|
Bacillaria Paradoxa
''Bacillaria'' is a diatom genus in the family Bacillariaceae. Species *'' Bacillaria paradoxa'' Gmelin 1788 *''Bacillaria paxillifer'' ( O.F. Müller) Hendey (1951) Lifecycle This genus is photosynthetic, and reproduces sexually and asexually. Description Cells are elongated and motile, sliding along each other, in stacked colonies. Cells are rectangular in girdle view (when in colonies), and lanceolate in valve view. Raphe system is slightly keeled and runs from pole to pole. Two large plate-like chloroplasts are present, one near each end of the cell. The nucleus is located centrally. Cells are yellow-brown in colour. Fibulae are strong, and the valve surface is covered in transverse parallel structures called striae. File:Bacillaria sp movement.webm, Video of several diatoms of the genus ''Bacillaria'' moving, in real time File:Bacillaria paxillifer.tif, ''Bacillaria paxillifer'' Space station Three diatom species were sent to the International Space Station, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillaria Paxillifer
''Bacillaria paxillifer'' is a colonial diatom A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma''), "a cutting through, a severance", from el, διάτομος, diátomos, "cut in half, divided equally" from el, διατέμνω, diatémno, "to cut in twain". is any member of a large group comprising sev ... species in the family Bacillariaceae. Colonies of this diatom are motile. Members (with their long axes parallel to one another) slide against their neighbors in a coordinated fashion, allowing the entire structure to expand or contract. File:Bacillaria paxillifera.jpg, ''Bacillaria paxillifer'' File:Bacillaria paxillifer.tif, ''Bacillaria paxillifer'' References External links Plants described in 1951 Bacillariales {{Diatom-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diatom
A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma''), "a cutting through, a severance", from el, διάτομος, diátomos, "cut in half, divided equally" from el, διατέμνω, diatémno, "to cut in twain". is any member of a large group comprising several genera of algae, specifically microalgae, found in the oceans, waterways and soils of the world. Living diatoms make up a significant portion of the Earth's biomass: they generate about 20 to 50 percent of the oxygen produced on the planet each year, take in over 6.7 billion metric tons of silicon each year from the waters in which they live, and constitute nearly half of the organic material found in the oceans. The shells of dead diatoms can reach as much as a half-mile (800 m) deep on the ocean floor, and the entire Amazon basin is fertilized annually by 27 million tons of diatom shell dust transported by transatlantic winds from the African Sahara, much of it from the Bodélé Depression, which was once made up of a system of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillariaceae
Bacillariaceae is a family of diatoms in the phylum Heterokontophyta, the only family in the order Bacillariales. Some species of genera such as ''Nitzchia'' are found in halophilic environments; for example, in the seasonally flooded Makgadikgadi Pans in Botswana. Genera This family includes these genera: *'' Allonitzschia'' (1) *''Bacillaria'' Gmelin (155) *'' Crucidenticula'' (8) *'' Cylindrotheca'' Rabenh. *'' Cymbellonitzschia'' Hustedt in A.Schmidt et al. (7) *'' Denticula'' Kütz. (178) *'' Denticulopsis'' R. Simonsen and T. Kanaya, 1961 (20) *'' Fragilariopsis'' Hustedt in A. Schmidt (41) *'' Gomphonitzschia'' (14) *'' Grunowia'' (19) *'' Hantzschia'' Grunow, 1877 (258) *'' Neodenticula'' Akiba and Yanagisawa, 1986 (2) *''Nitzschia'' Hassall, 1845 (2k) *'' Nitzschiella'' (18) *'' Ophidocampa'' (15) *'' Perrya'' (7) *'' Psammodictyona'' (5) *''Pseudo-nitzschia'' H. Perag. and Perag., 1900 (81) *'' Simonsenia'' (3) *'' Tryblionella'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillaria Paradoxa
''Bacillaria'' is a diatom genus in the family Bacillariaceae. Species *'' Bacillaria paradoxa'' Gmelin 1788 *''Bacillaria paxillifer'' ( O.F. Müller) Hendey (1951) Lifecycle This genus is photosynthetic, and reproduces sexually and asexually. Description Cells are elongated and motile, sliding along each other, in stacked colonies. Cells are rectangular in girdle view (when in colonies), and lanceolate in valve view. Raphe system is slightly keeled and runs from pole to pole. Two large plate-like chloroplasts are present, one near each end of the cell. The nucleus is located centrally. Cells are yellow-brown in colour. Fibulae are strong, and the valve surface is covered in transverse parallel structures called striae. File:Bacillaria sp movement.webm, Video of several diatoms of the genus ''Bacillaria'' moving, in real time File:Bacillaria paxillifer.tif, ''Bacillaria paxillifer'' Space station Three diatom species were sent to the International Space Station, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colony (biology)
In biology, a colony is composed of two or more conspecific individuals living in close association with, or connected to, one another. This association is usually for mutual benefit such as stronger defense or the ability to attack bigger prey. Colonies can form in various shapes and ways depending on the organism involved. For instance, the bacterial colony is a cluster of identical cells (clones). These colonies often form and grow on the surface of (or within) a solid medium, usually derived from a single parent cell. Colonies, in the context of development, may be composed of two or more unitary (or solitary) organisms or be modular organisms. Unitary organisms have determinate development (set life stages) from zygote to adult form and individuals or groups of individuals (colonies) are visually distinct. Modular organisms have indeterminate growth forms (life stages not set) through repeated iteration of genetically identical modules (or individuals), and it can be diffic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH while freeing oxygen from water in the cells. The ATP and NADPH is then used to make organic molecules from carbon dioxide in a process known as the Calvin cycle. Chloroplasts carry out a number of other functions, including fatty acid synthesis, amino acid synthesis, and the immune response in plants. The number of chloroplasts per cell varies from one, in unicellular algae, up to 100 in plants like ''Arabidopsis'' and wheat. A chloroplast is characterized by its two membranes and a high concentration of chlorophyll. Other plastid types, such as the leucoplast and the chromoplast, contain little chlorophyll and do not carry out photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are highly dynamic—they circulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Nucleus
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have no nuclei, and a few others including osteoclasts have many. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm; and the nuclear matrix, a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support. The cell nucleus contains nearly all of the cell's genome. Nuclear DNA is often organized into multiple chromosomes – long stands of DNA dotted with various proteins, such as histones, that protect and organize the DNA. The genes within these chromosomes are structured in such a way to promote cell function. The nucleus maintains the integrity of genes and controls the activities of the cell by regulating gene expres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), ESA (Europe), and CSA (Canada). The ownership and use of the space station is established by intergovernmental treaties and agreements. The station serves as a microgravity and space environment research laboratory in which scientific research is conducted in astrobiology, astronomy, meteorology, physics, and other fields. The ISS is suited for testing the spacecraft systems and equipment required for possible future long-duration missions to the Moon and Mars. The ISS programme evolved from the Space Station ''Freedom'', a 1984 American proposal to construct a permanently crewed Earth-orbiting station, and the contemporaneous Soviet/Russian '' Mir-2'' proposal from 1976 with similar aims. The ISS is the ninth space station to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
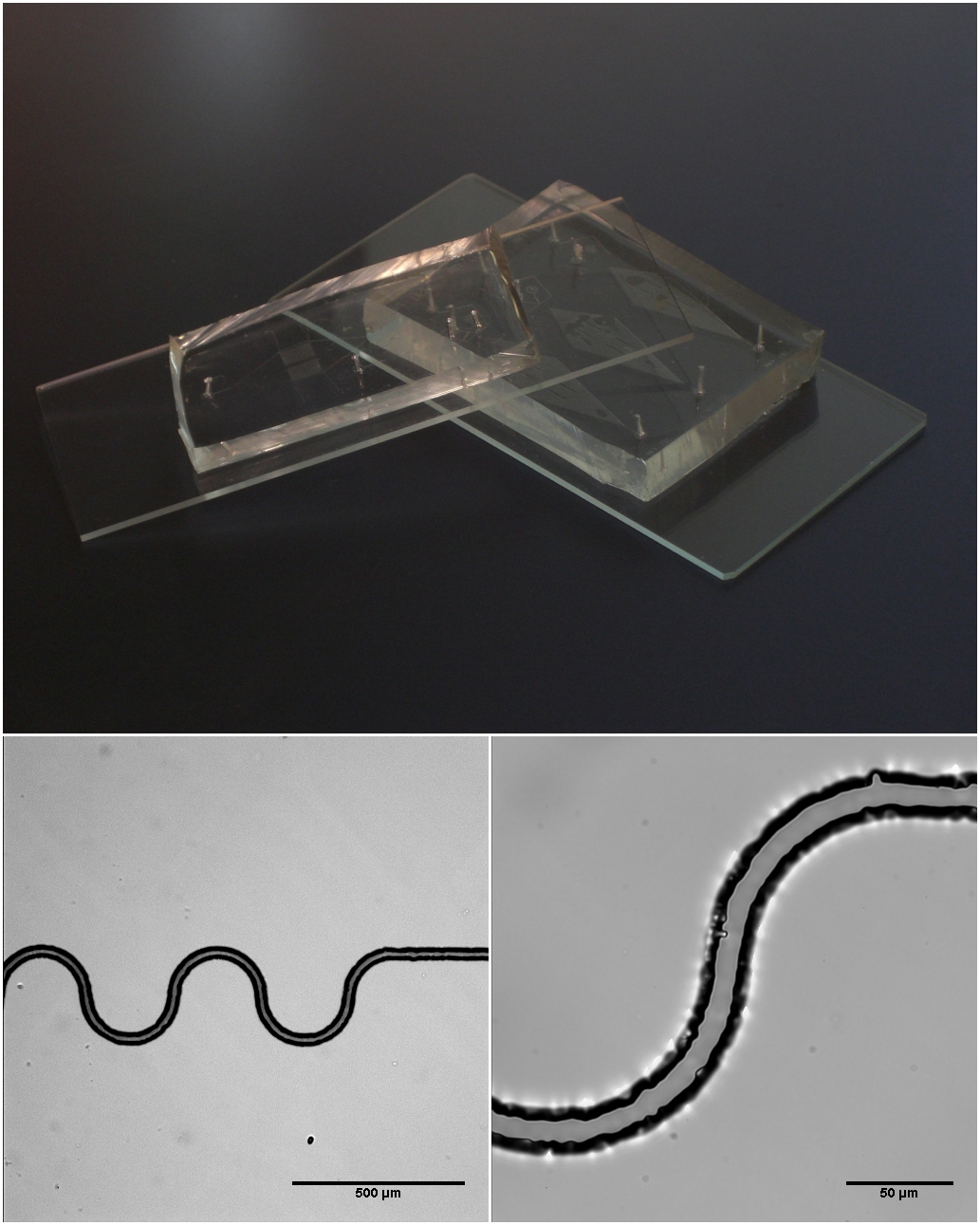
Microfluidic
Microfluidics refers to the behavior, precise control, and manipulation of fluids that are geometrically constrained to a small scale (typically sub-millimeter) at which surface forces dominate volumetric forces. It is a multidisciplinary field that involves engineering, physics, chemistry, biochemistry, nanotechnology, and biotechnology. It has practical applications in the design of systems that process low volumes of fluids to achieve multiplexing, automation, and high-throughput screening. Microfluidics emerged in the beginning of the 1980s and is used in the development of inkjet printheads, DNA chips, lab-on-a-chip technology, micro-propulsion, and micro-thermal technologies. Typically, micro means one of the following features: * Small volumes (μL, nL, pL, fL) * Small size * Low energy consumption * Microdomain effects Typically microfluidic systems transport, mix, separate, or otherwise process fluids. Various applications rely on passive fluid control using capillary for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CC-BY Icon
A Creative Commons (CC) license is one of several public copyright licenses that enable the free distribution of an otherwise copyrighted "work".A "work" is any creative material made by a person. A painting, a graphic, a book, a song/lyrics to a song, or a photograph of almost anything are all examples of "works". A CC license is used when an author wants to give other people the right to share, use, and build upon a work that the author has created. CC provides an author flexibility (for example, they might choose to allow only non-commercial uses of a given work) and protects the people who use or redistribute an author's work from concerns of copyright infringement as long as they abide by the conditions that are specified in the license by which the author distributes the work. There are several types of Creative Commons licenses. Each license differs by several combinations that condition the terms of distribution. They were initially released on December 16, 2002, by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benthic Zone
The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from ancient Greek, βένθος (bénthos), meaning "the depths." Organisms living in this zone are called benthos and include microorganisms (e.g., bacteria and fungi) as well as larger invertebrates, such as crustaceans and polychaetes. Organisms here generally live in close relationship with the substrate and many are permanently attached to the bottom. The benthic boundary layer, which includes the bottom layer of water and the uppermost layer of sediment directly influenced by the overlying water, is an integral part of the benthic zone, as it greatly influences the biological activity that takes place there. Examples of contact soil layers include sand bottoms, rocky outcrops, coral, and bay mud. Description Oceans The benthic region of the ocean begins at the shore line (intertida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |