|
BMW 801E
The BMW 801 was a powerful German air-cooled 14-cylinder-radial aircraft engine built by BMW and used in a number of German Luftwaffe aircraft of World War II. Production versions of the twin-row engine generated between 1,560 and 2,000 PS (1,540–1,970 hp, or 1,150–1,470 kW). It was the most produced radial engine of Germany in World War II with more than 61,000 built. The 801 was originally intended to replace existing radial types in German transport and utility aircraft. At the time, it was widely agreed among European designers that an inline engine was a requirement for high performance designs due to its smaller frontal area and resulting lower drag. Kurt Tank successfully fitted a BMW 801 to a new fighter design he was working on, and as a result the 801 became best known as the power plant for the famous Focke-Wulf Fw 190. The BMW 801 radial also pioneered the use of what would today be designated an engine control unit: its ''Kommandogerät'' engine manag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inline Engine (aviation)
In aviation, an inline engine is a reciprocating engine with banks of cylinders, one behind another, rather than rows of cylinders, with each bank having any number of cylinders, although more than six is uncommon. The major reciprocating-engine alternative configuration is the radial engine, where the cylinders are placed in a circular or "star" arrangement. The term "inline" is used somewhat differently for aircraft engines than automotive engines. For automotive engines, the term ‘inline’ refers only to straight engines (those with a single bank of cylinders). But for aircraft, ‘inline’ can also refer to engines which are not of the straight configuration, such as V, H, or horizontally opposed. Inline engine configurations ;Straight: Engines with a single bank of cylinders which can be arranged at any angle but typically upright or inverted, (e.g. upright ADC Cirrus, inverted de Havilland Gipsy Major). ; V:Engines with two banks of cylinders with less than 180° betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cowling
A cowling is the removable covering of a vehicle's engine, most often found on automobiles, motorcycles, airplanes, and on outboard boat motors. On airplanes, cowlings are used to reduce drag and to cool the engine. On boats, cowlings are a cover for an outboard motor. In addition to protecting the engine, outboard motor cowlings need to admit air while keeping water out of the air intake. Etymology "Cowling" comes from "cowl", which originated from Middle English coule, from Old English cūle, from earlier cugele (“hood, cowl”). This, in turn, came from Ecclesiastical Latin cuculla (“monk's cowl”), from Latin cucullus (“hood”), of uncertain origin. In aviation In aviation, a cowling may be used for drag reduction or engine cooling by directing airflow. Examples in aviation include the NACA cowling and Townend ring. On an airplane, the cowling may also cover part of the fuselage, the nacelles, the engine mount and part of the cockpit.Aviation Machinist's Mates' Manua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streamline
Streamline may refer to: Business * Streamline Air, American regional airline * Adobe Streamline, a discontinued line tracing program made by Adobe Systems * Streamline Cars, the company responsible for making the Burney car Engineering * Streamlines, streaklines, and pathlines, in fluid flows * Streamliner, any vehicle shaped to be less resistant to air Film * ''Streamline'' (film), an upcoming Australian film directed by Tyson Wade Johnston Media * Streamline Pictures, an American distribution company best known for distributing English dubbed Japanese animation * Streamline Studios, an independent Dutch outsourcing and game developing studio * Hal Roach's Streamliners, a series of short films made in the 1940s * Streamline (comics), a fictional super-hero character * Stream Line, the English title of the 1976 Italian film ''La linea del fiume'' starring Philippe Leroy (actor) * ''Streamline'', a newsletter published by the Migrant Clinicians Network Music ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Transport Aircraft
A military transport aircraft, military cargo aircraft or airlifter is a military aircraft, military-owned transport aircraft used to support military operations by airlifting troops and military equipment. Transport aircraft are crucial to maintaining supply lines to forward bases that are difficult to reach by ground transport, ground or maritime transport, waterborne access, and can be used for both strategic and tactical missions. They are also often used for civilian emergency relief missions by transporting humanitarian aid. Air frames Fixed-wing Fixed-wing transport aeroplanes are defined in terms of their range capability as strategic airlift or tactical airlift to reflect the needs of the land forces which they most often support. These roughly correspond to the commercial flight length distinctions: Eurocontrol defines short-haul routes as shorter than , long-haul routes as longer than and medium-haul between. The military glider is an unpowered tactical air tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bomber
A bomber is a military combat aircraft designed to attack ground and naval targets by dropping air-to-ground weaponry (such as bombs), launching aerial torpedo, torpedoes, or deploying air-launched cruise missiles. The first use of bombs dropped from an aircraft occurred in the Italo-Turkish War, with the first major deployments coming in the World War I, First World War and World War II, Second World War by all major airforces causing devastating damage to cities, towns, and rural areas. The first purpose built bombers were the Italy, Italian Caproni Ca 30 and United Kingdom, British Bristol T.B.8, both of 1913. Some bombers were decorated with nose art or victory markings. There are two major classifications of bomber: strategic and tactical. Strategic bombing is done by heavy bombers primarily designed for long-range bombing missions against strategic targets to diminish the enemy's ability to wage war by limiting access to resources through crippling infrastructure or reduci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bramo
Siemens-Schuckert (or Siemens-Schuckertwerke) was a German electrical engineering company headquartered in Berlin, Erlangen and Nuremberg that was incorporated into the Siemens AG in 1966. Siemens Schuckert was founded in 1903 when Siemens & Halske acquired Schuckertwerke. Subsequently, Siemens & Halske specialized in communications engineering and Siemens-Schuckert in power engineering and pneumatic instrumentation. During World War I Siemens-Schuckert also produced aircraft. It took over manufacturing of the renowned Protos vehicles in 1908. In World War II, the company had a factory producing aircraft and other parts at Monowitz near Auschwitz. There was a workers camp near the factory known as Bobrek concentration camp. The Siemens Schuckert logo consisted of an S with a smaller S superimposed on the middle with the smaller S rotated left by 45 degrees.Siemens used this as a theme for their logos with absorbed companies: Siemens & Halske's logo was a large S with a small sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reich Air Ministry
The Ministry of Aviation (german: Reichsluftfahrtministerium, abbreviated RLM) was a government department during the period of Nazi Germany (1933–45). It is also the original name of the Detlev-Rohwedder-Haus building on the Wilhelmstrasse in central Berlin, Germany, which today houses the German Finance Ministry (german: Bundesministerium der Finanzen). The Ministry was in charge of development and production of all aircraft developed, designed and built in Germany during the existence of the Third Reich, overseeing all matters concerning both military and civilian designs – it handled military aviation matters as its top priority, particularly for the Luftwaffe. As was characteristic of government departments in the Nazi era, the Ministry was personality-driven and formal procedures were often ignored in favour of the whims of the Minister, ''Reichsmarschall'' Hermann Göring. As a result, early successes in aircraft development progressed only slowly and erratically dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
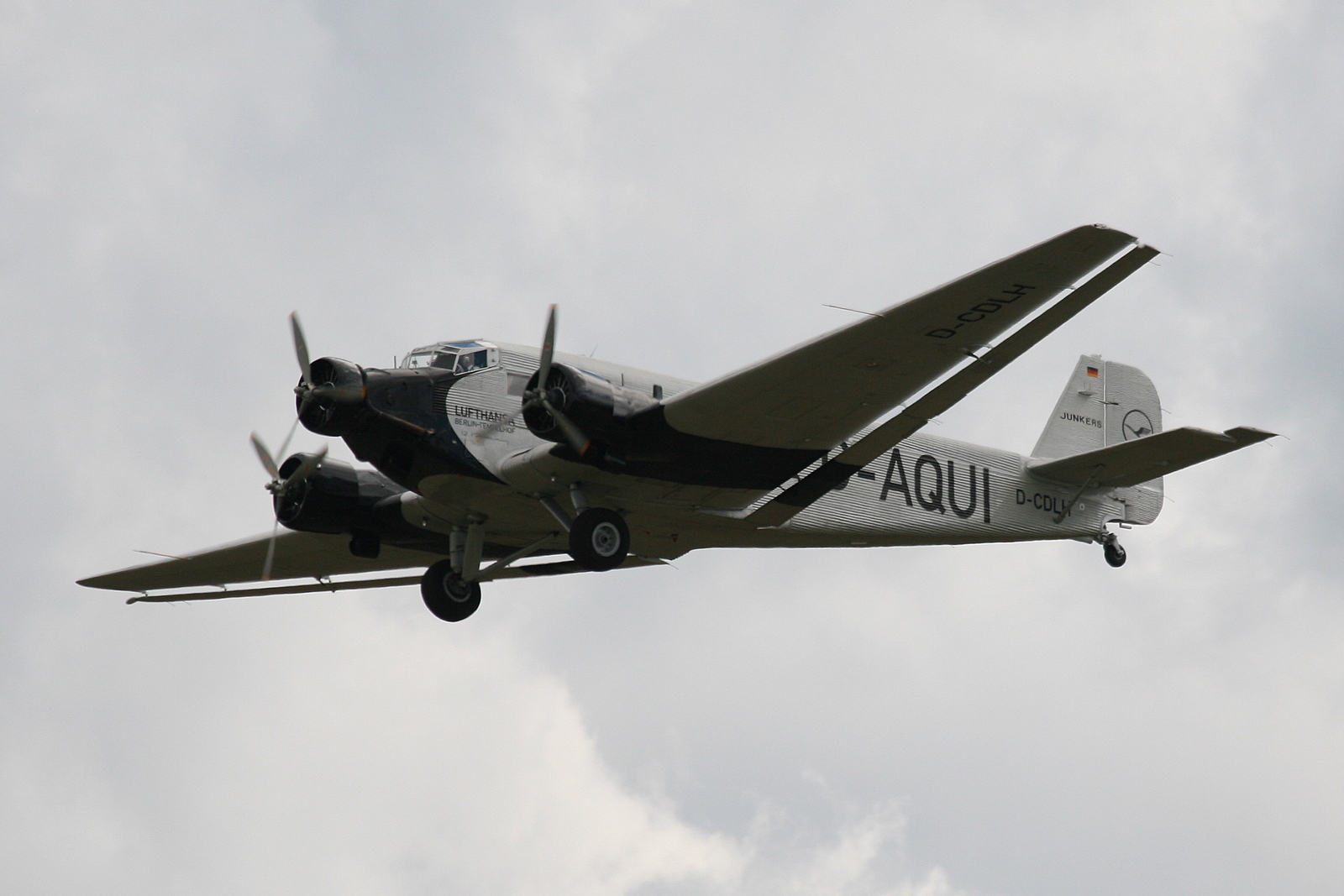
Junkers Ju 52
The Junkers Ju 52/3m (nicknamed ''Tante Ju'' ("Aunt Ju") and ''Iron Annie'') is a transport aircraft that was designed and manufactured by German aviation company Junkers. Development of the Ju 52 commenced during 1930, headed by German Aerospace engineering, aeronautical engineer Ernst Zindel. The aircraft's design incorporated a wikt:corrugated, corrugated duralumin metal skin as a strengthening measure, which was very unusual at the time. The Ju 52's maiden flight was performed on 13 October 1930. It was initially designed with a single engine, however, it was produced in quantity as a trimotor. The primary early production model, the ''Ju 52/3m'', was principally operated as a 17-seat airliner or utility transport aircraft by various civil operators during the 1930s. Following the rise of Nazi Germany, thousands of Ju 52s were procured as a staple military transport of the nation. The ''Ju 52/3mg7e'' was the principal production model. The Ju 52 was in production between 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMW 132
The BMW 132 was a nine-cylinder radial aircraft engine produced by BMW starting in 1933. Design and development BMW took over a license for manufacturing air-cooled radial engines from Pratt & Whitney on 3 January 1928. The nine-cylinder model Pratt & Whitney R-1690 Hornet was initially manufactured virtually unchanged under the designation BMW Hornet. Soon BMW embarked on its own development. The result was the BMW 132, essentially an improved version of the Hornet engine, that went into production in 1933. A number of different versions were built; aside from the carburetor designs used mainly in civilian aircraft, versions with direct fuel injection were manufactured for the German ''Luftwaffe''. The engines had a displacement of and generated up to depending on model. The 132 found widespread use in the transport role, remaining the primary powerplant of the Junkers Ju 52 for much of its life, turning the BMW 132 into one of the most important aircraft engines for civili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pratt & Whitney Hornet
The Pratt & Whitney R-1690 Hornet was a widely used American aircraft engine. Developed by Pratt & Whitney, 2,944 were produced from 1926 through 1942. It first flew in 1927. It was a single-row, 9-cylinder air-cooled radial design. Displacement was 1,690 cubic inches (27.7 L). It was built under license in Italy as the Fiat A.59. In Germany, the BMW 132 was a developed version of this engine. The R-1860 Hornet B was an enlarged version produced from 1929. Variants ;R-1690-3: ;R-1690-5: ;R-1690-11: ;R-1690-13: ;R-1690-S5D1G: ;R-1690-52: ;R-1690-SDG: ;R-1690-S1EG: ;R-1690-S2EG: ;R-1690-25: ;R-1690-S1C3G: ;Fiat A.59 R.: License built in Italy with reduction gearing. ;Fiat A.59 R.C.: License built in Italy with reduction gearing and supercharger. ;BMW Hornet:License production of the Hornet in Germany, independently developed as the BMW 132. Applications * Bach Air Yacht * Bellanca 31-40 * Boeing 80 * Boeing Model 95 * Boeing Model 299 * Burnelli UB-14 * Douglas O-38 * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_-_ASCOT482.jpg)
.jpg)


