|
Avicephala
Avicephala ("bird heads") is an extinct, potentially polyphyletic grouping of diapsid reptiles that lived during the Late Permian and Triassic periods characterised by superficially bird-like skulls and arboreal lifestyles. As a clade, Avicephala is defined as including the gliding weigeltisaurids and the arboreal drepanosaurs to the exclusion of other major diapsid groups. This relationship is not recovered in the majority of phylogenetic analyses of early diapsids and so Avicephala is typically regarded as an unnatural grouping. However, the clade was recovered again in 2021 in a redescription of ''Weigeltisaurus'', raising the possibility that the clade may be valid after all. Description Avicephalans were named in reference to their pointed, lightly constructed, superficially bird-like skulls. The resemblance is especially striking in some drepanosaurs such as ''Avicranium'' which possess toothless beaks, forward-facing eyes and large, rounded craniums. These superficial si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drepanosaurs
Drepanosaurs (members of the clade Drepanosauromorpha) are a group of extinct reptiles that lived between the Carnian and Rhaetian stages of the late Triassic Period, approximately between 230 and 210 million years ago. The various species of drepanosaurid were characterized by specialized grasping limbs and often prehensile tails, adaptions for arboreal (tree-dwelling) and fossorial (digging) lifestyles, with some having also been suggested to be aquatic. Fossils of drepanosaurs have been found in Arizona, New Mexico, New Jersey, Utah, England, and northern Italy. The name is taken from the family's namesake genus ''Drepanosaurus'', which means "sickle lizard," a reference to their strongly curved claws. Description Drepanosaurs are notable for their distinctive, triangular skulls, which resemble the skulls of birds. Some drepanosaurs, such as ''Avicranium,'' had pointed, toothless, bird-like beaks. This similarity to birds may have led to the misattribution of what may be a dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drepanosauromorpha
Drepanosaurs (members of the clade Drepanosauromorpha) are a group of extinct reptiles that lived between the Carnian and Rhaetian stages of the late Triassic Period, approximately between 230 and 210 million years ago. The various species of drepanosaurid were characterized by specialized grasping limbs and often prehensile tails, adaptions for arboreal (tree-dwelling) and fossorial (digging) lifestyles, with some having also been suggested to be aquatic. Fossils of drepanosaurs have been found in Arizona, New Mexico, New Jersey, Utah, England, and northern Italy. The name is taken from the family's namesake genus ''Drepanosaurus'', which means "sickle lizard," a reference to their strongly curved claws. Description Drepanosaurs are notable for their distinctive, triangular skulls, which resemble the skulls of birds. Some drepanosaurs, such as ''Avicranium,'' had pointed, toothless, bird-like beaks. This similarity to birds may have led to the misattribution of what may be a dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drepanosaur
Drepanosaurs (members of the clade Drepanosauromorpha) are a group of extinct reptiles that lived between the Carnian and Rhaetian stages of the late Triassic Period, approximately between 230 and 210 million years ago. The various species of drepanosaurid were characterized by specialized grasping limbs and often prehensile tails, adaptions for arboreal (tree-dwelling) and fossorial (digging) lifestyles, with some having also been suggested to be aquatic. Fossils of drepanosaurs have been found in Arizona, New Mexico, New Jersey, Utah, England, and northern Italy. The name is taken from the family's namesake genus ''Drepanosaurus'', which means "sickle lizard," a reference to their strongly curved claws. Description Drepanosaurs are notable for their distinctive, triangular skulls, which resemble the skulls of birds. Some drepanosaurs, such as ''Avicranium,'' had pointed, toothless, bird-like beaks. This similarity to birds may have led to the misattribution of what may be a dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weigeltisauridae
Weigeltisauridae is a family of gliding neodiapsid reptiles that lived during the Late Permian, between 258 and 252 million years ago. Fossils of weigeltisaurids have been found in Madagascar, Germany, Great Britain, and Russia. A possible weigeltisaurid, '' Wapitisaurus'', been found in Early Triassic strata in North America, but its poor preservation makes referral to the group questionable. They are characterized by long, hollow rod-shaped bones extending from the torso that probably supported wing-like membranes. Similar membranes are also found in several other extinct reptiles such as kuehneosaurids and ''Mecistotrachelos'', as well as living gliding lizards, although each group evolved these structures independently. Skeleton The skulls and jaws of weigeltisaurids are ornamented with horns and tubercles, including chameleon-like frills. The torso and limbs are slender. The skeletons of weigeltisaurds are lightened by large air spaces (skeletal pneumaticity) within the bone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weigeltisaurid
Weigeltisauridae is a family of gliding neodiapsid reptiles that lived during the Late Permian, between 258 and 252 million years ago. Fossils of weigeltisaurids have been found in Madagascar, Germany, Great Britain, and Russia. A possible weigeltisaurid, ''Wapitisaurus'', been found in Early Triassic strata in North America, but its poor preservation makes referral to the group questionable. They are characterized by long, hollow rod-shaped bones extending from the torso that probably supported wing-like membranes. Similar membranes are also found in several other extinct reptiles such as kuehneosaurids and ''Mecistotrachelos'', as well as living gliding lizards, although each group evolved these structures independently. Skeleton The skulls and jaws of weigeltisaurids are ornamented with horns and tubercles, including chameleon-like frills. The torso and limbs are slender. The skeletons of weigeltisaurds are lightened by large air spaces (skeletal pneumaticity) within the bones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longisquama
''Longisquama'' is a genus of extinct reptile. There is only one species, ''Longisquama insignis'', known from a poorly preserved skeleton and several incomplete fossil impressions from the Middle to Late Triassic Madygen Formation in Kyrgyzstan. It is known from the type fossil specimen, slab and counterslab (PIN 2548/4 and PIN 2584/5) and five referred specimens of possible integumentary appendages (PIN 2584/7 through 9). All specimens are in the collection of the Paleontological Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Moscow. ''Longisquama'' means "long scales"; the specific name ''insignis'' refers to its small size. The ''Longisquama'' holotype is notable for a number of long structures that appear to grow from its skin. The current opinion is that ''Longisquama'' is an ambiguous diapsid and has no bearing on the origin of birds. History Interpretation Researchers Haubold and Buffetaut believed that the structures were long, modified scales attached in pairs t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Draco (lizard)
''Draco'' is a genus of agamid lizards that are also known as flying lizards, flying dragons or gliding lizards. These lizards are capable of gliding flight via membranes that may be extended to create wings (patagia), formed by an enlarged set of ribs. They are arboreal insectivores. While not capable of powered flight they often obtain lift in the course of their gliding flights. Glides as long as have been recorded, over which the animal loses only in height, which is quite some distance, considering that one lizard is only around in total length, tail included. Piper, Ross (2007). 'Extraordinary Animals: An Encyclopedia of Curious and Unusual Animals'. Santa Barbara, California: Greenwood Press. They are found across Southeast Asia and southern India. and are fairly common in forests, areca gardens, teak plantations and shrub jungle. History of discovery Carl Linnaeus described the genus in 1758, with the type species being ''Draco volans.'' The name of the genus is from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoulder Blades
The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble. In compound terms, the prefix omo- is used for the shoulder blade in medical terminology. This prefix is derived from ὦμος (ōmos), the Ancient Greek word for shoulder, and is cognate with the Latin , which in Latin signifies either the shoulder or the upper arm bone. The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage. Structure The scapula is a thick, flat bone lying on the thoracic wall that provides an attachment for three groups of muscles: intrins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
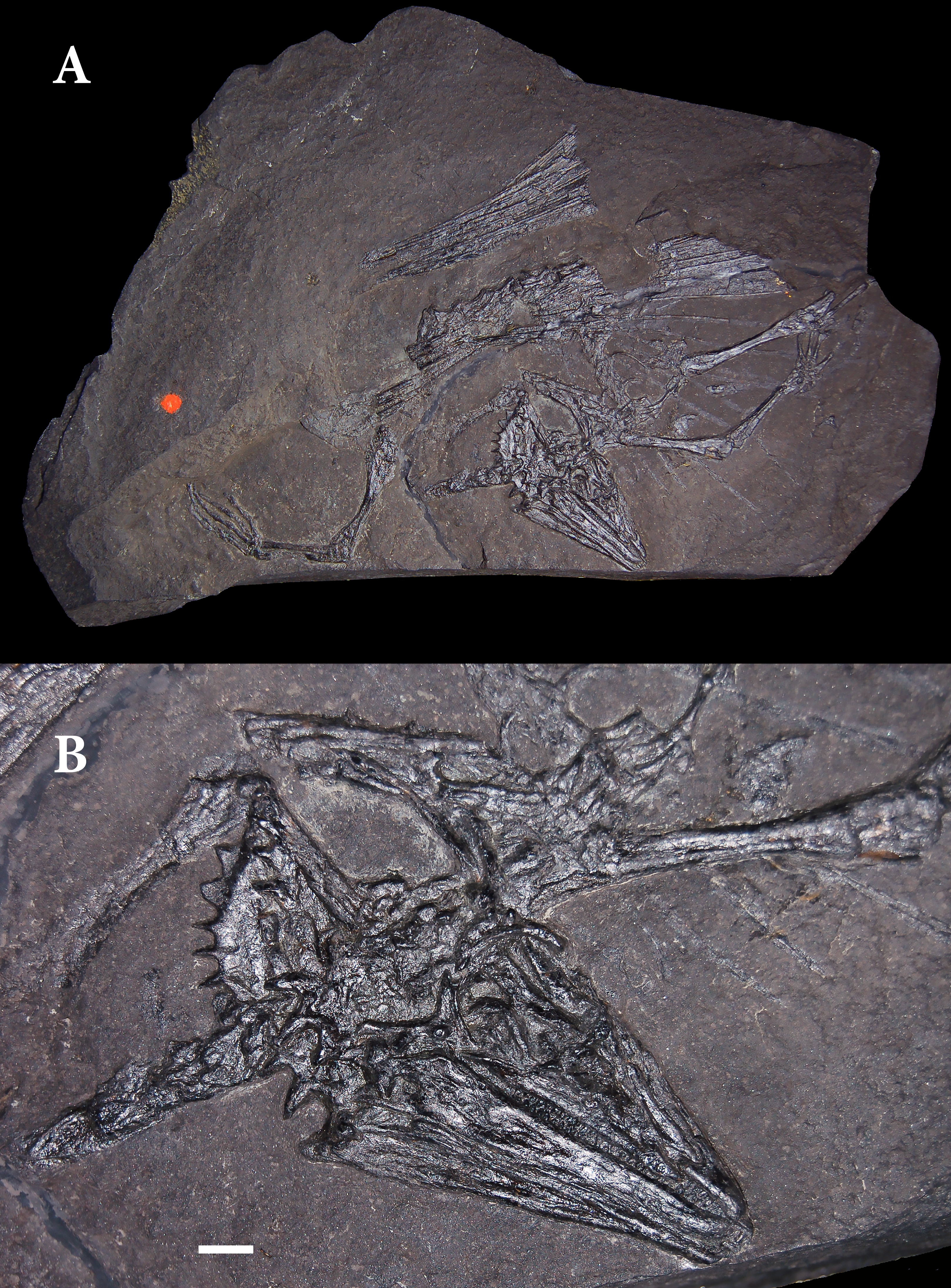
Weigeltisaurus Jaekeli Diagram
''Weigeltisaurus'' is an extinct genus of weigeltisaurid reptile from the Late Permian Kupferschiefer of Germany and Marl Slate of England. It has a single species, originally named as ''Palaechamaeleo jaekeli'' in 1930 and later assigned the name ''Weigeltisaurus jaekeli'' in 1939, when it was revealed that ''Palaeochamaeleo'' was a preoccupied name. A 1987 review by Evans and Haubold later lumped ''Weigeltisaurus jaekeli'' under ''Coelurosauravus'' as a second species of that genus. A 2015 reassessment of skull morphology study substantiated the validity of ''Weigeltisaurus'' and subsequent authors have used this genus. Like other Weigeltisaurids, they possessed long rod-like bones that radiated from the trunk that were likely used to support membranes used for gliding, similar to extant ''Draco'' lizards. History of discovery The first remains of ''Weigeltisaurus jaekeli'' were described by Johannes Weigelt in 1930 from a specimen (SSWG 113/7) found in the Kupferschiefer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avicranium
''Avicranium'' is a genus of extinct drepanosaur reptile known from the Chinle Formation of the late Triassic. The type species of ''Avicranium'' is ''Avicranium renestoi''. "''Avicranium''" is Latin for "bird cranium", in reference to its unusual bird-like skull, while "''renestoi''" references Silvio Renesto, a paleontologist known for studies of Italian drepanosaurs. Discovery The holotype and only known specimen of ''Avicranium'' is AMNH FARB 30834, a disarticulated skull attached to a few cervical (neck) vertebrae. This specimen hails from the ''Coelophysis'' (or Whitaker) quarry at Ghost Ranch in New Mexico, USA. This quarry belongs to the ' siltstone member' of the Chinle formation, which corresponds to the late Norian to early Rhaetian stages of the Triassic. Various unprepared blocks from this locality were excavated by American Museum of Natural History field parties during the 1940s. Long believed to only contain multiple specimens of the early dinosaur ''Coelophysis' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patagia
The patagium (plural: patagia) is a membranous Animal body, body part that assists an animal in obtaining lift (force), lift when gliding flight, gliding or flight. The structure is found in extant taxon, extant and extinct groups of flying and gliding animals including bats, birds, some dromaeosaurs, pterosaurs, gliding mammals, some flying lizards, and flying frogs. The patagium that stretches between an animal's hind limbs is called the uropatagium (especially in bats) or the interfemoral membrane. Bats In bats, the skin forming the surface of the wing is an extension of the skin of the abdomen that runs to the tip of each digit, uniting the forelimb with the body. The patagium of a bat has four distinct parts: #Propatagium: the patagium present from the neck to the first digit. #Dactylopatagium: the portion found within the digits. #Plagiopatagium: the portion found between the last digit and the hindlimbs. #Uropatagium: the posterior portion of the flap between the two hind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drepanosaurus
''Drepanosaurus'' (; "sickle lizard") is a genus of arboreal (tree-dwelling) reptile that lived during the Triassic Period. It is a member of the Drepanosauridae, a group of diapsid reptiles known for their prehensile tails. ''Drepanosaurus'' was probably an insectivore, and lived in a coastal environment in what is now modern day Italy, as well as in a streamside environment in the midwestern United States. Description ''Drepanosaurus'' is known to have a huge claw on the "index finger" (digit II) of each hand along with the tail claw. The skull of ''Drepanosaurus'' has never been found and is still unknown; however, the skull of ''Drepanosaurus'' was likely similar to other drepanosaurs, such as ''Megalancosaurus''. ''Megalancosaurus skull was approximately the same size as its enlarged claws, and had a bird-like jaw and head shape. The forelimb of ''Drepanosaurus'' is highly modified compared to other vertebrates. Its ulna was modified into a robust, crescent-shaped site fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |