|
Azores Hotspot
The Azores hotspot is a volcanic hotspot in the Northern Atlantic Ocean. The Azores is relatively young and is associated with a bathymetric swell, a gravity anomaly and ocean island basalt geochemistry. The Azores hotspot lies just east of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge Geological area The Azores domain comprises the Azores Plateau and the Azores archipelago (formed of 9 islands extending a distance of 480 km which have been volcanically active for around 7 Myr). The archipelago lies on the lateral branch of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge near the junction of three major tectonic plates; the North American Plate, the Eurasian Plate and the African Plate. This unique location causes the area to have ridge-hotspot interaction with a variation of volcanic processes. The Azores Plateau The Azores archipelago rises from Azores Plateau, which is an area of thickened oceanic crust thought to have formed over the last 20 Mya. Negative velocity S-wave anomalies have been mapped beneath the Azo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
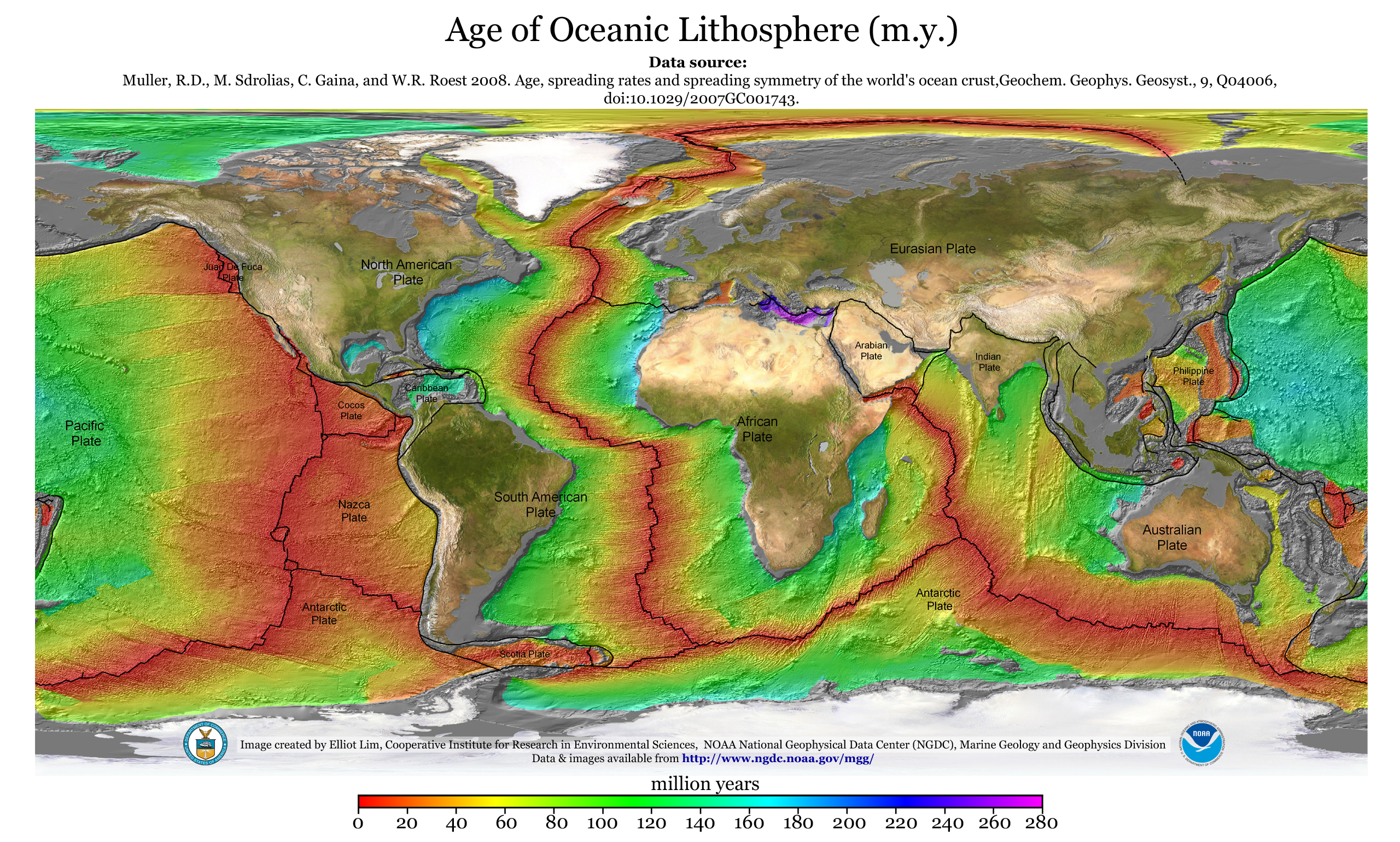
Eurasian Plate
The Eurasian Plate is a tectonic plate that includes most of the continent of Eurasia (a landmass consisting of the traditional continents of Europe and Asia), with the notable exceptions of the Indian subcontinent, the Arabian subcontinent and the area east of the Chersky Range in eastern Siberia. It also includes oceanic crust extending westward to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and northward to the Gakkel Ridge. The eastern edge is a boundary with the North American Plate to the north and a boundary with the Philippine Sea Plate to the south and possibly with the Okhotsk Plate and the Amurian Plate. The southern edge is a boundary with the African Plate to the west, the Arabian Plate in the middle and the Indo-Australian Plate to the east. The western edge is a divergent boundary with the North American Plate forming the northernmost part of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which is straddled by Iceland. All volcanic eruptions in Iceland, such as the 1973 eruption of Eldfell, the 1783 eruptio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hotspots Of The Atlantic Ocean
Hotspot, Hot Spot or Hot spot may refer to: Places * Hot Spot, Kentucky, a community in the United States Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * Hot Spot (comics), a name for the DC Comics character Isaiah Crockett * Hot Spot (Transformers), any of several characters Films * ''Hot Spot'' (1941 film), later retitled ''I Wake Up Screaming'' * ''Hot Spot'' (1945 film), a Private Snafu film * ''The Hot Spot'', a 1990 neo-noir film Other uses in arts, entertainment, and media * ''Hot Spot'' (board game), a 1979 board game published by Metagaming Concepts * "Hot Spot" (''Burn Notice''), a television episode * ''Hot Spot'' (musical), 1963 * "Hot Spot" (song), by Foxy Brown * ''Hotspot'' (album), a 2020 album by Pet Shop Boys * ''The Hot Spot'' (Podcast), a GameSpot podcast Computing * Hot spot (computer programming), a compute-intensive region of a program * Hot spot, an area which is customizable by users in software frameworks * Hotspot (Wi-Fi), a wireless n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geomorphology
Geomorphology (from Ancient Greek: , ', "earth"; , ', "form"; and , ', "study") is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of topographic and bathymetric features created by physical, chemical or biological processes operating at or near Earth's surface. Geomorphologists seek to understand why landscapes look the way they do, to understand landform and terrain history and dynamics and to predict changes through a combination of field observations, physical experiments and numerical modeling. Geomorphologists work within disciplines such as physical geography, geology, geodesy, engineering geology, archaeology, climatology, and geotechnical engineering. This broad base of interests contributes to many research styles and interests within the field. Overview Earth's surface is modified by a combination of surface processes that shape landscapes, and geologic processes that cause tectonic uplift and subsidence, and shape the coastal geography. Surface processes co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magma Chamber
A magma chamber is a large pool of liquid rock beneath the surface of the Earth. The molten rock, or magma, in such a chamber is less dense than the surrounding country rock, which produces buoyant forces on the magma that tend to drive it upwards. If the magma finds a path to the surface, then the result will be a volcanic eruption; consequently, many volcanoes are situated over magma chambers. These chambers are hard to detect deep within the Earth, and therefore most of those known are close to the surface, commonly between 1 km and 10 km down. Dynamics of magma chambers Magma rises through cracks from beneath and across the crust because it is less dense than the surrounding rock. When the magma cannot find a path upwards it pools into a magma chamber. These chambers are commonly built up over time, by successive horizontal or vertical magma injections. Influx of new magma causes reaction of pre-existing crystals and the pressure in the chamber to increase. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mid-ocean Ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a divergent plate boundary. The rate of seafloor spreading determines the morphology of the crest of the mid-ocean ridge and its width in an ocean basin. The production of new seafloor and oceanic lithosphere results from mantle upwelling in response to plate separation. The melt rises as magma at the linear weakness between the separating plates, and emerges as lava, creating new oceanic crust and lithosphere upon cooling. The first discovered mid-ocean ridge was the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which is a spreading center that bisects the North and South Atlantic basins; hence the origin of the name 'mid-ocean ridge'. Most oceanic spreading centers are not in the middle of their hosting ocean basis but regardless, are traditionally called mid-ocean rid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triple Junction
A triple junction is the point where the boundaries of three tectonic plates meet. At the triple junction each of the three boundaries will be one of three types – a ridge (R), trench (T) or transform fault (F) – and triple junctions can be described according to the types of plate margin that meet at them (e.g. Fault-Fault-Trench, Ridge-Ridge-Ridge, or abbreviated F-F-T, R-R-R). Of the ten possible types of triple junction only a few are stable through time ('stable' in this context means that the geometrical configuration of the triple junction will not change through geologic time). The meeting of four or more plates is also theoretically possible but junctions will only exist instantaneously. History The first scientific paper detailing the triple junction concept was published in 1969 by Dan McKenzie and W. Jason Morgan. The term had traditionally been used for the intersection of three divergent boundaries or spreading ridges. These three divergent boundaries ideally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-wave
__NOTOC__ In seismology and other areas involving elastic waves, S waves, secondary waves, or shear waves (sometimes called elastic S waves) are a type of elastic wave and are one of the two main types of elastic body waves, so named because they move through the body of an object, unlike surface wave In physics, a surface wave is a mechanical wave that propagates along the Interface (chemistry), interface between differing media. A common example is gravity waves along the surface of liquids, such as ocean waves. Gravity waves can also occu ...s. S waves are transverse waves, meaning that the direction of particle motion of a S wave is perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation, and the main restoring force comes from shear stress. Therefore, S waves cannot propagate in liquids with zero (or very low) viscosity; however, they may propagate in liquids with high viscosity. The name ''secondary wave'' comes from the fact that they are the second type of wave to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Crust
Oceanic crust is the uppermost layer of the oceanic portion of the tectonic plates. It is composed of the upper oceanic crust, with pillow lavas and a dike complex, and the lower oceanic crust, composed of troctolite, gabbro and ultramafic cumulates. The crust overlies the rigid uppermost layer of the mantle. The crust and the rigid upper mantle layer together constitute oceanic lithosphere. Oceanic crust is primarily composed of mafic rocks, or sima, which is rich in iron and magnesium. It is thinner than continental crust, or sial, generally less than 10 kilometers thick; however, it is denser, having a mean density of about 3.0 grams per cubic centimeter as opposed to continental crust which has a density of about 2.7 grams per cubic centimeter. The crust uppermost is the result of the cooling of magma derived from mantle material below the plate. The magma is injected into the spreading center, which consists mainly of a partly solidified crystal mush derived from earlier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Plate
The African Plate is a major tectonic plate that includes much of the continent of Africa (except for its easternmost part) and the adjacent oceanic crust to the west and south. It is bounded by the North American Plate and South American Plate to the west (separated by the Mid-Atlantic Ridge); the Arabian Plate and Somali Plate to the east; the Eurasian Plate, Aegean Sea Plate and Anatolian Plate to the north; and the Antarctic Plate to the south. Between and , the Somali Plate began rifting from the African Plate along the East African Rift. Since the continent of Africa consists of crust from both the African and the Somali plates, some literature refers to the African Plate as the Nubian Plate to distinguish it from the continent as a whole. Boundaries The western edge of the African Plate is a divergent boundary with the North American Plate to the north and the South American Plate to the south which forms the central and southern part of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. The A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North American Plate
The North American Plate is a tectonic plate covering most of North America, Cuba, the Bahamas, extreme northeastern Asia, and parts of Iceland and the Azores. With an area of , it is the Earth's second largest tectonic plate, behind the Pacific Plate (which borders the plate to the west). It extends eastward to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and westward to the Chersky Range in eastern Siberia. The plate includes both continental and oceanic crust. The interior of the main continental landmass includes an extensive granitic core called a craton. Along most of the edges of this craton are fragments of crustal material called terranes, which are accreted to the craton by tectonic actions over a long span of time. It is thought that much of North America west of the Rocky Mountains is composed of such terranes. Boundaries The southern boundary with the Cocos Plate to the west and the Caribbean Plate to the east is a transform fault, represented by the Swan Islands Transform Fault unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcano
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and most are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, deep in the Earth. This results in hotspot volcanism, of which the Hawaiian hotspot is an example. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |