|
BPPV
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is a disorder arising from a problem in the inner ear. Symptoms are repeated, brief periods of vertigo with movement, characterized by a spinning sensation upon changes in the position of the head. * This can occur with turning in bed or changing position. Each episode of vertigo typically lasts less than one minute. Nausea is commonly associated. BPPV is one of the most common causes of vertigo. BPPV is a type of balance disorder along with labyrinthitis and Ménière's disease. It can result from a head injury or simply occur among those who are older. Often, a specific cause is not identified. When found, the underlying mechanism typically involves a small calcified otolith moving around loose in the inner ear. Diagnosis is typically made when the Dix–Hallpike test results in nystagmus (a specific movement pattern of the eyes) and other possible causes have been ruled out. In typical cases, medical imaging is not needed. BPPV is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brandt–Daroff Exercises
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is a disorder arising from a problem in the inner ear. Symptoms are repeated, brief periods of vertigo with movement, characterized by a spinning sensation upon changes in the position of the head. * This can occur with turning in bed or changing position. Each episode of vertigo typically lasts less than one minute. Nausea is commonly associated. BPPV is one of the most common causes of vertigo. BPPV is a type of balance disorder along with labyrinthitis and Ménière's disease. It can result from a head injury or simply occur among those who are older. Often, a specific cause is not identified. When found, the underlying mechanism typically involves a small calcified otolith moving around loose in the inner ear. Diagnosis is typically made when the Dix–Hallpike test results in nystagmus (a specific movement pattern of the eyes) and other possible causes have been ruled out. In typical cases, medical imaging is not needed. BPPV is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
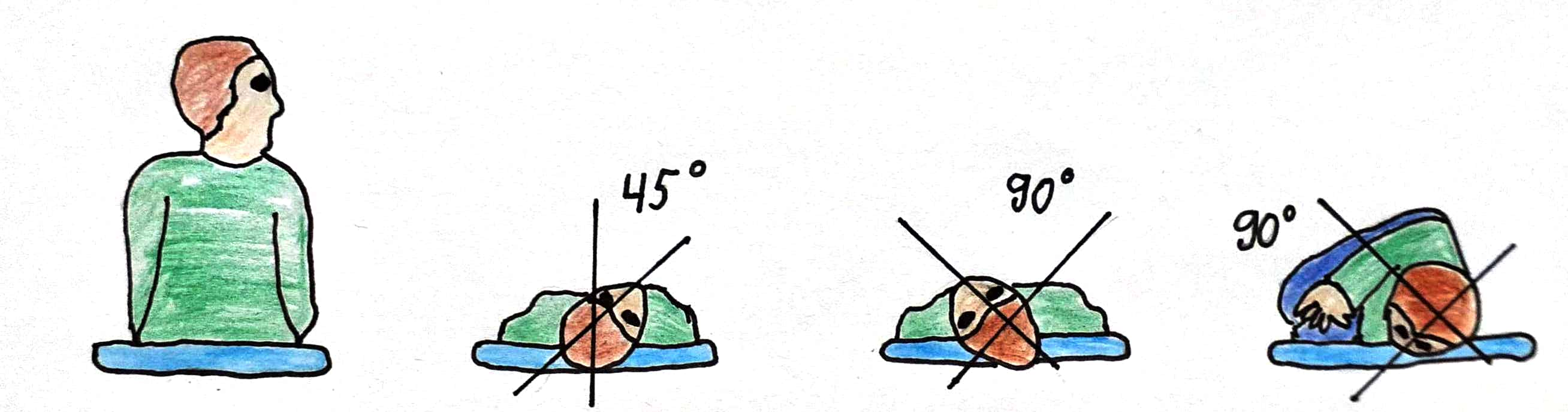
Epley Maneuver
The Epley maneuver or repositioning maneuver is a maneuver used by medical professionals to treat one common cause of vertigo, benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) of the posterior or anterior canals of the ear. The maneuver works by allowing free-floating particles, displaced otoconia, from the affected semicircular canal to be relocated by using gravity, back into the utricle, where they can no longer stimulate the cupula, therefore relieving the patient of bothersome vertigo. The maneuver was developed by the physician, John M. Epley, and was first described in 1980. A version of the maneuver called the "modified" Epley does not include vibrations of the mastoid process originally indicated by Epley, as the vibration procedures have been proven ineffective. The modified procedure has become that now described generally as the Epley maneuver. Effectiveness An Epley maneuver is a safe and effective treatment for BPPV, although the condition recurs in approximatel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertigo
Vertigo is a condition where a person has the sensation of movement or of surrounding objects moving when they are not. Often it feels like a spinning or swaying movement. This may be associated with nausea, vomiting, sweating, or difficulties walking. It is typically worse when the head is moved. Vertigo is the most common type of dizziness. The most common disorders that result in vertigo are benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), Ménière's disease, and labyrinthitis. Less common causes include stroke, brain tumors, brain injury, multiple sclerosis, migraines, trauma, and uneven pressures between the middle ears. Physiologic vertigo may occur following being exposed to motion for a prolonged period such as when on a ship or simply following spinning with the eyes closed. Other causes may include toxin exposures such as to carbon monoxide, alcohol, or aspirin. Vertigo typically indicates a problem in a part of the vestibular system. Other causes of dizziness incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertigo (medical)
Vertigo is a condition where a person has the sensation of movement or of surrounding objects moving when they are not. Often it feels like a spinning or swaying movement. This may be associated with nausea, vomiting, sweating, or difficulties walking. It is typically worse when the head is moved. Vertigo is the most common type of dizziness. The most common disorders that result in vertigo are benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), Ménière's disease, and labyrinthitis. Less common causes include stroke, brain tumors, brain injury, multiple sclerosis, migraines, trauma, and uneven pressures between the middle ears. Physiologic vertigo may occur following being exposed to motion for a prolonged period such as when on a ship or simply following spinning with the eyes closed. Other causes may include toxin exposures such as to carbon monoxide, alcohol, or aspirin. Vertigo typically indicates a problem in a part of the vestibular system. Other causes of dizziness include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dix–Hallpike Test
The Dix–Hallpike test — or Nylén–Bárány test — is a diagnostic maneuver from the group of rotation tests used to identify benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV). Procedure When performing the Dix–Hallpike test, patients are lowered quickly to a supine position (lying horizontally with the face and torso facing up) with the neck extended 30 degrees below horizontal by the clinician performing the maneuver. The Dix–Hallpike and the side-lying testing position have yielded similar results. As such, the side-lying position can be used if the Dix–Hallpike cannot be performed easily. Steps: The examiner looks for nystagmus (usually accompanied by vertigo). In BPPV, the nystagmus typically occurs in A or B only, and is torsional—the fast phase beating toward the lower ear. Its onset is usually delayed a few seconds, and it lasts 10–20 seconds. As the patient is returned to the upright position, transient nystagmus may occur in the opposite direction. Both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balance Disorder
A balance disorder is a disturbance that causes an individual to feel unsteady, for example when standing or walking. It may be accompanied by feelings of giddiness, or wooziness, or having a sensation of movement, spinning, or floating. Balance is the result of several body systems working together: the visual system (eyes), vestibular system (ears) and proprioception (the body's sense of where it is in space). Degeneration or loss of function in any of these systems can lead to balance deficits. Signs and symptoms Cognitive dysfunction (disorientation) may occur with vestibular disorders. Cognitive deficits are not just spatial in nature, but also include non-spatial functions such as object recognition memory. Vestibular dysfunction has been shown to adversely affect processes of attention and increased demands of attention can worsen the postural sway associated with vestibular disorders. Recent MRI studies also show that humans with bilateral vestibular damage (damage to bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
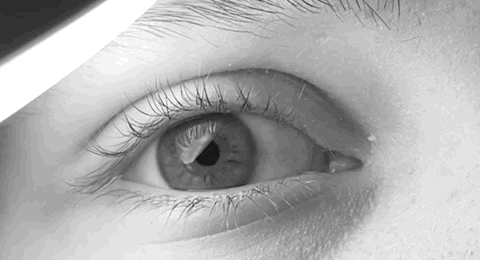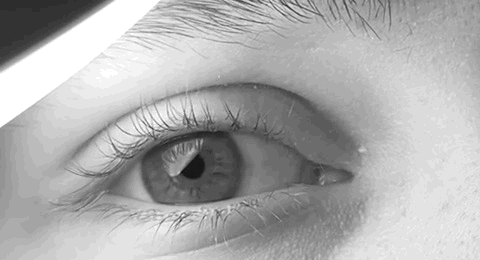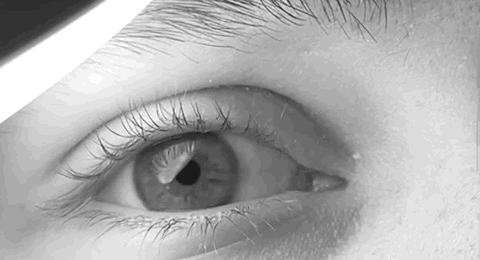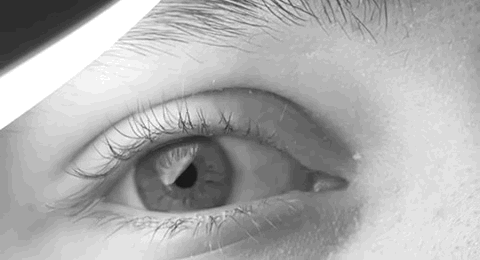
Pathologic Nystagmus
Nystagmus is a condition of involuntary (or voluntary, in some cases) eye movement. Infants can be born with it but more commonly acquire it in infancy or later in life. In many cases it may result in reduced or limited vision. Due to the involuntary movement of the eye, it has been called "dancing eyes". In normal eyesight, while the head rotates about an axis, distant visual images are sustained by rotating eyes in the opposite direction of the respective axis. The semicircular canals in the vestibule of the ear sense angular acceleration, and send signals to the nuclei for eye movement in the brain. From here, a signal is relayed to the extraocular muscles to allow one's gaze to fix on an object as the head moves. Nystagmus occurs when the semicircular canals are stimulated (e.g., by means of the caloric test, or by disease) while the head is stationary. The direction of ocular movement is related to the semicircular canal that is being stimulated. There are two key forms of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nystagmus
Nystagmus is a condition of involuntary (or voluntary, in some cases) eye movement. Infants can be born with it but more commonly acquire it in infancy or later in life. In many cases it may result in reduced or limited vision. Due to the involuntary movement of the eye, it has been called "dancing eyes". In normal eyesight, while the head rotates about an axis, distant visual images are sustained by rotating eyes in the opposite direction of the respective axis. The semicircular canals in the vestibule of the ear sense angular acceleration, and send signals to the nuclei for eye movement in the brain. From here, a signal is relayed to the extraocular muscles to allow one's gaze to fix on an object as the head moves. Nystagmus occurs when the semicircular canals are stimulated (e.g., by means of the caloric test, or by disease) while the head is stationary. The direction of ocular movement is related to the semicircular canal that is being stimulated. There are two key form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestibular Migraine
Vestibular migraine (VM) is vertigo with migraine, either as a symptom of migraine or as a related neurological disorder. A 2010 report from the University of British Columbia published in the journal ''Headache'' said that Migraine associated vertigo' is emerging as a popular diagnosis for patients with recurrent vertigo" but, "in contrast to basilar artery migraine, is neither clinically nor biologically plausible as a migraine variant." Epidemiological studies indicate a strong link between vertigo and migraine. Signs and symptoms Vertigo is a medically recognized term for the symptom of a vestibular system disturbance. It may include a feeling of rotation or illusory sensations of motion or both. The general term dizziness is used by nonmedical people for those symptoms but often refers to a feeling of light-headedness, giddiness, drowsiness, or faintness, all of which must be differentiated from true vertigo, since the latter symptoms might have other causes. Motion sic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otorhinolaryngology
Otorhinolaryngology ( , abbreviated ORL and also known as otolaryngology, otolaryngology–head and neck surgery (ORL–H&N or OHNS), or ear, nose, and throat (ENT)) is a surgical subspeciality within medicine that deals with the surgical and medical management of conditions of the head and neck. Doctors who specialize in this area are called otorhinolaryngologists, otolaryngologists, head and neck surgeons, or ENT surgeons or physicians. Patients seek treatment from an otorhinolaryngologist for diseases of the ear, nose, throat, base of the skull, head, and neck. These commonly include functional diseases that affect the senses and activities of eating, drinking, speaking, breathing, swallowing, and hearing. In addition, ENT surgery encompasses the surgical management of cancers and benign tumors and reconstruction of the head and neck as well as plastic surgery of the face and neck. Etymology The term is a combination of New Latin combining forms ('' oto-'' + ''rhino-'' + ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paroxysmal
Paroxysmal attacks or paroxysms (from Greek παροξυσμός) are a sudden recurrence or intensification of symptoms, such as a spasm or seizure. These short, frequent symptoms can be observed in various clinical conditions. They are usually associated with multiple sclerosis or pertussis, but they may also be observed in other disorders such as encephalitis, head trauma, stroke, asthma, trigeminal neuralgia, breath-holding spells, epilepsy, malaria, tabes dorsalis, and Behçet's disease, paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH). It has also been noted as a symptom of gratification disorder in children. The word paroxysm means "sudden attack, outburst", and comes from the Greek παροξυσμός (''paroxusmos''), "irritation, exasperation". Henry George Liddell, Rob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the throat. Over 30 definitions of nausea were proposed in a 2011 book on the topic. Nausea is a non-specific symptom, which means that it has many possible causes. Some common causes of nausea are gastroenteritis and other gastrointestinal disorders, food poisoning, motion sickness, dizziness, migraine, fainting, low blood sugar, anxiety, and lack of sleep. Nausea is a side effect of many medications including chemotherapy, or morning sickness in early pregnancy. Nausea may also be caused by disgust and depression. Medications taken to prevent and treat nausea and vomiting are called antiemetics. The most commonly prescribed antiemetics in the US are promethazine, metoclopramide, and the newer ondansetron. The word nausea is from Lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |