|
Autoionization
Autoionization is a process by which an atom or a molecule in an excited state spontaneously emits one of the outer-shell electrons, thus going from a state with charge to a state with charge , for example from an electrically neutral state to a singly ionized state. Autoionizing states are usually short- lived, and thus can be described as Fano resonances rather than normal bound states. They can be observed as variations in the ionization cross sections of atoms and molecules, by photoionization, electron ionization and other methods. Examples As examples, several Fano resonances in the extreme ultraviolet photoionization spectrum of neon are attributed to autoionizing states.Codling, K., Madden, R.P. and Ederer, D.L. (1967), ''Resonances in the Photoionization Continuum of Ne I (20-150 eV)'', Phys. Rev. ''155'', 26-37 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.155.26 Some are due to one-electron excitations, such as a series of three strong similarly shaped peaks at ener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fano Resonance
In physics, a Fano resonance is a type of resonant scattering phenomenon that gives rise to an asymmetric line-shape. Interference between a background and a resonant scattering process produces the asymmetric line-shape. It is named after Italian-American physicist Ugo Fano, who in 1961 gave a theoretical explanation for the scattering line-shape of inelastic scattering of electrons from helium; however, Ettore Majorana was the first to discover this phenomenon. Because it is a general wave phenomenon, examples can be found across many areas of physics and engineering. History The explanation of the Fano line-shape first appeared in the context of inelastic electron scattering by helium and autoionization. The incident electron doubly excites the atom to the 2s2p state, a sort of shape resonance. The doubly excited atom spontaneously decays by ejecting one of the excited electrons. Fano showed that interference between the amplitude to simply scatter the incident electron and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atom
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons. Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics, as if they were tennis balls for example, is not possible due to quantum effects. More than 99.94% of an atom's mass is in the nucleus. The protons have a positive electric charge, the electrons have a negative electric charge, and the neutrons have no electric charge. If the number of protons and electrons are equal, then the atom is electrically neutral. If an atom has more or fewer electrons than protons, then it has an overall negative or positive charge, respectively – such atoms are called ions. The electrons of an atom are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neon
Neon is a chemical element with the symbol Ne and atomic number 10. It is a noble gas. Neon is a colorless, odorless, inert monatomic gas under standard conditions, with about two-thirds the density of air. It was discovered (along with krypton and xenon) in 1898 as one of the three residual rare inert elements remaining in dry air, after nitrogen, oxygen, argon and carbon dioxide were removed. Neon was the second of these three rare gases to be discovered and was immediately recognized as a new element from its bright red emission spectrum. The name neon is derived from the Greek word, , neuter singular form of (), meaning 'new'. Neon is chemically inert, and no uncharged neon compounds are known. The compounds of neon currently known include ionic molecules, molecules held together by van der Waals forces and clathrates. During cosmic nucleogenesis of the elements, large amounts of neon are built up from the alpha-capture fusion process in stars. Although neon is a very co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Physics
Atomic physics is the field of physics that studies atoms as an isolated system of electrons and an atomic nucleus. Atomic physics typically refers to the study of atomic structure and the interaction between atoms. It is primarily concerned with the way in which electrons are arranged around the nucleus and the processes by which these arrangements change. This comprises ions, neutral atoms and, unless otherwise stated, it can be assumed that the term ''atom'' includes ions. The term ''atomic physics'' can be associated with nuclear power and nuclear weapons, due to the synonymous use of ''atomic'' and ''nuclear'' in standard English. Physicists distinguish between atomic physics—which deals with the atom as a system consisting of a nucleus and electrons—and nuclear physics, which studies nuclear reactions and special properties of atomic nuclei. As with many scientific fields, strict delineation can be highly contrived and atomic physics is often considered in the wider c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rydberg State
The Rydberg states of an atom or molecule are electronically excited states with energies that follow the Rydberg formula as they converge on an ionic state with an ionization energy. Although the Rydberg formula was developed to describe atomic energy levels, it has been used to describe many other systems that have electronic structure roughly similar to atomic hydrogen. In general, at sufficiently high principal quantum numbers, an excited electron-ionic core system will have the general character of a hydrogenic system and the energy levels will follow the Rydberg formula. Rydberg states have energies converging on the energy of the ion. The ionization energy threshold is the energy required to completely liberate an electron from the ionic core of an atom or molecule. In practice, a Rydberg wave packet is created by a laser pulse on a hydrogenic atom and thus populates a superposition of Rydberg states. Modern investigations using pump-probe experiments show molecular pathways ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
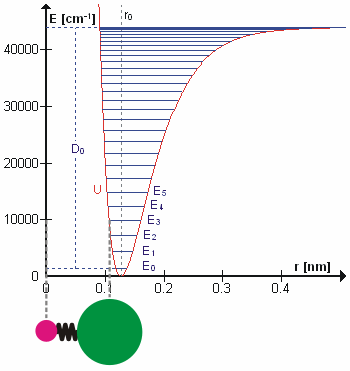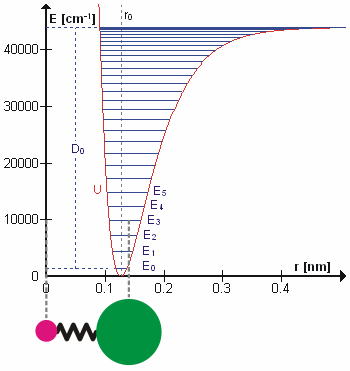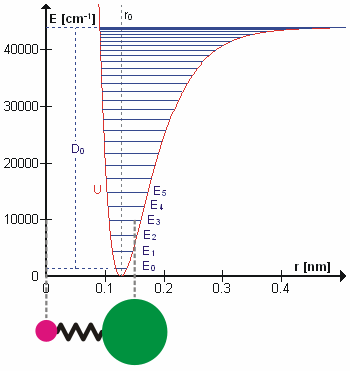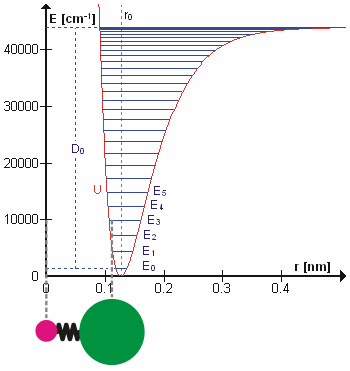
Molecular Vibration
A molecular vibration is a periodic motion of the atoms of a molecule relative to each other, such that the center of mass of the molecule remains unchanged. The typical vibrational frequencies range from less than 1013 Hz to approximately 1014 Hz, corresponding to wavenumbers of approximately 300 to 3000 cm−1 and wavelengths of approximately 30 to 3 µm. For a diatomic molecule A−B, the vibrational frequency in s−1 is given by \nu = \frac \sqrt , where k is the force constant in dyne/cm or erg/cm2 and μ is the reduced mass given by \frac = \frac+\frac. The vibrational wavenumber in cm−1 is \tilde \;= \frac \sqrt, where c is the speed of light in cm/s. Vibrations of polyatomic molecules are described in terms of normal modes, which are independent of each other, but each normal mode involves simultaneous vibrations of different parts of the molecule. In general, a non-linear molecule with ''N'' atoms has 3''N'' – 6 normal modes of vibration, but a ''linear'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auger Effect
The Auger effect or Auger−Meitner effect is a physical phenomenon in which the filling of an inner-shell vacancy of an atom is accompanied by the emission of an electron from the same atom. When a core electron is removed, leaving a vacancy, an electron from a higher energy level may fall into the vacancy, resulting in a release of energy. Although most often this energy is released in the form of an emitted photon, the energy can also be transferred to another electron, which is ejected from the atom; this second ejected electron is called an Auger electron. Effect The effect was first discovered by Lise Meitner in 1922; Pierre Victor Auger independently discovered the effect shortly after and is credited with the discovery in most of the scientific community. Upon ejection, the kinetic energy of the Auger electron corresponds to the difference between the energy of the initial electronic transition into the vacancy and the ionization energy for the electron shell from which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Core Electron
Core electrons are the electrons in an atom that are not valence electrons and do not participate in chemical bonding. The nucleus and the core electrons of an atom form the atomic core. Core electrons are tightly bound to the nucleus. Therefore, unlike valence electrons, core electrons play a secondary role in chemical bonding and reactions by screening the positive charge of the atomic nucleus from the valence electrons. The number of valence electrons of an element can be determined by the periodic table group of the element (see valence electron): *For main group elements, the number of valence electrons ranges from 1-8 electrons (''n''s and ''n''p orbitals). *For transition metals, the number of valence electrons ranges from 3-12 electrons (''n''s and (''n''−1)d orbitals). *For lanthanides and actinides, the number of valence electrons ranges from 3-16 electrons (''n''s, (''n''−2)f and (''n''−1)d orbitals). All other non-valence electrons for an atom of that element are c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Chemical Physics
''The Journal of Chemical Physics'' is a scientific journal published by the American Institute of Physics that carries research papers on chemical physics."About the Journal" from the ''Journal of Chemical Physics'' website. Two volumes, each of 24 issues, are published annually. It was established in 1933 when '''' editors refused to publish theoretical works. The editors have been: *2019-present: Tim Lian *2008–2018: *2007–2008: [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Marmet
Paul Marmet; (20 May 1932 – 20 May 2005) was a Canadian physicist and professor, best known for developing, along with his mentor Larkin Kerwin, a high resolution electron selector for the study of ionic electronic states. This instrument, along with a mass spectrometer he developed, had an energy resolution superior to previous instruments, and was widely used by scientists for electron scattering studies which led to the discovery of enhanced vibrational excitation in nitrogen, and of Feshbach resonances. Marmet and his research group used the electron selector to discover atomic and molecular states which are excited by electron impact but not by photons, such as doubly excited states which disobey spectroscopic selection rules, and negative-ion resonances in which the incident electron is temporarily attached to the target molecule. Career Beginning in 1967 Marmet served as director of the laboratory for Atomic and Molecular Physics at Laval University in Quebec City, Cana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Review
''Physical Review'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal established in 1893 by Edward Nichols. It publishes original research as well as scientific and literature reviews on all aspects of physics. It is published by the American Physical Society (APS). The journal is in its third series, and is split in several sub-journals each covering a particular field of physics. It has a sister journal, ''Physical Review Letters'', which publishes shorter articles of broader interest. History ''Physical Review'' commenced publication in July 1893, organized by Cornell University professor Edward Nichols and helped by the new president of Cornell, J. Gould Schurman. The journal was managed and edited at Cornell in upstate New York from 1893 to 1913 by Nichols, Ernest Merritt, and Frederick Bedell. The 33 volumes published during this time constitute ''Physical Review Series I''. The American Physical Society (APS), founded in 1899, took over its publication in 1913 and star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Ionization
Electron ionization (EI, formerly known as electron impact ionization and electron bombardment ionization) is an ionization method in which energetic electrons interact with solid or gas phase atoms or molecules to produce ions. EI was one of the first ionization techniques developed for mass spectrometry. However, this method is still a popular ionization technique. This technique is considered a hard (high fragmentation) ionization method, since it uses highly energetic electrons to produce ions. This leads to extensive fragmentation, which can be helpful for structure determination of unknown compounds. EI is the most useful for organic compounds which have a molecular weight below 600. Also, several other thermally stable and volatile compounds in solid, liquid and gas states can be detected with the use of this technique when coupled with various separation methods. History Electron ionization was first described in 1918 by Canadian-American Physicist Arthur J. Dempste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |