|
BABAR Collaboration
The BaBar experiment, or simply BaBar, is an international collaboration of more than 500 physicists and engineers studying the subatomic world at energies of approximately ten times the rest mass of a proton (~10 GeV). Its design was motivated by the investigation of charge-parity violation. BaBar is located at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, which is operated by Stanford University for the Department of Energy in California. Physics BaBar was set up to understand the disparity between the matter and antimatter content of the universe by measuring Charge Parity violation. CP symmetry is a combination of Charge-conjugation symmetry (C symmetry) and Parity symmetry (P symmetry), each of which are conserved separately except in weak interactions. BaBar focuses on the study of CP violation in the B meson system. The name of the experiment is derived from the nomenclature for the B meson (symbol ) and its antiparticle (symbol , pronounced B bar). The experiment' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronvolt
In physics, an electronvolt (symbol eV, also written electron-volt and electron volt) is the measure of an amount of kinetic energy gained by a single electron accelerating from rest through an electric potential difference of one volt in vacuum. When used as a unit of energy, the numerical value of 1 eV in joules (symbol J) is equivalent to the numerical value of the charge of an electron in coulombs (symbol C). Under the 2019 redefinition of the SI base units, this sets 1 eV equal to the exact value Historically, the electronvolt was devised as a standard unit of measure through its usefulness in electrostatic particle accelerator sciences, because a particle with electric charge ''q'' gains an energy after passing through a voltage of ''V.'' Since ''q'' must be an integer multiple of the elementary charge ''e'' for any isolated particle, the gained energy in units of electronvolts conveniently equals that integer times the voltage. It is a common unit of ene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decay Rate
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered radioactive. Three of the most common types of decay are alpha decay ( ), beta decay ( ), and gamma decay ( ), all of which involve emitting one or more particles. The weak force is the mechanism that is responsible for beta decay, while the other two are governed by the electromagnetism and nuclear force. A fourth type of common decay is electron capture, in which an unstable nucleus captures an inner electron from one of the electron shells. The loss of that electron from the shell results in a cascade of electrons dropping down to that lower shell resulting in emission of discrete X-rays from the transitions. A common example is iodine-125 commonly used in medical settings. Radioactive decay is a stochastic (i.e. random) proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bottom Quark
The bottom quark or b quark, also known as the beauty quark, is a third-generation heavy quark with a charge of − ''e''. All quarks are described in a similar way by electroweak and quantum chromodynamics, but the bottom quark has exceptionally low rates of transition to lower-mass quarks. The bottom quark is also notable because it is a product in almost all top quark decays, and is a frequent decay product of the Higgs boson. Name and history The bottom quark was first described theoretically in 1973 by physicists Makoto Kobayashi and Toshihide Maskawa to explain CP violation. The name "bottom" was introduced in 1975 by Haim Harari. The bottom quark was discovered in 1977 by the Fermilab E288 experiment team led by Leon M. Lederman, when collisions produced bottomonium. Kobayashi and Maskawa won the 2008 Nobel Prize in Physics for their explanation of CP-violation. While the name "beauty" is sometimes used, "bottom" became the predominant usage by analogy o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaon
KAON (Karlsruhe ontology) is an ontology infrastructure developed by the University of Karlsruhe and the Research Center for Information Technologies in Karlsruhe. Its first incarnation was developed in 2002 and supported an enhanced version of RDF ontologies. Several tools like the graphical ontology editor OIModeler or the KAON Server were based on KAON. There are ontology learning companion tools which take non-annotated natural language text as input: TextToOnto (KAON-based) and Text2Onto (KAON2-based). Text2Onto is based on the Probabilistic Ontology Model (POM). In 2005, the first version of KAON2 was released, offering fast reasoning support for OWL ontologies. KAON2 is not backward-compatible with KAON. KAON2 is developed as a joint effort of the Information Process Engineering (IPE) at the Research Center for Information Technologies (FZI), the Institute of Applied Informatics and Formal Description Methods (AIFB) at the University of Karlsruhe, and the Informati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pion
In particle physics, a pion (or a pi meson, denoted with the Greek letter pi: ) is any of three subatomic particles: , , and . Each pion consists of a quark and an antiquark and is therefore a meson. Pions are the lightest mesons and, more generally, the lightest hadrons. They are unstable, with the charged pions and decaying after a mean lifetime of 26.033 nanoseconds ( seconds), and the neutral pion decaying after a much shorter lifetime of 85 attoseconds ( seconds). Charged pions most often decay into muons and muon neutrinos, while neutral pions generally decay into gamma rays. The exchange of virtual pions, along with vector, rho and omega mesons, provides an explanation for the residual strong force between nucleons. Pions are not produced in radioactive decay, but commonly are in high-energy collisions between hadrons. Pions also result from some matter–antimatter annihilation events. All types of pions are also produced in natural pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrometre
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer ( American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Units (SI) equalling (SI standard prefix " micro-" = ); that is, one millionth of a metre (or one thousandth of a millimetre, , or about ). The nearest smaller common SI unit is the nanometre, equivalent to one thousandth of a micrometre, one millionth of a millimetre or one billionth of a metre (). The micrometre is a common unit of measurement for wavelengths of infrared radiation as well as sizes of biological cells and bacteria, and for grading wool by the diameter of the fibres. The width of a single human hair ranges from approximately 20 to . The longest human chromosome, chromosome 1, is approximately in length. Examples Between 1 μm and 10 μm: * 1–10 μm – length of a typical bacterium * 3–8 μm � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
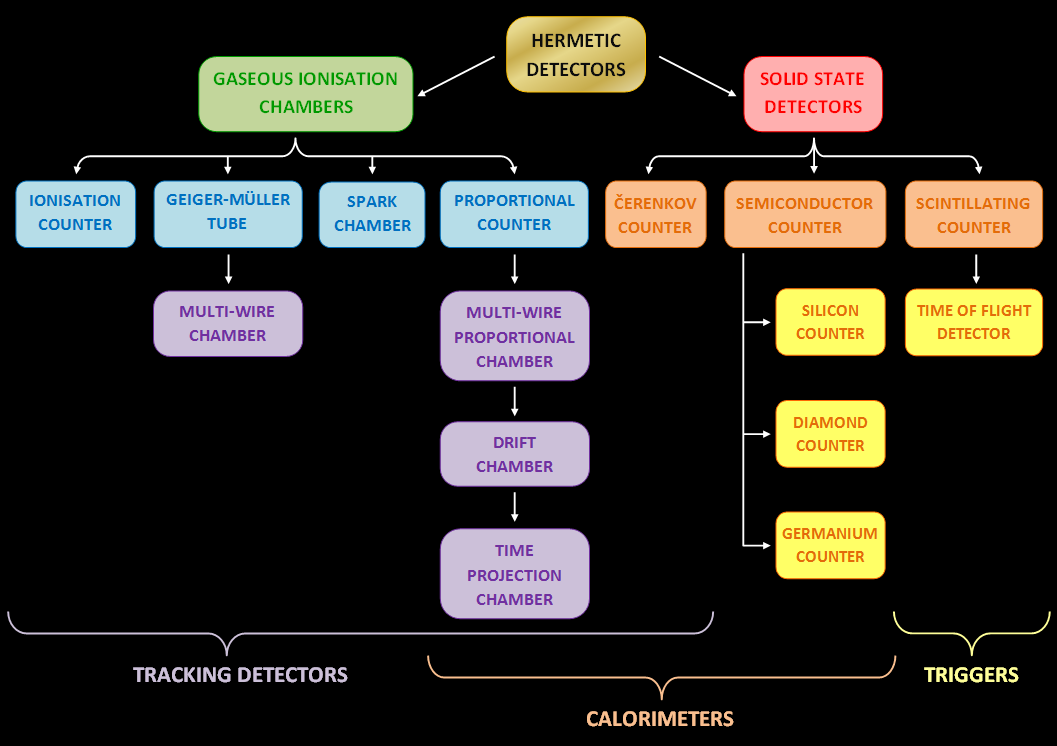
Hermetic Detector
In particle physics, a hermetic detector (also called a 4π detector) is a particle detector designed to observe all possible decay products of an interaction between subatomic particles in a collider by covering as large an area around the interaction point as possible and incorporating multiple types of sub-detectors. They are typically roughly cylindrical, with different types of detectors wrapped around each other in concentric layers; each detector type specializes in particular particles so that almost any particle will be detected and identified. Such detectors are called " hermetic" because they are constructed so as the motion of particles are ceased at the boundaries of the chamber without any moving beyond due to the seals;R. Sube 2001 �Retrieved 2012-02-12 the name "4π detector" comes from the fact that such detectors are designed to cover nearly all of the 4π steradians of solid angle around the interaction point; in terms of the standard coordinate system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid Angle
In geometry, a solid angle (symbol: ) is a measure of the amount of the field of view from some particular point that a given object covers. That is, it is a measure of how large the object appears to an observer looking from that point. The point from which the object is viewed is called the ''apex'' of the solid angle, and the object is said to ''subtend'' its solid angle at that point. In the International System of Units (SI), a solid angle is expressed in a dimensionless unit called a '' steradian'' (symbol: sr). One steradian corresponds to one unit of area on the unit sphere surrounding the apex, so an object that blocks all rays from the apex would cover a number of steradians equal to the total surface area of the unit sphere, 4\pi. Solid angles can also be measured in squares of angular measures such as degrees, minutes, and seconds. A small object nearby may subtend the same solid angle as a larger object farther away. For example, although the Moon is much small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Detector
In experimental and applied particle physics, nuclear physics, and nuclear engineering, a particle detector, also known as a radiation detector, is a device used to detect, track, and/or identify ionizing particles, such as those produced by nuclear decay, cosmic radiation, or reactions in a particle accelerator. Detectors can measure the particle energy and other attributes such as momentum, spin, charge, particle type, in addition to merely registering the presence of the particle. Examples and types Many of the detectors invented and used so far are ionization detectors (of which gaseous ionization detectors and semiconductor detectors are most typical) and scintillation detectors; but other, completely different principles have also been applied, like Čerenkov light and transition radiation. Historical examples * Bubble chamber * Wilson cloud chamber (diffusion chamber) *Photographic plate ;Detectors for radiation protection The following types of particle detec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaon
KAON (Karlsruhe ontology) is an ontology infrastructure developed by the University of Karlsruhe and the Research Center for Information Technologies in Karlsruhe. Its first incarnation was developed in 2002 and supported an enhanced version of RDF ontologies. Several tools like the graphical ontology editor OIModeler or the KAON Server were based on KAON. There are ontology learning companion tools which take non-annotated natural language text as input: TextToOnto (KAON-based) and Text2Onto (KAON2-based). Text2Onto is based on the Probabilistic Ontology Model (POM). In 2005, the first version of KAON2 was released, offering fast reasoning support for OWL ontologies. KAON2 is not backward-compatible with KAON. KAON2 is developed as a joint effort of the Information Process Engineering (IPE) at the Research Center for Information Technologies (FZI), the Institute of Applied Informatics and Formal Description Methods (AIFB) at the University of Karlsruhe, and the Informati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
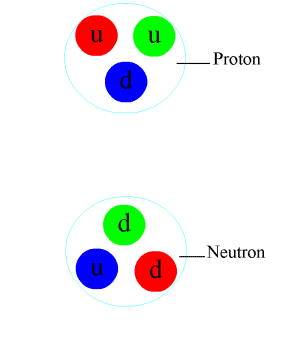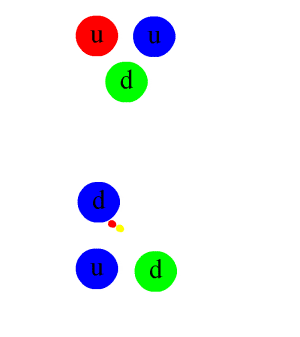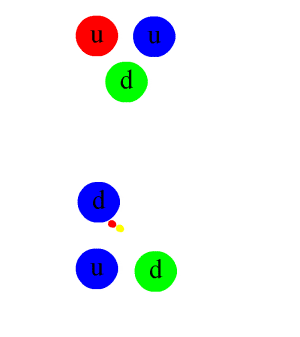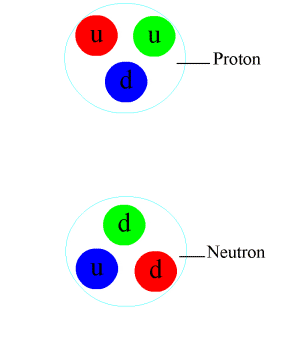
Particle Physics
Particle physics or high energy physics is the study of fundamental particles and forces that constitute matter and radiation. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) and bosons (force-carrying particles). There are three generations of fermions, but ordinary matter is made only from the first fermion generation. The first generation consists of up and down quarks which form protons and neutrons, and electrons and electron neutrinos. The three fundamental interactions known to be mediated by bosons are electromagnetism, the weak interaction, and the strong interaction. Quarks cannot exist on their own but form hadrons. Hadrons that contain an odd number of quarks are called baryons and those that contain an even number are called mesons. Two baryons, the proton and the neutron, make up most of the mass of ordinary matter. Mesons are unstable and the longest-lived last for only a few hundre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |