|
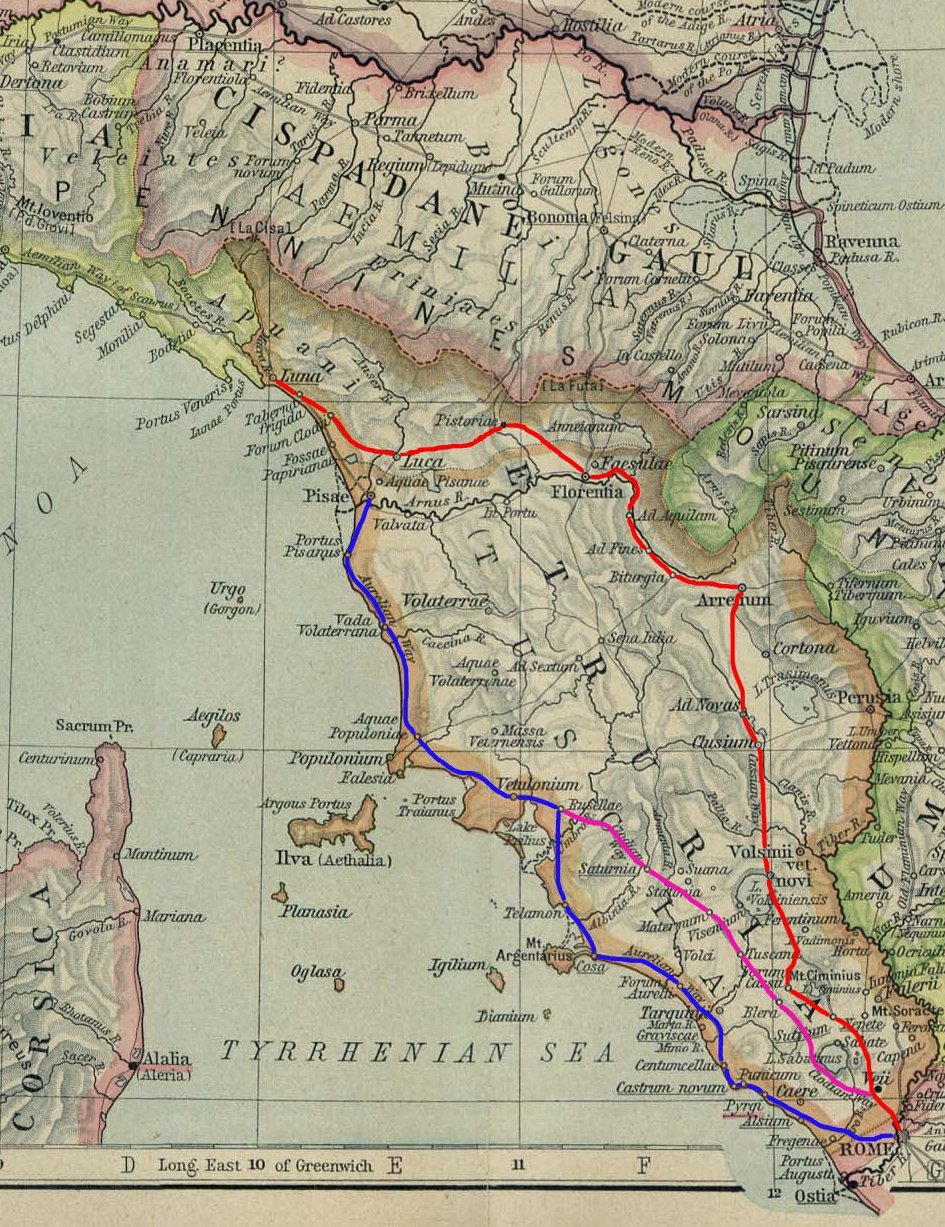
Aurelian Way
The ''Via Aurelia'' (Latin for "Aurelian Way") is a Roman road in Italy constructed in approximately 241 BC. The project was undertaken by Gaius Aurelius Cotta, who at that time was censor.Hornblower, Simon, & Antony Spawforth. ''The Oxford Classical Dictionary.'' 3rd ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1996. Cotta had a history of building roads for Rome, as he had overseen the construction of a military road in Sicily (as consul in 252 BC, during the First Punic War) connecting ''Agrigentum'' (modern Agrigento) and ''Panormus'' (modern Palermo). Background In the middle Republic, a series of roads were built throughout Italy to serve the needs of Roman expansion, including swift army movements and reasonably quick communication with Roman colonies spread throughout Italy. There also was the unintended (but beneficial) consequence of an increase in trade among Italian cities and with Rome. The roads were standardized to wide allowing two chariots to pass, and distance was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceriale
Ceriale ( lij, O Çejâ, locally ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Savona in the Italian region of Liguria, located about southwest of Genoa and about southwest of Savona. Ceriale borders the following municipalities: Albenga, Balestrino, Borghetto Santo Spirito, Cisano sul Neva, and Toirano. Geography The town is located in the Riviera di Ponente, east of the plain of Albenga, on the slopes of Mount Croce, at an elevation of . History The village, an territorial dominion of the bishop of Diocese of Albenga-Imperia, Albenga since the early Middle Ages, was acquired in the 14th century by the Republic of Genoa. In that period the nearby village of ''Capriolo'' was abandoned, according to local sources, as a result of an invasion of ants. Following the frequent raids by Saracens on the Ligurian coast, a circular bastion was built adjacent to the beach in 1563; however, the town was again attacked and sackrf by Barbary pirates in 1637. Along with other town ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alsium
Alsium ( el, ; modern: Palo) was an ancient city on the coast of Etruria, between Pyrgi and Fregenae, on the Via Aurelia, by which it is about 35 km from Rome near the modern Ladispoli. It was one of the oldest towns of Etruria, but does not appear in history until the Roman colonisation of 247 BC. It was never of great importance, except as a resort of wealthy Romans, many of whom (including Pompey and the Antonine emperors) had villas there. History It is mentioned by Dionysius among the cities which were founded by the Pelasgians in connection with the aborigines, and afterwards wrested from them by the Tyrrhenians (Etruscans). But no mention of it occurs in history as an Etruscan city, or during the wars of that people with Rome. In 247 BC a Roman ''colonia maritima'' was established there and which gave them exemption from all military service, which was, however, overruled during the exigencies of the Second Punic War. It is mentioned by Strabo, Pliny, and Ptolem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Via Julia Augusta
The Via Julia Augusta (modern Italian Via Giulia Augusta) is the name given to the Roman road formed by the merging of the Via Aemilia Scauri with the Via Postumia. The road runs from Placentia (modern Piacenza) to Arelate (modern Arles), initially westward along the edge of the plain of the River Po to Derthona (Tortona), then southward to the Ligurian coast. There it formed a continuous route westward along the precipitous descent of the Ligurian mountains into the sea. This takes it to Vada Sabatia (Vado Ligure), Albingaunum (Albenga) and Album Intimilium (Ventimiglia), continuing to La Turbie (above modern Monaco), where its original terminus was marked by a triumphal arch. Later it was extended, taking a route away from the coast via the valley of the River Laghet, north of Nice and westward to Arles where it joined the Via Domitia. It was begun in 13 BCE by Augustus, and its engineering works were repeatedly renewed by later emperors. However by about 420 CE, when Rutiliu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Via Postumia
The Via Postumia was an ancient Roman road of northern Italy constructed in 148 BC by the ''consul'' Spurius Postumius Albinus Magnus. It ran from the coast at Genua through the mountains to Dertona, Placentia (the termination of the Via Aemilia) and Cremona, just east of the point where it crossed the Po River. From Cremona the road ran eastward to Bedriacum, the current town of Calvatone, where it forked, one branch running to the right to Mantua, the other to the left to Verona, crossing the Adige river on the Ponte Pietra, the only bridge on the Adige river at that time, and then traversing the Venetian plain, crossing the Piave River at Maserada sul Piave until finally reaching Aquileia, an important military frontier town founded by Rome in 181 BC. The Roman conquest of Liguria depended upon this road, and several of the more important towns owed their origin largely to it. Cremona was its central point, the distance being reckoned from it both eastwards and westwards. V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cremona
Cremona (, also ; ; lmo, label= Cremunés, Cremùna; egl, Carmona) is a city and ''comune'' in northern Italy, situated in Lombardy, on the left bank of the Po river in the middle of the ''Pianura Padana'' ( Po Valley). It is the capital of the province of Cremona and the seat of the local city and province governments. The city of Cremona is especially noted for its musical history and traditions, including some of the earliest and most renowned luthiers, such as Giuseppe Guarneri, Antonio Stradivari, Francesco Rugeri, Vincenzo Rugeri, and several members of the Amati family. History Ancient Celtic origin Cremona is first mentioned in history as a settlement of the Cenomani, a Gallic ( Celtic) tribe that arrived in the Po valley around 400 BC. However, the name Cremona most likely dates back to earlier settlers and puzzled the ancients, who gave many fanciful interpretations. Roman military outpost In 218 BC the Romans established on that spot their first military o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tortona
Tortona (; pms, Torton-a , ; lat, Dhertona) is a ''comune'' of Piemonte, in the Province of Alessandria, Italy. Tortona is sited on the right bank of the Scrivia between the plain of Marengo and the foothills of the Ligurian Apennines. History Known in ancient times as Dertona, the city was probably the oldest colony under Roman rule in the westernmost section of the Valley of the Po, on the road leading from Genua (Genoa) to Placentia (Piacenza). The city was founded c. 123–118 BC at the junction of the great roads; the Via Postumia and the Via Aemilia Scauri which merged to become the Via Julia Augusta. The site made Dertona an important military station under the Romans. Strabo speaks of it as one of the most considerable towns in this part of Italy, and from Pliny wrote that it was a Roman colony. Velleius mentions it among those founded under the Republic, it appears to have been recolonised under Augustus, from whence we find it bearing in inscriptions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Aemilius Scaurus (consul 115 BC)
{{hndis, Scaurus, Marcus ...
Marcus Scaurus may refer to: * Marcus Aemilius Scaurus (consul 115 BC) * Marcus Aemilius Scaurus (praetor 56 BC) * Marcus Aemilius Scaurus (son of Mucia) * Marcus Aurelius Scaurus Marcus Aurelius Scaurus (died 105 BC) was a Roman politician and general during the Cimbrian War. After one of the consul designates was prosecuted and condemned, Scaurus was made consul suffectus in 108 BC. In 105 BC he went as a senior legate wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Via Aemilia Scauri
The ''Via Aemilia Scauri'' was an ancient Roman road built by the consul Marcus Aemilius Scaurus during his term as censor in 109 BC. E. Fentress, 'Via Aurelia, Via Aemilia' ''Papers of the British School at Rome'' LII, 1984, 72-76. Route It is mainly a coastal road, doubling Via Aurelia, and connecting Rome to Placentia and Pisa, passing through Genoa. Near the town of Cosa it runs inland and parallel to the Via Aurelia. Further north the ''Via Aemilia Scauri'' merged with the ''Via Postumia'' to become the ''Via Julia Augusta The Via Julia Augusta (modern Italian Via Giulia Augusta) is the name given to the Roman road formed by the merging of the Via Aemilia Scauri with the Via Postumia. The road runs from Placentia (modern Piacenza) to Arelate (modern Arles), init ...''. References Aemilia Scauri, Via Transport in Emilia-Romagna Transport in Liguria Transport in Tuscany 110s BC establishments 2nd-century BC establishments in the Roman Republic 2nd-ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carthaginians
The Punic people, or western Phoenicians, were a Semitic people in the Western Mediterranean who migrated from Tyre, Phoenicia to North Africa during the Early Iron Age. In modern scholarship, the term ''Punic'' – the Latin equivalent of the Greek-derived term ''Phoenician'' – is exclusively used to refer to Phoenicians in the western Mediterranean, following the line of the Greek East and Latin West. The largest Punic settlement was Ancient Carthage (essentially modern Tunis), but there were 300 other settlements along the North African coast from Leptis Magna in modern Libya to Mogador in southern Morocco, as well as western Sicily, southern Sardinia, the southern and western coasts of the Iberian Peninsula, Malta, and Ibiza. Their language, Punic, was a dialect of Phoenician, one of the Northwest Semitic languages originating in the Levant. Literary sources report two moments of Tyrian settlements in the west, the first in the 12th century BCE (the cities Utica, Lixu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauls
The Gauls ( la, Galli; grc, Γαλάται, ''Galátai'') were a group of Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age and the Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). They spoke Gaulish, a continental Celtic language. The Gauls emerged around the 5th century BC as bearers of La Tène culture north and west of the Alps. By the 4th century BC, they were spread over much of what is now France, Belgium, Switzerland, Southern Germany, Austria, and the Czech Republic, by virtue of controlling the trade routes along the river systems of the Rhône, Seine, Rhine, and Danube. They reached the peak of their power in the 3rd century BC. During the 4th and 3rd centuries BC, the Gauls expanded into Northern Italy ( Cisalpine Gaul), leading to the Roman–Gallic wars, and into the Balkans, leading to war with the Greeks. These latter Gauls eventually settled in Anatolia, becoming known as Galatians. After the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligures
The Ligures (singular Ligur; Italian: liguri; English: Ligurians) were an ancient people after whom Liguria, a region of present-day north-western Italy, is named. Ancient Liguria corresponded more or less to the current Italian region of Liguria. However, this region was much larger than today's borders. To the north the boundary was the Po river in present-day Piedmont, to the west it was the Var river in the Alpes Maritimes, to the east it was the Magra river as is still the case . And to the south, the region has been bordered since the dawn of time by the Ligurian Sea. This region is therefore very mountainous including the south of the Alps and the Ligurian Apennines. Little is known about the ancient language of the Ligurians because there are no known written records or inscriptions in it, and because it is not known where the ancient Ligurian people originally came from, an autochthonous origin is increasingly probable. This mysterious alphabet is found t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |