|
BTBD9
BTB domain containing 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BTBD9 gene. BTBD9 is in a subgroup of BTB(POZ) proteins, which contribute to the forming of limbs and determination of cell fate in developing Drosophila melanogaster. BTB(POZ) proteins also play a role in cellular functions such as: cytoskeleton regulation, transcription regulation, the gating and assembly of ion channels, and ubiquitination of proteins. BTBD9 is highly expressed throughout the brain and shows variable levels of expression in most other body tissues. The gene is located on the short arm of chromosome 6 and the domain contains eight exons and seven introns. The chromosome 6 locational domain that codes for BTB(POZ) proteins is understood to contain genes encoding protein-protein interactions. BTBD9 is a protein located in cellular cytosol and also expressed within Human embryonic kidney cell lineages. There is also evidence suggesting that BTBD9 is highly expressed within the human nervou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BTBD9
BTB domain containing 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BTBD9 gene. BTBD9 is in a subgroup of BTB(POZ) proteins, which contribute to the forming of limbs and determination of cell fate in developing Drosophila melanogaster. BTB(POZ) proteins also play a role in cellular functions such as: cytoskeleton regulation, transcription regulation, the gating and assembly of ion channels, and ubiquitination of proteins. BTBD9 is highly expressed throughout the brain and shows variable levels of expression in most other body tissues. The gene is located on the short arm of chromosome 6 and the domain contains eight exons and seven introns. The chromosome 6 locational domain that codes for BTB(POZ) proteins is understood to contain genes encoding protein-protein interactions. BTBD9 is a protein located in cellular cytosol and also expressed within Human embryonic kidney cell lineages. There is also evidence suggesting that BTBD9 is highly expressed within the human nervou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Restless Legs Syndrome
Restless legs syndrome (RLS), also known as Willis-Ekbom disease (WED), is generally a long-term disorder that causes a strong urge to move one's legs. There is often an unpleasant feeling in the legs that improves somewhat by moving them. This is often described as aching, tingling, or crawling in nature. Occasionally, arms may also be affected. The feelings generally happen when at rest and therefore can make it hard to sleep. Due to the disturbance in sleep, people with RLS may have daytime sleepiness, low energy, irritability and a depressed mood. Additionally, many have limb twitching during sleep. RLS is not the same as habitual foot tapping or leg rocking. Risk factors for RLS include low iron levels, kidney failure, Parkinson's disease, diabetes mellitus, rheumatoid arthritis, pregnancy and celiac disease. A number of medications may also trigger the disorder including antidepressants, antipsychotics, antihistamines, and calcium channel blockers. There are two main ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebellum
The cerebellum (Latin for "little brain") is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger. In humans, the cerebellum plays an important role in motor control. It may also be involved in some cognition, cognitive functions such as attention and language as well as emotion, emotional control such as regulating fear and pleasure responses, but its movement-related functions are the most solidly established. The human cerebellum does not initiate movement, but contributes to Motor coordination, coordination, precision, and accurate timing: it receives input from sensory systems of the spinal cord and from other parts of the brain, and integrates these inputs to fine-tune motor activity. Cerebellar damage produces disorders in Fine motor skill, fine movement, Equilibrioception, equilibrium, Human positions, posture, and motor learning in humans. Anatomica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocytosis
Endocytosis is a cellular process in which substances are brought into the cell. The material to be internalized is surrounded by an area of cell membrane, which then buds off inside the cell to form a vesicle containing the ingested material. Endocytosis includes pinocytosis (cell drinking) and phagocytosis (cell eating). It is a form of active transport. History The term was proposed by De Duve in 1963. Phagocytosis was discovered by Élie Metchnikoff in 1882. Pathways Endocytosis pathways can be subdivided into four categories: namely, receptor-mediated endocytosis (also known as clathrin-mediated endocytosis), caveolae, pinocytosis, and phagocytosis Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is .... *Clathrin-mediated endocytosis is mediated by the production of smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synaptic Vesicle
In a neuron, synaptic vesicles (or neurotransmitter vesicles) store various neurotransmitters that are released at the synapse. The release is regulated by a voltage-dependent calcium channel. Vesicles are essential for propagating nerve impulses between neurons and are constantly recreated by the cell. The area in the axon that holds groups of vesicles is an axon terminal or "terminal bouton". Up to 130 vesicles can be released per bouton over a ten-minute period of stimulation at 0.2 Hz. In the visual cortex of the human brain, synaptic vesicles have an average diameter of 39.5 nanometers (nm) with a standard deviation of 5.1 nm. Structure Synaptic vesicles are relatively simple because only a limited number of proteins fit into a sphere of 40 nm diameter. Purified vesicles have a protein:phospholipid ratio of 1:3 with a lipid composition of 40% phosphatidylcholine, 32% phosphatidylethanolamine, 12% phosphatidylserine, 5% phosphatidylinositol, and 10% chole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synaptic Plasticity
In neuroscience, synaptic plasticity is the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time, in response to increases or decreases in their activity. Since memories are postulated to be represented by vastly interconnected neural circuits in the brain, synaptic plasticity is one of the important neurochemical foundations of learning and memory (''see Hebbian theory''). Plastic change often results from the alteration of the number of neurotransmitter receptors located on a synapse. There are several underlying mechanisms that cooperate to achieve synaptic plasticity, including changes in the quantity of neurotransmitters released into a synapse and changes in how effectively cells respond to those neurotransmitters. Synaptic plasticity in both excitatory and inhibitory synapses has been found to be dependent upon postsynaptic calcium release. Historical discoveries In 1973, Terje Lømo and Tim Bliss first described the now widely studied phenomenon of long-term pote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knockout Mouse
A knockout mouse, or knock-out mouse, is a genetically modified mouse (''Mus musculus'') in which researchers have inactivated, or "knocked out", an existing gene by replacing it or disrupting it with an artificial piece of DNA. They are important animal models for studying the role of genes which have been sequenced but whose functions have not been determined. By causing a specific gene to be inactive in the mouse, and observing any differences from normal behaviour or physiology, researchers can infer its probable function. Mice are currently the laboratory animal species most closely related to humans for which the knockout technique can easily be applied. They are widely used in knockout experiments, especially those investigating genetic questions that relate to human physiology. Gene knockout in rats is much harder and has only been possible since 2003. The first recorded knockout mouse was created by Mario R. Capecchi, Martin Evans, and Oliver Smithies in 1989, for whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drosophila
''Drosophila'' () is a genus of flies, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "small fruit flies" or (less frequently) pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many species to linger around overripe or rotting fruit. They should not be confused with the Tephritidae, a related family, which are also called fruit flies (sometimes referred to as "true fruit flies"); tephritids feed primarily on unripe or ripe fruit, with many species being regarded as destructive agricultural pests, especially the Mediterranean fruit fly. One species of ''Drosophila'' in particular, ''D. melanogaster'', has been heavily used in research in genetics and is a common model organism in developmental biology. The terms "fruit fly" and "''Drosophila''" are often used synonymously with ''D. melanogaster'' in modern biological literature. The entire genus, however, contains more than 1,500 species and is very diverse in appearance, be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
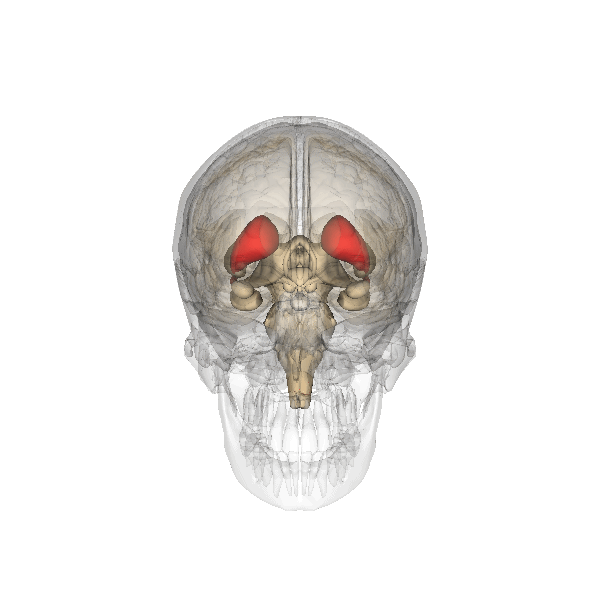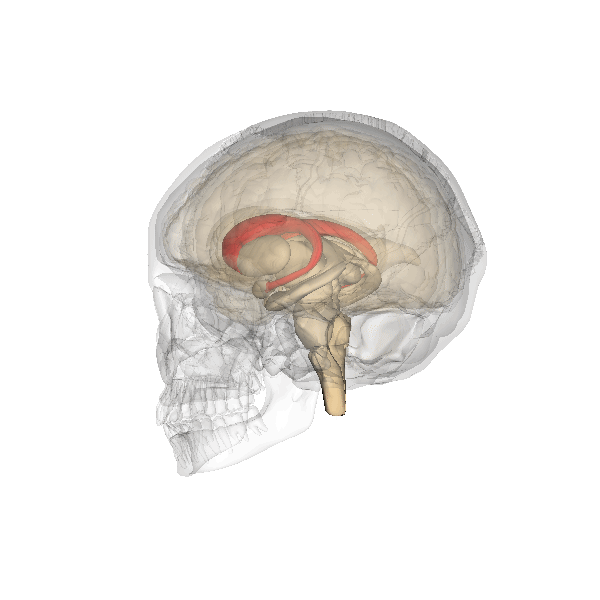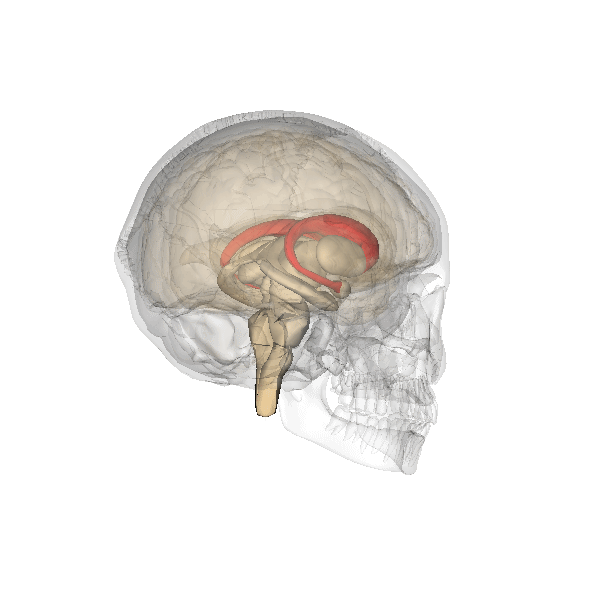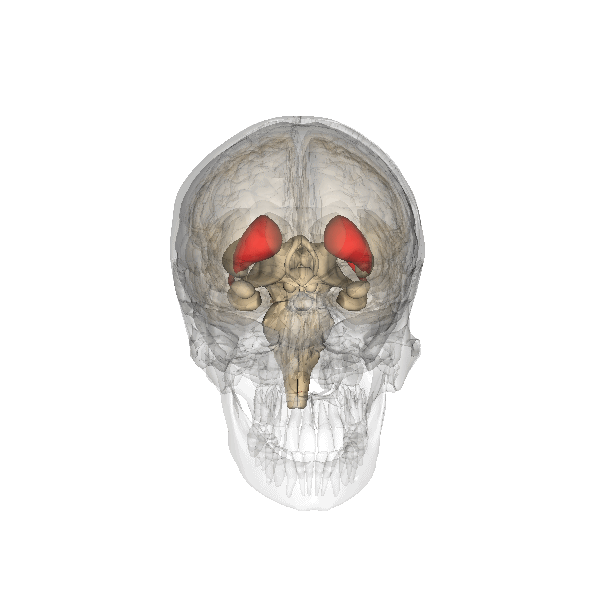
Caudate Nucleus
The caudate nucleus is one of the structures that make up the corpus striatum, which is a component of the basal ganglia in the human brain. While the caudate nucleus has long been associated with motor processes due to its role in Parkinson's disease, it plays important roles in various other nonmotor functions as well, including procedural learning, associative learning and inhibitory control of action, among other functions. The caudate is also one of the brain structures which compose the reward system and functions as part of the cortico–basal ganglia– thalamic loop. Structure Together with the putamen, the caudate forms the dorsal striatum, which is considered a single functional structure; anatomically, it is separated by a large white matter tract, the internal capsule, so it is sometimes also referred to as two structures: the medial dorsal striatum (the caudate) and the lateral dorsal striatum (the putamen). In this vein, the two are functionally distinct not a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippocampus
The hippocampus (via Latin from Greek , 'seahorse') is a major component of the brain of humans and other vertebrates. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in each side of the brain. The hippocampus is part of the limbic system, and plays important roles in the consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory, and in spatial memory that enables navigation. The hippocampus is located in the allocortex, with neural projections into the neocortex in humans, as well as primates. The hippocampus, as the medial pallium, is a structure found in all vertebrates. In humans, it contains two main interlocking parts: the hippocampus proper (also called ''Ammon's horn''), and the dentate gyrus. In Alzheimer's disease (and other forms of dementia), the hippocampus is one of the first regions of the brain to suffer damage; short-term memory loss and disorientation are included among the early symptoms. Damage to the hippocampus can also result from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consisting of allocortex. It is separated into two cortices, by the longitudinal fissure that divides the cerebrum into the left and right cerebral hemispheres. The two hemispheres are joined beneath the cortex by the corpus callosum. The cerebral cortex is the largest site of neural integration in the central nervous system. It plays a key role in attention, perception, awareness, thought, memory, language, and consciousness. The cerebral cortex is part of the brain responsible for cognition. In most mammals, apart from small mammals that have small brains, the cerebral cortex is folded, providing a greater surface area in the confined volume of the cranium. Apart from minimising brain and cranial volume, cortical folding is crucial for the brain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |