|
BSC SWOT
BSC SWOT, or the Balanced Scorecard SWOT analysis, was first introduced, in 2001, by Lennart Norberg and Terry Brown. BSC SWOT is a simple concept that combines the two powerful tools BSC (Balanced Scorecard) and SWOT analysis when identifying factors that drives or hinders strategy. The four perspectives in BSC is combined with the four dimensions of SWOT in a matrix where findings may be inserted. Example: *To identify FINANCIAL (first perspective of the BSC) STRENGTHS (the first dimension of SWOT analysis). *Or to identify INTERNAL PROCESS (third perspective of the BSC) WEAKNESSES (the second dimension of SWOT analysis). The full matrix looks like this: The traditional SWOT analysis would look at external factors when looking at opportunities and threats. However the BSC SWOT would consider these attributes from both an external and internal perspective. Each field in the matrix may be looked upon as a question. For instance: 'What are my internal strengths?' or 'What op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balanced Scorecard
A balanced scorecard is a strategy performance management tool – a well structured report, that can be used by managers to keep track of the execution of activities by the staff within their control and to monitor the consequences arising from these actions. The phrase 'balanced scorecard' primarily refers to a performance management report used by a management team, and typically this team is focused on managing the implementation of a strategy or operational activities – in a 2020 survey 88% of respondents reported using Balanced Scorecard for strategy implementation management, 63% for operational management. Balanced Scorecard is also used by individuals to track personal performance, but this is uncommon – only 17% of respondents in the survey using Balanced Scorecard in this way, however it is clear from the same survey that a larger proportion (about 30%) use corporate Balanced Scorecard elements to inform personal goal setting and incentive calculations. The cri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis (or SWOT matrix) is a strategic planning and strategic management technique used to help a person or organization identify Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to business competition or project planning. It is sometimes called situational assessment or situational analysis. Additional acronyms using the same components include TOWS and WOTS-UP. This technique is designed for use in the preliminary stages of decision-making processes and can be used as a tool for evaluation of the strategic position of organizations of many kinds (for-profit enterprises, local and national governments, NGOs, etc.). It is intended to identify the internal and external factors that are favorable and unfavorable to achieving the objectives of the venture or project. Users of a SWOT analysis often ask and answer questions to generate meaningful information for each category to make the tool useful and identify their competitive advantage. SWOT has been describe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strategy
Strategy (from Greek στρατηγία ''stratēgia'', "art of troop leader; office of general, command, generalship") is a general plan to achieve one or more long-term or overall goals under conditions of uncertainty. In the sense of the " art of the general", which included several subsets of skills including military tactics, siegecraft, logistics etc., the term came into use in the 6th century C.E. in Eastern Roman terminology, and was translated into Western vernacular languages only in the 18th century. From then until the 20th century, the word "strategy" came to denote "a comprehensive way to try to pursue political ends, including the threat or actual use of force, in a dialectic of wills" in a military conflict, in which both adversaries interact. Strategy is important because the resources available to achieve goals are usually limited. Strategy generally involves setting goals and priorities, determining actions to achieve the goals, and mobilizing resources to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strategic Planning
Strategic planning is an organization's process of defining its strategy or direction, and making decisions on allocating its resources to attain strategic goals. It may also extend to control mechanisms for guiding the implementation of the strategy. Strategic planning became prominent in corporations during the 1960s and remains an important aspect of strategic management. It is executed by strategic planners or strategists, who involve many parties and research sources in their analysis of the organization and its relationship to the environment in which it competes. ''Strategy'' has many definitions, but it generally involves setting strategic goals, determining actions to achieve the goals, setting a timeline, and mobilizing resources to execute the actions. A strategy describes how the ends (goals) will be achieved by the means (resources) in a given span of time. Often, Strategic Planning is long term and organizational action steps are established from two to five ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
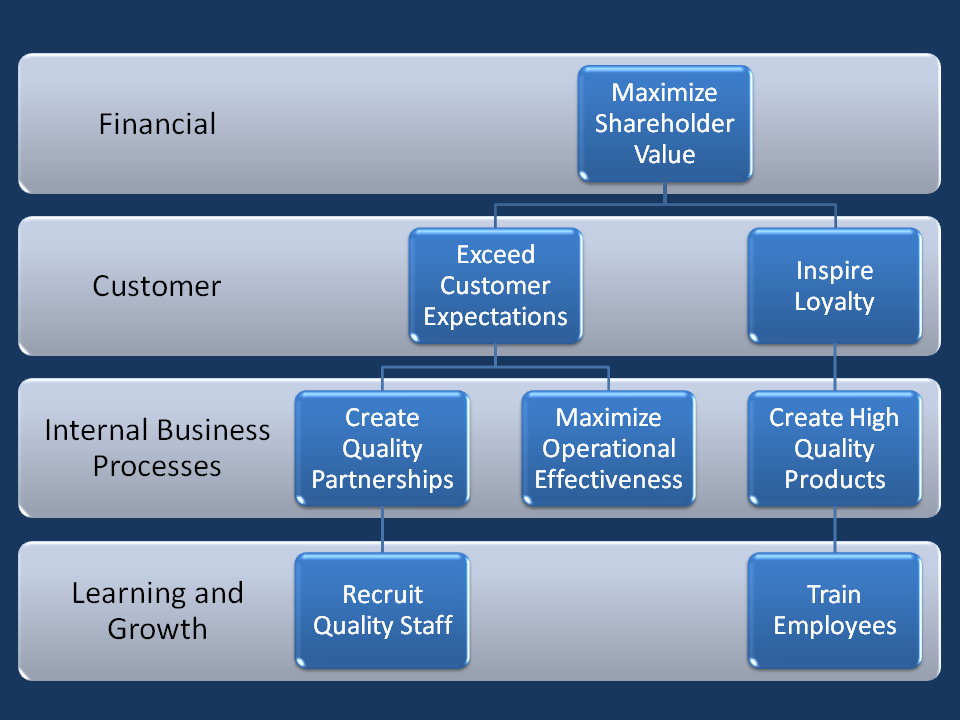
Strategy Map
A strategy map is a diagram that documents the strategic goals being pursued by an organization or management team. It is an element of the documentation associated with the Balanced Scorecard, and in particular is characteristic of the second generation of Balanced Scorecard designs that first appeared during the mid-1990s. The first diagrams of this type appeared in the early 1990s, and the idea of using this type of diagram to help document Balanced Scorecard was discussed in a paper by Robert S. Kaplan and David P. Norton in 1996. The strategy map idea featured in several books and articles during the late 1990s by Robert S. Kaplan and David P. Norton. Their original book in 1996, "The Balanced Scorecard, Translating strategy into action", contained diagrams which are later called strategy maps, but at this time they did not refer to them as such. Kaplan & Norton's second book, The Strategy Focused Organization, explicitly refers to strategy maps and includes a chapter on how ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Causality
Causality (also referred to as causation, or cause and effect) is influence by which one event, process, state, or object (''a'' ''cause'') contributes to the production of another event, process, state, or object (an ''effect'') where the cause is partly responsible for the effect, and the effect is partly dependent on the cause. In general, a process has many causes, which are also said to be ''causal factors'' for it, and all lie in its past. An effect can in turn be a cause of, or causal factor for, many other effects, which all lie in its future. Some writers have held that causality is metaphysically prior to notions of time and space. Causality is an abstraction that indicates how the world progresses. As such a basic concept, it is more apt as an explanation of other concepts of progression than as something to be explained by others more basic. The concept is like those of agency and efficacy. For this reason, a leap of intuition may be needed to grasp it. Acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porter Generic Strategies
Porter's generic strategies describe how a company pursues competitive advantage across its chosen market scope. There are three/four generic strategies, either lower cost, differentiated, or focus. A company chooses to pursue one of two types of competitive advantage, either via lower costs than its competition or by differentiating itself along dimensions valued by customers to command a higher price. A company also chooses one of two types of scope, either focus (offering its products to selected segments of the market) or industry-wide, offering its product across many market segments. The generic strategy reflects the choices made regarding both the type of competitive advantage and the scope. The concept was described by Michael Porter in 1980. Concept Porter wrote in 1980 that strategy targets either cost leadership, differentiation, or focus. These are known as Porter's three generic strategies and can be applied to any size or form of business. Porter claimed that a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strategy Dynamics
The word ‘dynamics’ appears frequently in discussions and writing about strategy, and is used in two distinct, though equally important senses. The dynamics of strategy and performance concerns the ‘content’ of strategy – initiatives, choices, policies and decisions adopted in an attempt to improve performance, and the results that arise from these managerial behaviors. The dynamic model of the strategy process is a way of understanding how strategic actions occur. It recognizes that strategic planning is dynamic, that is, strategy-making involves a complex pattern of actions and reactions. It is partially planned and partially unplanned. A literature search shows the first of these senses to be both the earliest and most widely used meaning of ‘strategy dynamics’, though that is not to diminish the importance of the dynamic view of the strategy process. Static models of strategy and performance The static assessment of strategy and performance, and its tools and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strategic Management
In the field of management, strategic management involves the formulation and implementation of the major goals and initiatives taken by an organization's managers on behalf of stakeholders, based on consideration of resources and an assessment of the internal and external environments in which the organization operates.qn, date=June 2018 Strategic management provides overall direction to an enterprise and involves specifying the organization's objectives, developing policies and plans to achieve those objectives, and then allocating resources to implement the plans. Academics and practicing managers have developed numerous models and frameworks to assist in strategic decision-making in the context of complex environments and competitive dynamics. Strategic management is not static in nature; the models can include a feedback loop to monitor execution and to inform the next round of planning. Michael Porter identifies three principles underlying strategy: * creating a " un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |