|
Ba Đình Hall
The old National Assembly Building (Nhà Quốc hội), also Ba Đình Hall (Hội trường Ba Đình), was a public large building, located on Ba Đình Square across the Ho Chi Minh Mausoleum, in Hanoi, Vietnam. The building was used by the National Assembly of Vietnam for its sessions and other official functions. One of the architects was Nguyễn Cao Luyện (1907–1987, vi). The hall was demolished in 2008 to make room for a new parliament house. However archaeological remains of the old imperial city of Hanoi, Thăng Long Hanoi or Ha Noi ( or ; vi, Hà Nội ) is the capital and second-largest city of Vietnam. It covers an area of . It consists of 12 urban districts, one district-leveled town and 17 rural districts. Located within the Red River Delta, Hanoi i ..., were found on the site and therefore the construction of a new building on the site was delayed. General Giáp, credited with defeating the United States in the Vietnam War, objected to the demolition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
越南 河内 大会堂 - Panoramio
Throughout the history of Vietnam, many names were used in reference to Vietnam. History Throughout the history of Vietnam, official and unofficial names have been used in reference to the territory of Vietnam. Vietnam was called Văn Lang during the Hồng Bàng dynasty, Âu Lạc under Thục dynasty, Nam Việt during the Triệu dynasty, Vạn Xuân during the Early Lý dynasty, Đại Cồ Việt during the Đinh dynasty and Early Lê dynasty. Starting in 1054, Vietnam was called Đại Việt (Great Việt). During the Hồ dynasty, Vietnam was called Đại Ngu. Việt Nam ( in Vietnamese) is a variation of Nam Việt (Southern Việt), a name that can be traced back to the Triệu dynasty (2nd century BC, also known as Nanyue Kingdom). The word "Việt" originated as a shortened form of Bách Việt, a word used to refer to a people who lived in what is now southern China in ancient times. The word "Việt Nam", with the syllables in the modern order, first appears ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ba Đình Square
Ba Đình Square ( vi, Quảng trường Ba Đình) is the name of a square in Hanoi where president Ho Chi Minh read the Proclamation of Independence of the Democratic Republic of Vietnam on September 2, 1945. It is named after the Ba Đình Uprising, an anti-French rebellion that occurred in Vietnam in 1886–1887 as part of the Cần Vương movement.Origines: the streets of Vietnam : a historical companion J. Wills Burke - 2001 "Ba Đình Square, Where HỔ Chí Minh proclaimed Vietnamese independence On 2 September 1945, derives its name from this uprising. When Ho Chi Minh died, the granite Ho Chi Minh Mausoleum was built here to display his embalmed body. It remains a major site of tourism and pilgrimage. Ba Dinh Square is in the center of Ba Đình District, with several important buildings located around it, including the President's Palace, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, the Ministry of Planning and Investment, and the National Assembly In politics, a national ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ho Chi Minh Mausoleum
The President Ho Chi Minh Mausoleum ( vi, Lăng Chủ tịch Hồ Chí Minh) is a mausoleum which serves as the resting place of Vietnamese revolutionary leader and President Ho Chi Minh in Hanoi, Vietnam. It is a large building located in the center of Ba Dinh Square, where Ho, Chairman of the Workers' Party of Vietnam from 1951 until his death in 1969, read the Declaration of Independence on 2 September 1945, establishing the Democratic Republic of Vietnam. It is open to the public every morning except Monday. Building Construction work began on September 2, 1973, and the mausoleum was formally inaugurated on August 29, 1975. It was inspired by Lenin's Mausoleum in Moscow but incorporates distinct Vietnamese architectural elements, such as the sloping roof. The exterior is made of grey granite, while the interior is grey, black and red polished stone. The mausoleum's portico has the words "Chủ tịch Hồ-Chí-Minh" (President Ho Chi Minh) inscribed across it. The bann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
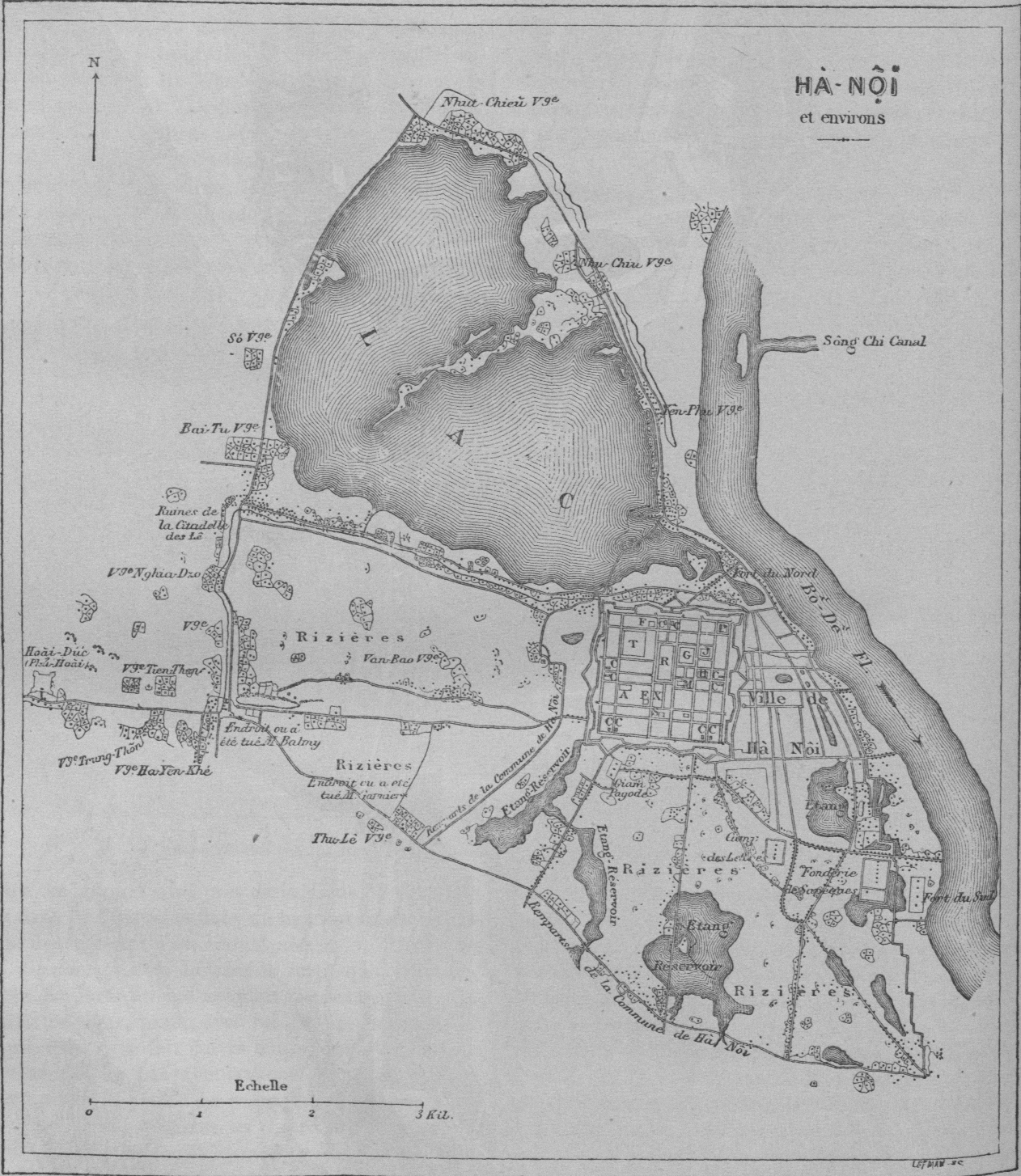
Hanoi
Hanoi or Ha Noi ( or ; vi, Hà Nội ) is the capital and second-largest city of Vietnam. It covers an area of . It consists of 12 urban districts, one district-leveled town and 17 rural districts. Located within the Red River Delta, Hanoi is the cultural and political centre of Vietnam. Hanoi can trace its history back to the third century BCE, when a portion of the modern-day city served as the capital of the historic Vietnamese nation of Âu Lạc. Following the collapse of Âu Lạc, the city was part of Han China. In 1010, Vietnamese emperor Lý Thái Tổ established the capital of the imperial Vietnamese nation Đại Việt in modern-day central Hanoi, naming the city Thăng Long (literally 'Ascending Dragon'). Thăng Long remained Đại Việt's political centre until 1802, when the Nguyễn dynasty, the last imperial Vietnamese dynasty, moved the capital to Huế. The city was renamed Hanoi in 1831, and served as the capital of French Indochina from 1902 to 1945. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Assembly Of Vietnam
The National Assembly of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam ( vi, Quốc hội nước Cộng hoà xã hội chủ nghĩa Việt Nam) is the national legislature of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam. The Constitution of Vietnam recognizes the assembly as "the highest organ of state power." The National Assembly, a 500-delegate unicameral body elected to a five-year term, meets in the session twice a year. The assembly appoints the president (head of state), the prime minister (head of government), the chief justice of the Supreme People's Court of Vietnam, the head of the Supreme People's Procuracy of Vietnam (or 'Supreme People's Office of Supervision and Inspection'), and the 21-member Government. Vietnam is an authoritarian state. The National Assembly has been characterized as a rubber stamp for the Vietnamese Communist Party (VCP) or as only being able to affect issues of low sensitivity to the regime. The VCP controls nomination and election processes at every level. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Citadel Of Thăng Long
The Imperial Citadel of Thăng Long ( vi, Hoàng thành Thăng Long; Hán-Nôm: ) is a complex of historic buildings associated with the history of Vietnam located in the centre of Hanoi, Vietnam. Its construction began in 1010 and was completed in early 1011 under the reign of Emperor Lý Thái Tổ of the Lý dynasty. History Pre-Thăng Long period During the early and middle Tang dynasty, modern Vietnam was administered as the Annan protectorate (Vietnamese: ''An Nam đô hộ phủ)'', with the seat of power located in Tong Binh (the area of modern Hanoi). In 866, after recapturing the protectorate from Nanzhao forces, Tang Dynasty general Gao Pian re-established the protectorate as the Jinghaijun ordered the construction of the Đại La Citadel, which would later become the Imperial Citadel of Thăng Long. The fall of the Tang Dynasty brought about a period of turbulent independence in Vietnam called the Anarchy of the 12 Warlords, which ended after the creation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Võ Nguyên Giáp
Võ Nguyên Giáp (; 25 August 1911 – 4 October 2013) was a Vietnamese general and communist politician who is regarded as having been one of the greatest military strategists of the 20th century. He served as interior minister in President Hồ Chí Minh's Việt Minh government, the military commander of the Việt Minh, the commander of the People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN), minister of defence, and deputy prime minister. He also served as a member of the Politburo of the Vietnam Workers' Party, which in 1976 became the Communist Party of Vietnam. Giáp first rose to prominence during World War II, when he served as the military leader of the Viet Minh resistance against the Japanese occupation of Vietnam. He had no direct military training and was a history teacher at a French-speaking academy, influenced by historical military leaders and personally citing T. E. Lawrence and Napoleon as his two greatest influences. He later earned the moniker "Red Napoleon" from some Wester ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures Demolished In 2008
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governmental Office In Hanoi
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state. In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a means by which organizational policies are enforced, as well as a mechanism for determining policy. In many countries, the government has a kind of constitution, a statement of its governing principles and philosophy. While all types of organizations have governance, the term ''government'' is often used more specifically to refer to the approximately 200 independent national governments and subsidiary organizations. The major types of political systems in the modern era are democracies, monarchies, and authoritarian and totalitarian regimes. Historically prevalent forms of government include monarchy, aristocracy, timocracy, oligarchy, democracy, theocracy, and tyranny. These forms are not always mutually exclusive, and mixed governme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demolished Buildings And Structures In Vietnam
Demolition (also known as razing, cartage, and wrecking) is the science and engineering in safely and efficiently tearing down of buildings and other artificial structures. Demolition contrasts with deconstruction, which involves taking a building apart while carefully preserving valuable elements for reuse purposes. For small buildings, such as houses, that are only two or three stories high, demolition is a rather simple process. The building is pulled down either manually or mechanically using large hydraulic equipment: elevated work platforms, cranes, excavators or bulldozers. Larger buildings may require the use of a wrecking ball, a heavy weight on a cable that is swung by a crane into the side of the buildings. Wrecking balls are especially effective against masonry, but are less easily controlled and often less efficient than other methods. Newer methods may use rotational hydraulic shears and silenced rock-breakers attached to excavators to cut or break through wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |