|
B3 Domain
The B3 DNA binding domain (DBD) is a highly conserved domain found exclusively in transcription factors (≥40 species) () combined with other domains (). It consists of 100-120 residues, includes seven beta strands and two alpha helices that form a DNA-binding pseudobarrel protein fold (); it interacts with the major groove of DNA. B3 families In '' Arabidopsis thaliana'', there are three main families of transcription factors that contain B3 domain: * ARF ( Auxin Response Factors) * ABI3 ( ABscisic acid Insensitive3) * RAV (Related to ABI3/VP1) and are only known NMR solution phase structures of the B3 DNA Binding Domain. Related proteins The N-terminal domain of restriction endonuclease EcoRII; the C-terminal domain of restriction endonuclease BfiI possess a similar DNA-binding pseudobarrel protein fold. See also *Restriction endonuclease EcoRII Restriction endonuclease (REase) EcoRII (pronounced "eco R two") is an enzyme of restriction modification system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
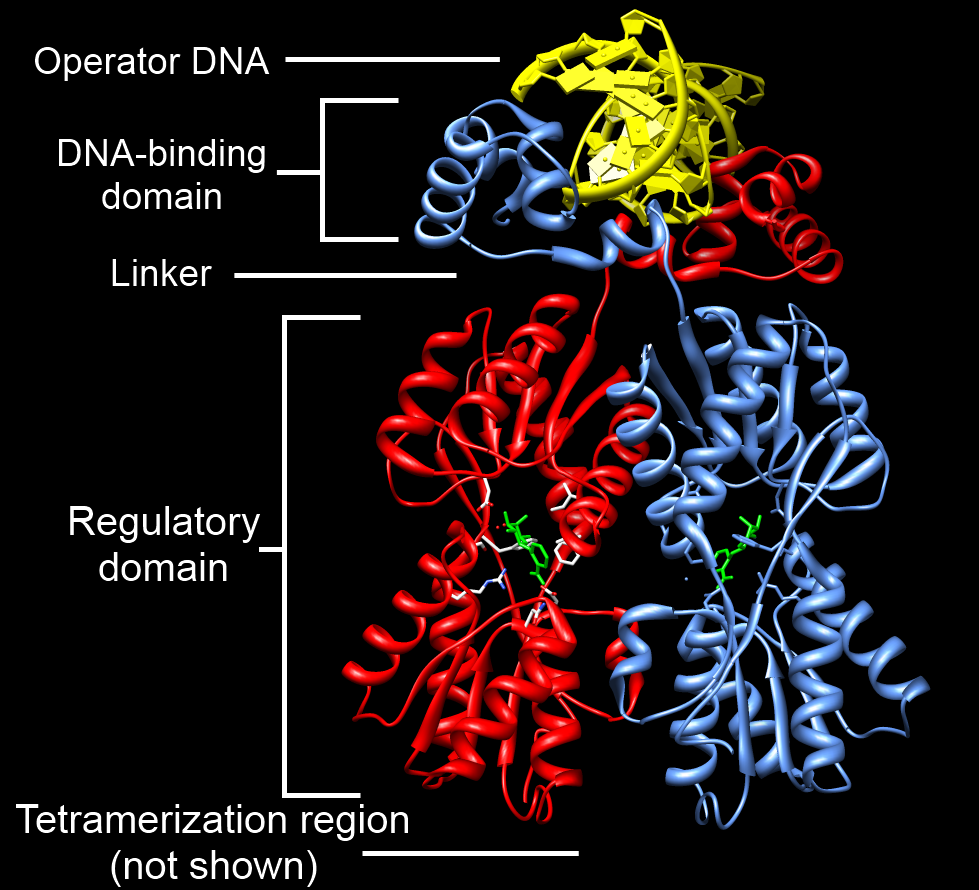
DNA Binding Domain
A DNA-binding domain (DBD) is an independently folded protein domain that contains at least one structural motif that recognizes double- or single-stranded DNA. A DBD can recognize a specific DNA sequence (a recognition sequence) or have a general affinity to DNA. Some DNA-binding domains may also include nucleic acids in their folded structure. Function One or more DNA-binding domains are often part of a larger protein consisting of further protein domains with differing function. The extra domains often regulate the activity of the DNA-binding domain. The function of DNA binding is either structural or involves transcription regulation, with the two roles sometimes overlapping. DNA-binding domains with functions involving DNA structure have biological roles in DNA replication, repair, storage, and modification, such as methylation. Many proteins involved in the regulation of gene expression contain DNA-binding domains. For example, proteins that regulate transcription by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Modelling
Molecular modelling encompasses all methods, theoretical and computational, used to model or mimic the behaviour of molecules. The methods are used in the fields of computational chemistry, drug design, computational biology and materials science to study molecular systems ranging from small chemical systems to large biological molecules and material assemblies. The simplest calculations can be performed by hand, but inevitably computers are required to perform molecular modelling of any reasonably sized system. The common feature of molecular modelling methods is the atomistic level description of the molecular systems. This may include treating atoms as the smallest individual unit (a molecular mechanics approach), or explicitly modelling protons and neutrons with its quarks, anti-quarks and gluons and electrons with its photons (a quantum chemistry approach). Molecular mechanics Molecular mechanics is one aspect of molecular modelling, as it involves the use of classical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |