kinnaird, Stirlingshire, and educated at Harrow School and Edinburgh University, and began to study for the bar, but his marriage to the daughter of a wine importer and merchant resulted in him entering that business instead. His wife died in October 1754, within nine months of marriage, and Bruce thereafter travelled in Portugal and Spain as part of the wine trade. The examination of oriental manuscripts at the Escorial in Spain led him to the study of Arabic and Ge'ez and determined his future career. In 1758 his father's death placed him in possession of the estate of Kinnaird. To North Africa On the outbreak of war ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Pankhurst (academic)
Richard Keir Pethick Pankhurst OBE (3 December 1927 – 16 February 2017) was a British-Ethiopian scholar, founding member of the Institute of Ethiopian Studies, and former professor at the University of Addis Ababa in Ethiopia. His books have been reviewed in scholarly journals, with Edward Ullendorff calling his ''The Ethiopians'' as another testimony to his "remarkable diligence and industry in the service of Ethiopian studies". He is known for his research on economic history and socio-cultural studies on Ethiopia. Early life and education Pankhurst was born in 1927 in Woodford Green to left communist and former suffragette Sylvia Pankhurst and Italian anarchist Silvio Corio. His maternal grandparents were Emmeline and Richard Pankhurst. Pankhurst studied at Bancroft's School in Woodford, then at the London School of Economics, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohammed IV Mansur
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monotheistic teachings of Adam, Abraham, Moses, Jesus, and other prophets. He is believed to be the Seal of the Prophets within Islam. Muhammad united Arabia into a single Muslim polity, with the Quran as well as his teachings and practices forming the basis of Islamic religious belief. Muhammad was born approximately 570CE in Mecca. He was the son of Abdullah ibn Abd al-Muttalib and Amina bint Wahb. His father Abdullah was the son of Quraysh tribal leader Abd al-Muttalib ibn Hashim, and he died a few months before Muhammad's birth. His mother Amina died when he was six, leaving Muhammad an orphan. He was raised under the care of his grandfather, Abd al-Muttalib, and paternal uncle, Abu Talib. In later years, he would periodically seclude himsel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harar
Harar ( amh, ሐረር; Harari: ሀረር; om, Adare Biyyo; so, Herer; ar, هرر) known historically by the indigenous as Gey (Harari: ጌይ ''Gēy'', ) is a walled city in eastern Ethiopia. It is also known in Arabic as the City of Saints ( ar, مدينة الأَوْلِيَاء). Harar is the capital city of the Harari Region. The ancient city is located on a hilltop in the eastern part of the country and is about five hundred kilometers from the Ethiopian capital Addis Ababa at an elevation of . For centuries, Harar has been a major commercial center, linked by the trade routes with the rest of Ethiopia, the entire Horn of Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, Asia, and through its ports, the outside world. Harar Jugol, the old walled city, was listed as a World Heritage Site in 2006 by UNESCO in recognition of its cultural heritage. Because of Harar's long history of involvement during times of trade in the Arabian Peninsula, the Government of Ethiopia has made it a crimina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarsa Dengel
Sarsa Dengel ( gez, ሠርጸ ድንግል ; 1550 – 4 October 1597), also known as Sarsa the Great, was Emperor of Ethiopia, and a member of the Solomonic dynasty. His throne name was throne name Malak Sagad I (መለክ ሰገድ ). Biography The son of Emperor Menas and Empress Admas Mogasa, and thus hailing from the Amhara people, Sarsa Dengel was elected king by the Shewan commanders of the army and the Dowager Empress. He was barely fourteen years old, but was supported by the Amhara aristocracy who feared Tigrayan influence in the person of Yishaq who frequently aligned with the Ottomans. Upon his coming of age, Sarsa Dengel had to put down a number of revolts: such as his cousin Hamalmal in 1563 at the Battle of Endagabatan, and another by his cousin Fasil two years later. Sarsa Dengel moved the center of the empire from Shewa to Begemder, especially around the Lake Tana area where he established his imperial residence and built many castles. War against the Otto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tigray Province
Tigray Province (Amharic and ), also known as Tigre ( tigrē), was a historical province of northern Ethiopia that overlayed the present day Afar and Tigray regions. Akele Guzai borders with the Tigray province It was one It encompassed most of the territories of Tigrinya-speakers (and a few minority groups) in Ethiopia. Tigray was separated from the northern Tigrinya speaking territories by the Mareb River, now serving as the state border to Eritrea (formerly Eritrea Province), with the Tekezé River separating it from the Amhara dominated south. The great majority of inhabitants were Orthodox Christians (95.5% in 1994), with the exception of a small, but important Muslim subgroup ( Jeberti) and a few Catholics (mainly Irob). Protestantism is only a very recent urban phenomenon. Despite a general impression of ethnic and cultural homogeneity, there were a few ethnic minorities, especially at the borders of Tigray, belonging to a non-Tigrinya groups, such as the Saho-speakin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menas Of Ethiopia
Menas ( gez, ሜናስ, mēnās) or Minas, throne name Admas Sagad I (Ge’ez: አድማስ ሰገድ, died 1563), was Emperor of Ethiopia from 1559 until his death in 1563, and a member of the Solomonic dynasty. He was a brother of Gelawdewos and the son of Emperor Dawit II Early life According to a genealogy collected by James Bruce, Menas' father Lebna Dengel arranged Menas to be married to the daughter of Robel, governor of Bora and Selawe; upon becoming empress she took the name Adimas Moas. They had two children, Fiqtor and Theodora. During Ahmad ibn Ibrahim al-Ghazi's invasion of Ethiopia, Menas had been captured but treated well as a valuable prisoner. The typical fate of prisoners of war at the time was to be castrated and enslaved. This clemency came to an end in 1542, when the Imam, desperate for help from his fellow Muslims, included Menas in an assortment of extravagant gifts to the sultan of Yemen in return for military aid. However, Imam Ahmad's son was late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debarwa
Debarwa ( ) is a market town in central Eritrea. It is situated about 25 kilometers south of the capital Asmara, and has a population of about 25,000 inhabitants. It is the capital of the Debarwa district (''Tsilima'') in the Debub ("Southern") administrative region (one of five in Eritrea). History Debarwa was formerly the capital of an Kingdom named Medri Bahri, which roughly translates as ''Land of the Sea''. It was ruled by the Bahr Negus (''King of the Sea''). The Portuguese expedition under Cristóvão da Gama spent the rainy season of 1542 in Debarwa as the guests of the Bahr Negus. The Ottomans invaded part of Medri Bahri in 1557, and for several decades struggled for control over the local population and their Ethiopian neighbors. By the time everything settled, the Ottomans were confined to Suakin, Massawa, Hergigo and the immediate hinterlands, but at times their raids would reach into the Bogos, Hamasien and Habab districts of Eritrea. In 1576 the Ethiopian Emperor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |