|
Azo Coupling
In organic chemistry, an azo coupling is an organic reaction between a diazonium compound () and another aromatic compound that produces an azo compound (). In this electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, the aryldiazonium cation is the electrophile and the activated arene is a nucleophile. In most cases, including the examples below, the diazonium compound is also aromatic. Diazotization The process of conversion of primary aromatic amines into its diazonium salt is called diazotization. Diazonium salts are important synthetic intermediates that can undergo coupling reactions to form azo dyes and electrophilic substitution reactions to introduce functional groups. Uses of the reaction Aromatic azo compounds tend to be brightly colored due to the extended conjugated systems. Many are used as dyes (see azo dye). Important azo dyes include methyl red and pigment red 170. Azo printing exploits this reaction as well. Azo coupling is also used to produce prontosil and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dye Coupler
Dye coupler is present in Chromogen, chromogenic photographic film, film and photographic paper, paper used in photography, primarily color photography. When a color developer Redox, reduces ionized (exposed) silver halide crystals, the developer is oxidized, and the oxidized molecules react with dye coupler molecules to form a dye ''in situ.'' The silver image is removed by subsequent bleach and Photographic fixer, fix processes, so the final image will consist of the dye image. Dye coupler technology has seen considerable advancement since the beginning of modern color photography. Major film and paper manufacturers have continually improved the stability of the image dye by improving couplers, particularly since the 1980s, so that Archive, archival properties of images are enhanced in newer color papers and films. Generally speaking, dye couplers for paper use are given more emphasis on the image permanence than those for film use, but some modern films (such as Fujifilm, Fujic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the rest of the molecule's composition. This enables systematic prediction of chemical reactions and behavior of chemical compounds and the design of chemical synthesis. The reactivity of a functional group can be modified by other functional groups nearby. Functional group interconversion can be used in retrosynthetic analysis to plan organic synthesis. A functional group is a group of atoms in a molecule with distinctive chemical properties, regardless of the other atoms in the molecule. The atoms in a functional group are linked to each other and to the rest of the molecule by covalent bonds. For repeating units of polymers, functional groups attach to their nonpolar core of carbon atoms and thus add chemical character to carbon chains. Fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthesis Of Organol Brown N
Synthesis or synthesize may refer to: Science Chemistry and biochemistry *Chemical synthesis, the execution of chemical reactions to form a more complex molecule from chemical precursors **Organic synthesis, the chemical synthesis of organic compounds ***Total synthesis, the complete organic synthesis of complex organic compounds, usually without the aid of biological processes ***Convergent synthesis or linear synthesis, a strategy to improve the efficiency of multi-step chemical syntheses **Dehydration synthesis, a chemical synthesis resulting in the loss of a water molecule *Biosynthesis, the creation of an organic compound in a living organism, usually aided by enzymes **Photosynthesis, a biochemical reaction using a carbon molecule to produce an organic molecule, using sunlight as a catalyst **Chemosynthesis, the synthesis of biological compounds into organic waste, using methane or an oxidized molecule as a catalyst **Amino acid synthesis, the synthesis of an amino acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1-Naphthol
1-Naphthol, or α-naphthol, is a fluorescent organic compound with the formula . It is a white solid. It is an isomer of 2-naphthol differing by the location of the hydroxyl group on the naphthalene ring. The naphthols are naphthalene homologues of phenol, with the hydroxyl group being more reactive than in the phenols. Both isomers are soluble in simple alcohols, ethers, and chloroform. They are precursors to a variety of useful compounds. Naphthols (both 1 and 2 isomers) are used as biomarkers for livestock and humans exposed to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Production 1-Naphthol is prepared by two main routes. In one method, naphthalene is nitrated to give 1-nitronaphthalene, which is hydrogenated to the amine followed by hydrolysis: : : : Alternatively, naphthalene is hydrogenated to tetralin, which is oxidized to 1-tetralone, which undergoes dehydrogenation. Occurrence and degradation 1-Naphthol is a metabolite of the insecticide carbaryl and naphthalene. Along wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aniline
Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6 H5 NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the simplest aromatic amine In organic chemistry, an aromatic amine is an organic compound consisting of an aromatic ring attached to an amine. It is a broad class of compounds that encompasses aniline Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6 H5 NH2. Consi .... It is an industrially significant Commodity chemicals, commodity chemical, as well as a versatile starting material for fine chemical synthesis. Its main use is in the manufacture of precursors to polyurethane, dyes, and other industrial chemicals. Like most volatile amines, it has the odor of rotten fish. It Combustion, ignites readily, burning with a smoky flame characteristic of aromatic compounds. It is toxic to humans. Relative to benzene, it is electron-rich. It thus participates more rapidly in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Likewise, it is also prone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solvent Yellow 7
Solvent Yellow 7 is a common azo dye with a formula of C6H5N2C6H4OH. Synthesis Like most azobenzenes, Solvent Yellow 7 can be synthesized by the reaction of phenyldiazonium salt with phenol. The optimal pH value for this azo coupling is 8.5-10. The reaction is carried out in water, since sodium chloride (or potassium chloride) formed in the reaction is soluble in water, while the product precipitates. References See also * Benzenediazonium chloride * Azo compound *Solvent Yellow 1 Aniline Yellow is a yellow azo dye and an aromatic amine. It is a derivative of azobenzene. It has the appearance of an orange powder. Aniline Yellow was the first azo dye. it was first produced in 1861 by C. Mene. The second azo dye was Bisma ... {{aromatic-compound-stub Phenols Azo compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzenediazonium Chloride
Benzenediazonium tetrafluoroborate is an organic compound with the formula 6H5N2F4. It is a salt of a diazonium cation and tetrafluoroborate. It exists as a colourless solid that is soluble in polar solvents. It is the parent member of the aryldiazonium compounds, which are widely used in organic chemistry. Synthesis Diazotization of aniline in the presence of hydrochloric acid: : C6H5NH2 + HNO2 + HCl → 6H5N2l + 2 H2O The tetrafluoroborate can be obtained from crude benzenediazonium chloride by salt metathesis using tetrafluoroboric acid. : 6H5N2l + HBF4 → 6H5N2F4 + HCl The tetrafluoroborate is more stable than the chloride. Properties The diazo group (N2) can be replaced by many other groups, usually anions, giving a variety of substituted phenyl derivatives: :C6H5N2+ + Nu− → C6H5Nu + N2 These transformations are associated with many named reactions including the Schiemann reaction, Sandmeyer reaction, and Gomberg-Bachmann reaction. A wide range of groups th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenol
Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns. Phenol was first extracted from coal tar, but today is produced on a large scale (about 7 billion kg/year) from petroleum-derived feedstocks. It is an important industrial commodity as a precursor to many materials and useful compounds. It is primarily used to synthesize plastics and related materials. Phenol and its chemical derivatives are essential for production of polycarbonates, epoxies, Bakelite, nylon, detergents, herbicides such as phenoxy herbicides, and numerous pharmaceutical drugs. Properties Phenol is an organic compound appreciably soluble in water, with about 84.2 g dissolving in 1000 mL (0.895 M). Homogeneous mixtures of phenol and water at phenol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
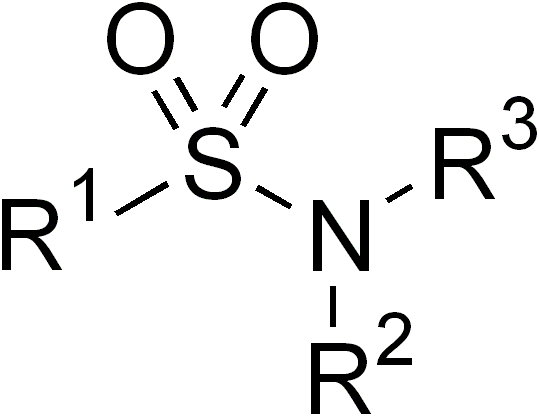
Sulfa Drugs
Sulfonamide is a functional group (a part of a molecule) that is the basis of several groups of drugs, which are called sulphonamides, sulfa drugs or sulpha drugs. The original antibacterial sulfonamides are synthetic (nonantibiotic) antimicrobial agents that contain the sulfonamide group. Some sulfonamides are also devoid of antibacterial activity, e.g., the anticonvulsant sultiame. The sulfonylureas and thiazide diuretics are newer drug groups based upon the antibacterial sulfonamides. Allergies to sulfonamides are common. The overall incidence of adverse drug reactions to sulfa antibiotics is approximately 3%, close to penicillin; hence medications containing sulfonamides are prescribed carefully. Sulfonamide drugs were the first broadly effective antibacterials to be used systemically, and paved the way for the antibiotic revolution in medicine. Function In bacteria, antibacterial sulfonamides act as competitive inhibitors of the enzyme dihydropteroate synthase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prontosil
Prontosil is an antibacterial drug of the sulfonamide group. It has a relatively broad effect against gram-positive cocci but not against enterobacteria. One of the earliest antimicrobial drugs, it was widely used in the mid-20th century but is little used today because better options now exist. The discovery and development of this first sulfonamide drug opened a new era in medicine, because it greatly widened the success of antimicrobial chemotherapy in an era when many physicians doubted its still largely untapped potential. At the time, disinfectant cleaners and topical antiseptic wound care were widely used but there were very few antimicrobial drugs to use safely inside living bodies. Antibiotic drugs derived from microbes, which we rely on heavily today, did not yet exist. Prontosil was discovered in 1932 by a research team at the Bayer Laboratories of the IG Farben conglomerate in Germany. Names The capitalized name "Prontosil" is Bayer's trade name; the nonproprietary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pigment Red 170
Naphthol Red (Pigment red 170 or PR170) is an organic pigment extensively used in automotive coatings and painting. It is produced synthetically by converting p-aminobenzamide into the corresponding diazonium compound followed by coupling with 3-hydroxy-2-naphththoic acid (2-ethoxy)anilide ("Naphtol AS-PH" dye precursor). : In the solid state the hydrazo tautomer forms and several crystal structures exist. In the initial α polymorph the molecules are arranged in a herringbone pattern with extensive hydrogen bonding. The φ polymorph is more dense and more stable and produced industrially by thermal treatment in water at 130°C under pressure. In this phase the molecules are planar and arranged in layers. Extensive hydrogen bonding exists within the layer but between layers the only interactions are Van der Waals forces. Dense crystal structures are preferred for pigments used in coatings because in the event of photochemical decomposition the fragments are locked in place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |