|
Backpack Palsy
A brachial plexus injury (BPI), also known as brachial plexus lesion, is an injury to the brachial plexus, the network of nerves that conducts signals from the spinal cord to the shoulder, arm and hand. These nerves originate in the fifth, sixth, seventh and eighth cervical (C5–C8), and first thoracic (T1) spinal nerves, and innervate the muscles and skin of the chest, shoulder, arm and hand. Brachial plexus injuries can occur as a result of shoulder trauma, tumours, or inflammation, or obstetric. Obstetric injuries may occur from mechanical injury involving shoulder dystocia during difficult childbirth, with a prevalence of 1 in 1000 births. "The brachial plexus may be injured by falls from a height on to the side of the head and shoulder, whereby the nerves of the plexus are violently stretched. The brachial plexus may also be injured by direct violence or gunshot wounds, by violent traction on the arm, or by efforts at reducing a dislocation of the shoulder joint". The rare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachial Plexus
The brachial plexus is a network () of nerves formed by the anterior rami of the lower four cervical nerves and first thoracic nerve ( C5, C6, C7, C8, and T1). This plexus extends from the spinal cord, through the cervicoaxillary canal in the neck, over the first rib, and into the armpit, it supplies afferent and efferent nerve fibers the to chest, shoulder, arm, forearm, and hand. Structure The brachial plexus is divided into five ''roots'', three ''trunks'', six ''divisions'' (three anterior and three posterior), three ''cords'', and five ''branches''. There are five "terminal" branches and numerous other "pre-terminal" or "collateral" branches, such as the subscapular nerve, the thoracodorsal nerve, and the long thoracic nerve, that leave the plexus at various points along its length. A common structure used to identify part of the brachial plexus in cadaver dissections is the M or W shape made by the musculocutaneous nerve, lateral cord, median nerve, medial cord, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dura Mater
In neuroanatomy, dura mater is a thick membrane made of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. It is the outermost of the three layers of membrane called the meninges that protect the central nervous system. The other two meningeal layers are the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. It envelops the arachnoid mater, which is responsible for keeping in the cerebrospinal fluid. It is derived primarily from the neural crest cell population, with postnatal contributions of the paraxial mesoderm. Structure The dura mater has several functions and layers. The dura mater is a membrane that envelops the arachnoid mater. It surrounds and supports the dural sinuses (also called dural venous sinuses, cerebral sinuses, or cranial sinuses) and carries blood from the brain toward the heart. Cranial dura mater has two layers called '' lamellae'', a superficial layer (also called the periosteal layer), which serves as the skull's inner periosteum, ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Spinal Nerve 8
The cervical spinal nerve 8 (C8) is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment. Nervous System -- Groups of Nerves It originates from the spinal column from below the cervical vertebra 7 (C7). Innervation The C8 nerve forms part of the radial and s via the , and therefore has motor and sensory function in the |
Forceps In Childbirth
Obstetrical forceps are a medical instrument used in childbirth. Their use can serve as an alternative to the ventouse (vacuum extraction) method. Medical uses Forceps births, like all assisted births, should only be undertaken to help promote the health of the mother or baby. In general, a forceps birth is likely to be safer for both the mother and baby than the alternatives – either a ventouse birth or a caesarean section – although caveats such as operator skill apply. Advantages of forceps use include avoidance of caesarean section (and the short and long-term complications that accompany this), reduction of delivery time, and general applicability with cephalic presentation (head presentation). Common complications include the possibility of bruising the baby and causing more severe vaginal tears (perineal laceration) than would otherwise be the case (although it is important to recognise that almost all women will sustain some form of tear when delivering thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
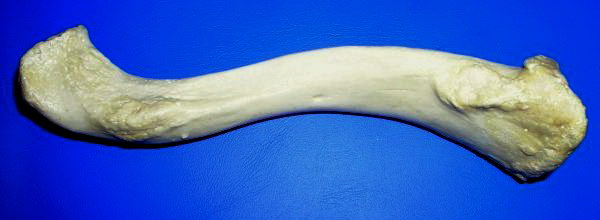
Scapula
The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble. In compound terms, the prefix omo- is used for the shoulder blade in medical terminology. This prefix is derived from ὦμος (ōmos), the Ancient Greek word for shoulder, and is cognate with the Latin , which in Latin signifies either the shoulder or the upper arm bone. The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage. Structure The scapula is a thick, flat bone lying on the thoracic wall that provides an attachment for three groups of muscles: i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motorcycle
A motorcycle (motorbike, bike, or trike (if three-wheeled)) is a two or three-wheeled motor vehicle steered by a handlebar. Motorcycle design varies greatly to suit a range of different purposes: long-distance travel, commuting, cruising, sport (including racing), and off-road riding. Motorcycling is riding a motorcycle and being involved in other related social activity such as joining a motorcycle club and attending motorcycle rallies. The 1885 Daimler Reitwagen made by Gottlieb Daimler and Wilhelm Maybach in Germany was the first internal combustion, petroleum-fueled motorcycle. In 1894, Hildebrand & Wolfmüller became the first series production motorcycle. Globally, motorcycles are comparably popular to cars as a method of transport. In 2021, approximately 58.6 million new motorcycles were sold around the world, fewer than the 66.7 million cars sold over the same period. In 2014, the three top motorcycle producers globally by volume were Honda (28%), Yama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Trauma
An injury is any physiological damage to living tissue caused by immediate physical stress. An injury can occur intentionally or unintentionally and may be caused by blunt trauma, penetrating trauma, burning, toxic exposure, asphyxiation, or overexertion. Injuries can occur in any part of the body, and different symptoms are associated with different injuries. Treatment of a major injury is typically carried out by a health professional and varies greatly depending on the nature of the injury. Traffic collisions are the most common cause of accidental injury and injury-related death among humans. Injuries are distinct from chronic conditions, psychological trauma, infections, or medical procedures, though injury can be a contributing factor to any of these. Several major health organizations have established systems for the classification and description of human injuries. Occurrence Injuries may be intentional or unintentional. Intentional injuries may be acts o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axon Reflex
The axon reflex (or the flare response) is the response stimulated by peripheral nerves of the body that travels away from the nerve cell body and branches to stimulate target organs. Reflexes are single reactions that respond to a stimulus making up the building blocks of the overall signaling in the body's nervous system. Neurons are the excitable cells that process and transmit these reflex signals through their axons, dendrites, and cell bodies. Axons directly facilitate intercellular communication projecting from the neuronal cell body to other neurons, local muscle tissue, glands and arterioles. In the axon reflex, signaling starts in the middle of the axon at the stimulation site and transmits signals directly to the effector organ skipping both an integration center and a chemical synapse present in the spinal cord reflex. The impulse is limited to a single bifurcated axon, or a neuron whose axon branches into two divisions and does not cause a general response to surroundin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clavicle
The clavicle, or collarbone, is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately 6 inches (15 cm) long that serves as a strut between the shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on the left and one on the right. The clavicle is the only long bone in the body that lies horizontally. Together with the shoulder blade, it makes up the shoulder girdle. It is a palpable bone and, in people who have less fat in this region, the location of the bone is clearly visible. It receives its name from the Latin ''clavicula'' ("little key"), because the bone rotates along its axis like a key when the shoulder is abducted. The clavicle is the most commonly fractured bone. It can easily be fractured by impacts to the shoulder from the force of falling on outstretched arms or by a direct hit. Structure The collarbone is a thin doubly curved long bone that connects the arm to the trunk of the body. Located directly above the first rib, it acts as a strut t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve Fibers
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons) in the peripheral nervous system. A nerve transmits electrical impulses. It is the basic unit of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses called action potentials that are transmitted along each of the axons to peripheral organs or, in the case of sensory nerves, from the periphery back to the central nervous system. Each axon, within the nerve, is an extension of an individual neuron, along with other supportive cells such as some Schwann cells that coat the axons in myelin. Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the endoneurium. The axons are bundled together into groups called fascicles, and each fascicle is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the perineurium. Finally, the entire nerve is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the epineurium. Nerve cells (often called neurons) ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesarean Section
Caesarean section, also known as C-section or caesarean delivery, is the surgical procedure by which one or more babies are delivered through an incision in the mother's abdomen, often performed because vaginal delivery would put the baby or mother at risk. Reasons for the operation include obstructed labor, twin pregnancy, high blood pressure in the mother, breech birth, and problems with the placenta or umbilical cord. A caesarean delivery may be performed based upon the shape of the mother's pelvis or history of a previous C-section. A trial of vaginal birth after C-section may be possible. The World Health Organization recommends that caesarean section be performed only when medically necessary. Most C-sections are performed without a medical reason, upon request by someone, usually the mother. A C-section typically takes 45 minutes to an hour. It may be done with a spinal block, where the woman is awake, or under general anesthesia. A urinary catheter is used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |