|
Bafra
Bafra is a district of Samsun Province of Turkey. It is a settlement located from the Black Sea, in the fertile delta of the Kızılırmak River. The Bafra Plain is famous in Turkey for its rich soil and high quality tobacco growing conditions. The city is well known in Turkey for its ice cream, cigarettes, tobacco and agricultural produce. In 2020, the district reported a population of 143,366. The city is located 52 km northwest of Samsun and is connected by State road D.010. History The name of the municipality is thought to have come from the Phoenician name "bafira" or "bavra". Other beliefs about the etymology of the region come from the name "Ba-Hura" (Great River) given to Kizilirmak which generates the delta upon which the city is located. Historical records of human settlement in Bafra and the Kizilirmak delta date to as early as 5000 BC. Researchers working at the nearby İkiztepe ruins have found traces of human settlement belonging to the Chalcolithic peri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samsun
Samsun, historically known as Sampsounta ( gr, Σαμψούντα) and Amisos (Ancient Greek: Αμισός), is a List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, city on the north coast of Turkey and is a major Black Sea port. In 2021, Samsun recorded a population of 710,000 people. The city is the provincial capital of Samsun Province which has a population of 1,356,079. The city is home to Ondokuz Mayıs University, several hospitals, three large shopping malls, Samsunspor football club, an opera and a large and modern manufacturing district. A former Greeks, Greek settlement, the city is best known as the place where Mustafa Kemal Atatürk began the Turkish War of Independence in 1919. Name The present name of the city is believed to have come from its former Greek name of () by a Rebracketing#In Greek, reinterpretation of (meaning "to Amisós") and (Greek suffix for place names) to (: ) and then Samsun (). The early Greek historian Hecataeus of Miletus, Hecataeus wrote t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kızılırmak River
The Kızılırmak (, Turkish for "Red River"), once known as the Halys River ( grc, Ἅλυς) and Alis River ( hy, Ալիս), is the longest river flowing entirely within Turkey. It is a source of hydroelectric power and is not used for navigation. Geography The Kızılırmak flows for a total of , rising in Eastern Anatolia around , flowing first to the west and southwest until , then forming a wide arch, the "Halys bend", flowing first to the west, then to the northwest, passing to the northeast of Lake Tuz (''Tuz Gölü'' in Turkish), then to the north and northeast, where it is joined by its major tributary, the Delice River (once known in Greek as the Cappadox river) at . After zigzagging to the northwest to the confluence with the Devrez River at , and back to the northeast, it joins the Gökırmak (''Blue River'' in Turkish) before finally flowing via a wide delta into the Black Sea east of Samsun at . There are dams on the river at Boyabat, Altınkaya and Derben ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samsun Province
Samsun Province ( tr, Samsun ili) is a Provinces of Turkey, province of Turkey on the Black Sea coast with a population of 1,252,693 (2010). Its adjacent provinces are Sinop Province, Sinop on the northwest, Çorum Province, Çorum on the west, Amasya Province, Amasya on the south, Tokat Province, Tokat on the southeast on the east. Its Turkish car number plates#Location codes, traffic code is 55. The provincial capital is Samsun, one of the most populated cities in Turkey. History Surgical instruments are manufactured in the province today and were 4000 years ago. The founder of the Turkey, Turkish Republic, Kemal Atatürk, Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, started the Turkish War of Independence here on May 19, 1919. Geography Lakes Ladik Lake, Akgöl, Dumanlı lake, Semenlik lake. Rivers Kızılırmak, Yeşilırmak, Terme river, Aptal Suyu, Mert Irmağı, Kürtün Suyu. Forest There are also small areas of bottomland forest. Districts Samsun province is divided into 17 Dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countries Of The World
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, 2 United Nations General Assembly observers#Present non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (2 states, both in associated state, free association with New Zealand). Compi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The region is bounded by the Turkish Straits to the northwest, the Black Sea to the north, the Armenian Highlands to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and the Aegean Sea to the west. The Sea of Marmara forms a connection between the Black and Aegean seas through the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits and separates Anatolia from Thrace on the Balkan peninsula of Southeast Europe. The eastern border of Anatolia has been held to be a line between the Gulf of Alexandretta and the Black Sea, bounded by the Armenian Highlands to the east and Mesopotamia to the southeast. By this definition Anatolia comprises approximately the western two-thirds of the Asian part of Turkey. Today, Anatolia is sometimes considered to be synonymous with Asian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalcolithic
The Copper Age, also called the Chalcolithic (; from grc-gre, χαλκός ''khalkós'', "copper" and ''líthos'', "stone") or (A)eneolithic (from Latin '' aeneus'' "of copper"), is an archaeological period characterized by regular human manipulation of copper, but prior to the discovery of bronze alloys. Modern researchers consider the period as a subset of the broader Neolithic, but earlier scholars defined it as a transitional period between the Neolithic and the Bronze Age. The archaeological site of Belovode, on Rudnik mountain in Serbia, has the world's oldest securely dated evidence of copper smelting at high temperature, from (7000 BP). The transition from Copper Age to Bronze Age in Europe occurred between the late 5th and the late In the Ancient Near East the Copper Age covered about the same period, beginning in the late and lasting for about a millennium before it gave rise to the Early Bronze Age. Terminology The multiple names result from m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second principal period of the three-age system proposed in 1836 by Christian Jürgensen Thomsen for classifying and studying ancient societies and history. An ancient civilization is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age because it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from production areas elsewhere. Bronze is harder and more durable than the other metals available at the time, allowing Bronze Age civilizations to gain a technological advantage. While terrestrial iron is naturally abundant, the higher temperature required for smelting, , in addition to the greater difficulty of working with the metal, placed it out of reach of common use until the end o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
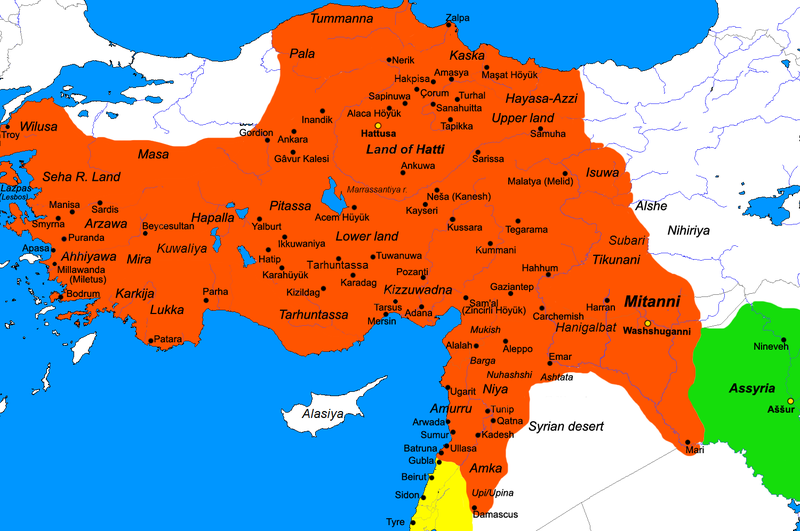
Hattusa
Hattusa (also Ḫattuša or Hattusas ; Hittite: URU''Ḫa-at-tu-ša'', Turkish: Hattuşaş , Hattic: Hattush) was the capital of the Hittite Empire in the late Bronze Age. Its ruins lie near modern Boğazkale, Turkey, within the great loop of the Kızılırmak River (Hittite: ''Marashantiya''; Greek: '' Halys''). Hattusa was added to the UNESCO World Heritage Site list in 1986. Surroundings The landscape surrounding the city included rich agricultural fields and hill lands for pasture as well as woods. Smaller woods are still found outside the city, but in ancient times, they were far more widespread. This meant the inhabitants had an excellent supply of timber when building their houses and other structures. The fields provided the people with a subsistence crop of wheat, barley and lentils. Flax was also harvested, but their primary source for clothing was sheep wool. They also hunted deer in the forest, but this was probably only a luxury reserved for the nobility. Dome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th Century BC
The 6th century BC started the first day of 600 BC and ended the last day of 501 BC. In Western Asia, the first half of this century was dominated by the Neo-Babylonian Empire, which had risen to power late in the previous century after successfully rebelling against Assyrian rule. The Kingdom of Judah came to an end in 586 BC when Babylonian forces under Nebuchadnezzar II captured Jerusalem, and removed most of its population to their own lands. Babylonian rule was ended in the 540s by Cyrus, who founded the Persian Empire in its stead. The Persian Empire continued to expand and grew into the greatest empire the world had known at the time. In Iron Age Europe, the Celtic expansion was in progress. China was in the Spring and Autumn period. *Mediterranean: Beginning of Greek philosophy, flourishes during the 5th century BC *The late Hallstatt culture period in Eastern and Central Europe, the late Bronze Age in Northern Europe *East Asia: the Spring and Autumn period. Confucia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paphlagonia
Paphlagonia (; el, Παφλαγονία, Paphlagonía, modern translit. ''Paflagonía''; tr, Paflagonya) was an ancient region on the Black Sea coast of north-central Anatolia, situated between Bithynia to the west and Pontus to the east, and separated from Phrygia (later, Galatia) by a prolongation to the east of the Bithynian Olympus. According to Strabo, the river Parthenius formed the western limit of the region, and it was bounded on the east by the Halys River. ''Paphlagonia'' was said to be named after Paphlagon, a son of the mythical Phineus.Eustath. ad Horn. II. ii. 851, ad Dion. Per. 787; Steph. B. t.v.; Const. Porph. de Them. i. 7. Geography The greater part of Paphlagonia is a rugged mountainous country, but it contains fertile valleys and produces a great abundance of hazelnuts and fruit – particularly plums, cherries and pears. The mountains are clothed with dense forests, notable for the quantity of boxwood that they furnish. Hence, its coasts were occupied by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenician Language
Phoenician ( ) is an extinct language, extinct Canaanite languages, Canaanite Semitic languages, Semitic language originally spoken in the region surrounding the cities of Tyre, Lebanon, Tyre and Sidon. Extensive Tyro-Sidonian trade and commercial dominance led to Phoenician becoming a lingua franca of the maritime Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean during the Iron Age. The Phoenician alphabet History of the Greek alphabet, spread to Greece during this period, where it became the source of all modern Alphabet#European_alphabets, European scripts. The area in which Phoenician was spoken includes the northern Levant and, at least as a prestige language, Anatolia, specifically the areas now including Syria, Lebanon, parts of Cyprus and some adjacent areas of Turkey. It was also spoken in the area of Phoenician colonies, Phoenician colonization along the coasts of the southwestern Mediterranean Sea, including those of modern Tunisia, Morocco, Libya and Algeria as well as Malta, the we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian. The ancient Persians were originally an ancient Iranian people who had migrated to the region of Persis (corresponding to the modern-day Iranian province of Fars) by the 9th century BCE. Together with their compatriot allies, they established and ruled some of the world's most powerful empires that are well-recognized for their massive cultural, political, and social influence, which covered much of the territory and population of the ancient world.. Throughout history, the Persian people have contributed greatly to art and science. Persian literature is one of the world's most prominent literary traditions. In contemporary terminology, people from Afghanistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan who natively speak the Persian language are know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)