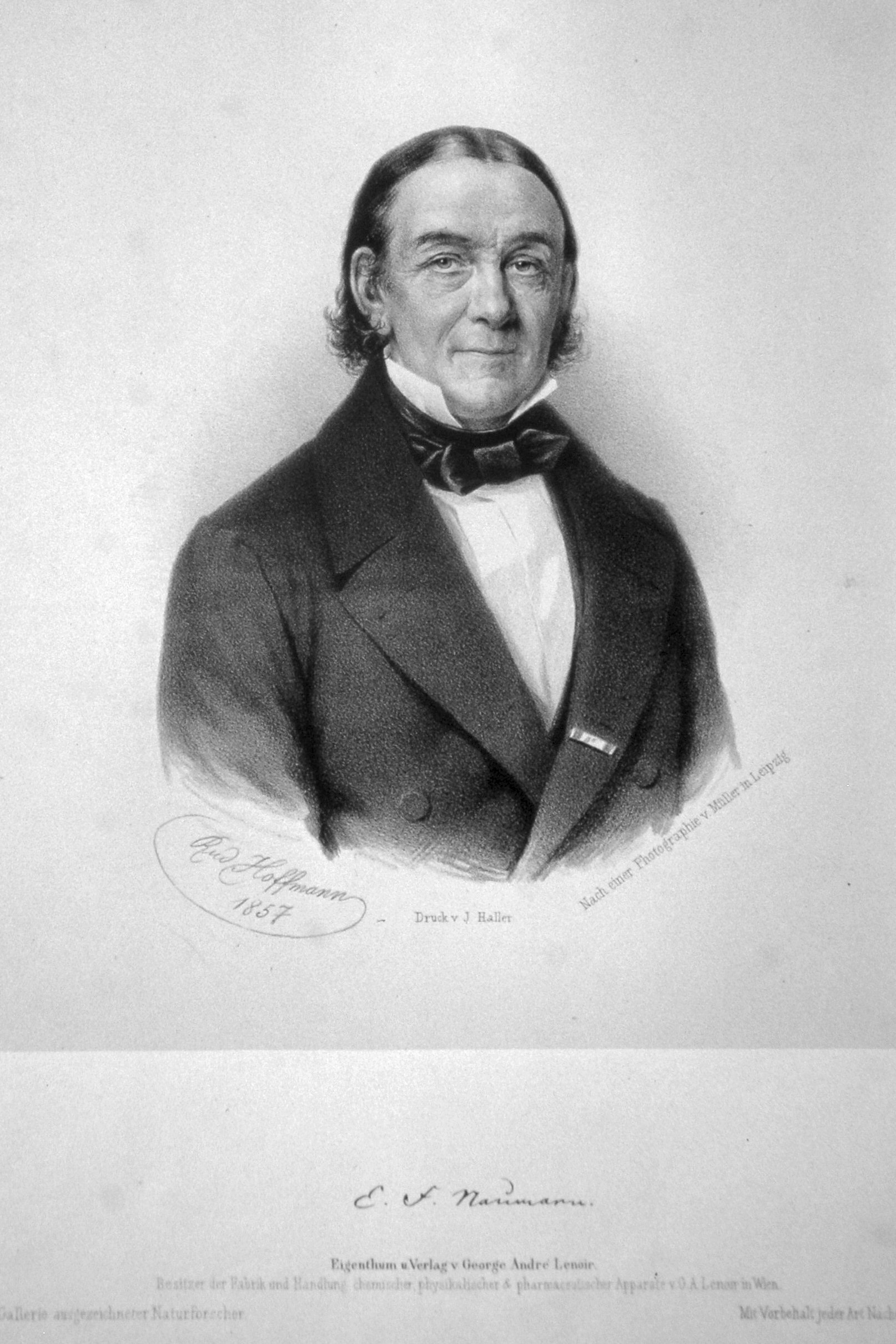|
August Carl Eduard Baldamus
August Carl Eduard Baldamus (April 18, 1812 in Giersleben, Saxony-Anhalt – October 30, 1893 in Coburg) was a German ornithologist. August Baldamus studied theology at the University of Berlin. In 1859 he became professor at the Gymnasium in Köthen where he met Carl Andreas Naumann and his brother Johann Friedrich Naumann both ornithologists. In 1849 he became Pastor in Diebzig, in 1859 moving to the same office in Osternienburg. He retired to Coburg in 1870. Baldamus was the founder of the Deutsche Ornithologen-Gesellschaft The German Ornithologists' Society (german: Deutsche Ornithologen-Gesellschaft) was founded in 1850, and is one of the world's oldest existing scientific societies. Its goal is to support and further scientific ornithology in Germany on all levels. ... (German Ornithologists' Society) and published the ornithological journal ''Naumannia'' between 1849 and 1858. Works *Johann Andreas Naumann u. Johann Friedrich Naumann: ''Naturgeschichte der Vögel De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E Baldamus 1864
E, or e, is the fifth letter and the second vowel letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''e'' (pronounced ); plural ''ees'', ''Es'' or ''E's''. It is the most commonly used letter in many languages, including Czech, Danish, Dutch, English, French, German, Hungarian, Latin, Latvian, Norwegian, Spanish, and Swedish. History The Latin letter 'E' differs little from its source, the Greek letter epsilon, 'Ε'. This in turn comes from the Semitic letter '' hê'', which has been suggested to have started as a praying or calling human figure ('' hillul'' 'jubilation'), and was most likely based on a similar Egyptian hieroglyph that indicated a different pronunciation. In Semitic, the letter represented (and in foreign words); in Greek, ''hê'' became the letter epsilon, used to represent . The various forms of the Old Italic script and the Latin alp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giersleben
Giersleben is a municipality in the district of Salzlandkreis, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe .... References Salzlandkreis {{Salzlandkreis-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coburg
Coburg () is a town located on the Itz river in the Upper Franconia region of Bavaria, Germany. Long part of one of the Thuringian states of the Wettin line, it joined Bavaria by popular vote only in 1920. Until the revolution of 1918, it was one of the capitals of the Duchy of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha and the Duchy of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld. Through successful dynastic policies, the ruling princely family married into several of the royal families of Europe, most notably in the person of Prince Albert, who married Queen Victoria in 1840. As a result of these close links with the royal houses of Europe in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Coburg was frequently visited by the crowned heads of Europe and their families. Coburg is also the location of Veste Coburg, one of Germany's largest castles. In 1530, Martin Luther lived there for six months while translating the Bible into German (the Luther Bible). Today, Coburg's population is close to 41,500. Since it was little dam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ornithologist
Ornithology is a branch of zoology that concerns the "methodological study and consequent knowledge of birds with all that relates to them." Several aspects of ornithology differ from related disciplines, due partly to the high visibility and the aesthetic appeal of birds. It has also been an area with a large contribution made by amateurs in terms of time, resources, and financial support. Studies on birds have helped develop key concepts in biology including evolution, behaviour and ecology such as the definition of species, the process of speciation, instinct, learning, ecological niches, guilds, island biogeography, phylogeography, and conservation. While early ornithology was principally concerned with descriptions and distributions of species, ornithologists today seek answers to very specific questions, often using birds as models to test hypotheses or predictions based on theories. Most modern biological theories apply across life forms, and the number of scientists who i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Berlin
Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (german: Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, abbreviated HU Berlin) is a German public research university in the central borough of Mitte in Berlin. It was established by Frederick William III on the initiative of Wilhelm von Humboldt, Johann Gottlieb Fichte and Friedrich Ernst Daniel Schleiermacher as the University of Berlin () in 1809, and opened in 1810, making it the oldest of Berlin's four universities. From 1828 until its closure in 1945, it was named Friedrich Wilhelm University (german: Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität). During the Cold War, the university found itself in East Berlin and was ''de facto'' split in two when the Free University of Berlin opened in West Berlin. The university received its current name in honour of Alexander and Wilhelm von Humboldt in 1949. The university is divided into nine faculties including its medical school shared with the Freie Universität Berlin. The university has a student enrollment of around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gymnasium (Germany)
''Gymnasium'' (; German plural: ''Gymnasien''), in the German education system, is the most advanced and highest of the three types of German secondary schools, the others being ''Hauptschule'' (lowest) and ''Realschule'' (middle). ''Gymnasium'' strongly emphasizes academic learning, comparable to the British sixth form system or with prep schools in the United States. A student attending ''Gymnasium'' is called a ''Gymnasiast'' (German plural: ''Gymnasiasten''). In 2009/10 there were 3,094 gymnasia in Germany, with students (about 28 percent of all precollegiate students during that period), resulting in an average student number of 800 students per school.Federal Statistical office of Germany, Fachserie 11, Reihe 1: Allgemeinbildende Schulen – Schuljahr 2009/2010, Wiesbaden 2010 Gymnasia are generally public, state-funded schools, but a number of parochial and private gymnasia also exist. In 2009/10, 11.1 percent of gymnasium students attended a private gymnasium. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köthen (Anhalt)
Köthen () is a town in Germany. It is the capital of the district of Anhalt-Bitterfeld in Saxony-Anhalt, about north of Halle (Saale), Halle. Köthen is the location of the main campus and the administrative centre of the regional university, Anhalt University of Applied Sciences/Hochschule Anhalt which is especially strong in information technology. The city is conveniently located at the hub of the Magdeburg–Leipzig railway, Magdeburg–Leipzig, Dessau–Köthen railway, Dessau–Köthen and Köthen–Aschersleben railways. Köthen is situated in a fertile area with rich black soil suitable to the cultivation of sugar-beets. Industry includes high-tech engineering, manufacture of cranes, as well as chemicals, printing, and foodstuffs. In English, the name of the city is often spelt anachronistically as Cöthen, a practice that has become standard in the literature relating to the life and work of Johann Sebastian Bach, who resided and worked there from 1717 to 1723. Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Amadeus Carl Friedrich Naumann
Georg Amadeus Carl Friedrich Naumann (30 May 1797 – 26 November 1873), also known as Karl Friedrich Naumann, was a German mineralogist and geologist. The crater Naumann on the Moon is named after him. Life Naumann was born at Dresden, the son of a distinguished musician and composer. He received his early education at Pforta, studied at Freiberg under Werner, and afterwards at Leipzig and Jena. He graduated at Jena, and was occupied in 1823 in teaching in that town and in 1824 at Leipzig. In 1826 he succeeded Mohs as professor of crystallography, in 1835 he became professor also of geognosy at Freiberg; and in 1842 he was appointed professor of mineralogy and geognosy in the University of Leipzig. At Freiberg he was charged with the preparation of a geological map of Saxony, which he carried out with the aid of Bernhard von Cotta in 1846. Naumann was a man of encyclopedic knowledge, lucid and fluent as a teacher. Early in life (1821-1822) he traveled in Norway, and his ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Friedrich Naumann
Johann Friedrich Naumann (14 February 1780 – 15 August 1857) was a German scientist, engraver, and editor. He is regarded as the founder of scientific ornithology in Europe. He published ''The Natural History of German Birds'' (1820–1844) and ''The Eggs of German Birds'' (1818–1828). His father Johann Andreas Naumann (1744–1826) was a naturalist, and his brother Georg Amadeus Carl Friedrich Naumann, Carl Andreas Naumann (1786–1854) was also an ornithologist. The German ornithological society named its journal ''Naumannia''. The lesser kestrel (''Falco naumanni'') is also named for him. Biography Johann Friedrich Naumann was born in Ziebigk, about 10 km southeast of Köthen (Anhalt), Köthen, on 14 February 1780, as the son of Johann Andreas Naumann, a well-known natural historian. After attending school at Dessau, he returned home and devoted himself to the study of agriculture, botany, geology, and ornithology. His later work was devoted more exclusively to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diebzig
Diebzig is a village and a former municipality in the district of Anhalt-Bitterfeld, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Since 1 January 2010, it is part of the municipality Osternienburger Land Osternienburger Land is a municipality in the district of Anhalt-Bitterfeld, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It was formed on 1 January 2010 by the merger of the former municipalities Chörau, Diebzig, Dornbock, Drosa, Elsnigk, Großpaschleben, Kleinpa .... Former municipalities in Saxony-Anhalt Osternienburger Land Duchy of Anhalt {{AnhaltBitterfeld-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osternienburg
Osternienburg is a village and a former municipality in the district of Anhalt-Bitterfeld, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Since 1 January 2010, it is part of the municipality Osternienburger Land. It is situated approximately 6 km northeast of Köthen (Anhalt) Köthen () is a town in Germany. It is the capital of the district of Anhalt-Bitterfeld in Saxony-Anhalt, about north of Halle. Köthen is the location of the main campus and the administrative centre of the regional university, Anhalt Univer ..., and 15 km west of Dessau-Rosslau. Former municipalities in Saxony-Anhalt Osternienburger Land Duchy of Anhalt {{AnhaltBitterfeld-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsche Ornithologen-Gesellschaft
The German Ornithologists' Society (german: Deutsche Ornithologen-Gesellschaft) was founded in 1850, and is one of the world's oldest existing scientific societies. Its goal is to support and further scientific ornithology in Germany on all levels. It publishes the ''Journal of Ornithology The ''Journal of Ornithology'' (formerly ''Journal für Ornithologie'') is a scientific journal published by Springer Science+Business Media on behalf of the Deutsche Ornithologen-Gesellschaft. It was founded by Jean Cabanis in 1853, becoming the ...'', founded in 1853. ReferencesHistory of the Society Ornithological organizations Animal welfare organisations based in Germany 1850 establishments in Germany Scientific societies based in Germany {{ornithology-org-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


.jpg)